Germany Economy Growth Shows 0.2% Increase in Q1 2023
Germany’s economy growth has shown signs of life, expanding by 0.2% in the first quarter despite ongoing global challenges. With the recent release of the gross domestic product (GDP) figures by the German federal statistics office, the numbers align closely with forecasts from economists, highlighting a cautious but steady economic outlook Germany can build upon. The increase in household consumption and capital formation indicates a slight recovery, even as Germany faces inflation rates hovering near the European Central Bank’s 2% target. Additionally, the nation’s export challenges, particularly in the automotive sector, underscore the complexities that could impact Germany’s GDP growth in the near future. As we delve deeper into the nuances of Germany financial news, it’s crucial to consider how these figures might shape future economic strategies and government policies.
The economic landscape in Germany, often referred to as a powerhouse within Europe, is currently navigating a period marked by both resilience and vulnerability. The recent quarterly expansion reflects ongoing efforts to stimulate growth amid fluctuating conditions that impact various industries. Even as inflation rates approach regulatory targets, sectors such as manufacturing are grappling with external pressures, particularly from global trade tensions. Observing the economic outlook in Germany sheds light on the intricate dynamics at play, from consumer behavior to policy shifts. In this context, understanding the gross domestic product trends will be pivotal for both local and international stakeholders.
Germany Economy Growth Overview
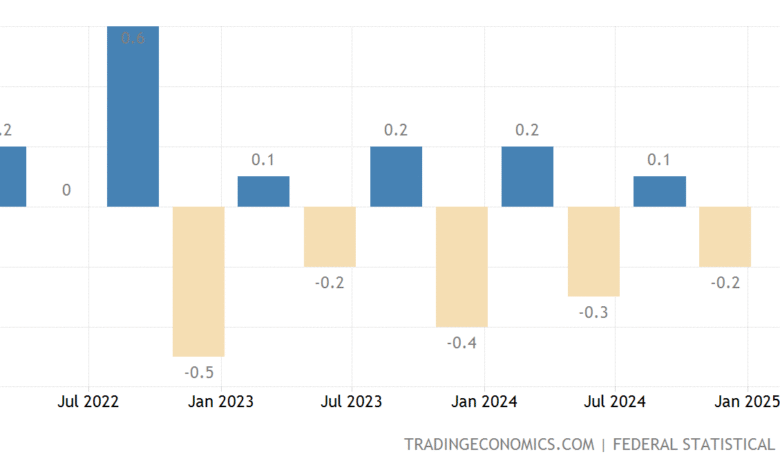
Germany’s economy expanded by 0.2% in the first quarter, meeting expectations set by recent forecasts. This growth report, released by the German federal statistics office, signals a slight but crucial uptick in the economic performance of a nation that has been wrestling with fluctuations in GDP throughout 2023 and 2024. The consistent economic activity is encouraging, considering the uneven growth patterns observed recently. As economists analyze such data, they remain vigilant about the implications on future economic policies and the overall economic outlook for Germany.
Despite the moderate growth figures, there are underlying concerns regarding the sustainability of this growth as various economic challenges loom. Many analysts are keeping a close watch on evolving factors such as global trade policies and internal market conditions. The slow recovery from previous downturns and potential trade tensions can complicate projections for the next quarters. Nonetheless, the commitment of the government to address issues such as infrastructure and climate investments might offer crucial support to ensure that the Germany economy growth trajectory remains, albeit slowly, positive.
Impact of Domestic Demand on German GDP
The uptick in Germany’s economic growth can largely be attributed to solid domestic demands, particularly in household final consumption expenditure. As consumers regain confidence, their spending habits contribute significantly to the overall economic activity. This increase in household expenditure paired with investments in capital formation suggests a robust internal market that might counterbalance the external pressures coming from trade disputes and global uncertainty.
Moreover, shifts in consumption patterns indicate that while external economic environments, like those in the U.S. or China, pose challenges, internal trends can provide a cushion. The boost in consumption is a positive indicator, yet experts warn that dependency on household spending alone is not sustainable for long-term growth. A more diversified approach that balances domestic consumption with export strength would be crucial for mitigating risks associated with global economic volatility.
Navigating Export Challenges
With Germany’s economy heavily reliant on exports, recent developments concerning international trade policies have generated significant concern among industry leaders. Challenges such as U.S. tariff tensions threaten Germany’s pivotal trade relationships, particularly in manufacturing and automotive sectors. Furthermore, increased competition from countries such as China presents additional hurdles, as these nations are enhancing their production capacity and market penetration.
On the other hand, Germany must recognize opportunities within its export framework. Addressing these challenges could lead to innovations in trade strategies and reinforce Germany’s position in the global market. Collaborations, investment in technology, and diversified export markets might provide pathways to navigate through these tumultuous times, reducing reliance on traditional markets that are currently experiencing uncertainty.
Germany Financial News and Economic Outlook
Recent updates from financial analysts highlight a cautious economic outlook for Germany, with predictions leaning towards stagnation by 2025. This forecast is shaped largely by the external economic environment, including shifts in U.S. policy and domestic challenges such as rising costs in infrastructure and housing. As significant investments are loosened with changes to fiscal rules, particularly intentions to ramp up defense spending, there may be hope for revitalizing growth prospects.
However, consistency in achieving economic stability requires careful navigation of current financial realities. Investors and policymakers alike must remain alert to evolving inflation rates and consumer behavior trends, which directly affect the domestic economy’s health. As the German government reassesses its strategy and adapts to both internal and external pressures, the economic outlook remains a vital topic in Germany financial news, guiding decisions for both consumers and businesses moving forward.
Inflation Rates and Their Role in Economic Stability
Inflation rates in Germany are on the rise, which presents both challenges and opportunities for the economy. The recent figures showing a 2.3% harmonized consumer price index in March signify an uptick from February, drawing attention to the need for governmental and ECB intervention. With inflation nearing the European Central Bank’s target of 2%, economic analysts are assessing the implications of stable inflation on consumer spending and investment.
A balance between managing inflation and promoting economic growth is essential for maintaining stability. Should inflation rates rise beyond the acceptable limits, the implication could extend to increased interest rates, which would subsequently impact household consumption and capital investments. Continuous monitoring of these trends will be crucial for understanding their effects on the overall economic landscape in Germany, as stakeholders navigate these complexities in the months to come.
Sector-Specific Challenges and Opportunities
The German automotive sector, a linchpin of the economy, is facing a multitude of challenges amid rising competition and external pressures. Not only are companies struggling with the demands of innovation in electric vehicles, but they are also contending with trade issues that affect export viability. The push for sustainable practices offers both a challenge and an opportunity for growth as manufacturers adapt to evolving consumer demands and regulatory requirements.
Moreover, while some sectors like automotive grapple with competition, housing and infrastructure are affected by rising costs and investment hesitance. Yet, potential long-term growth exists as the government injects funds into these sectors, stimulating advancements and job creation. Partnerships with private enterprises and increased investment in technology will be vital for overcoming existing hurdles and ensuring that these key sectors contribute positively to the German economic landscape.
The Role of Fiscal Policy in Economic Recovery
Germany’s recent adjustments to fiscal policy come at a critical time, aiming to boost economic resilience through increased investment. The establishment of a €500 billion fund focused on infrastructure and climate initiatives signals the government’s proactive approach to stimulate economic recovery. By investing strategically in critical areas, the government hopes to promote job creation and stabilize the economy amidst external pressures impacting growth.
However, the success of these policies ultimately depends on execution and integration within the broader economic framework. Policymakers must ensure that funds are allocated effectively to maximize impact and stimulate growth in sectors that require immediate support. Continuous evaluations and adjustments will be necessary as the economic landscape evolves, allowing Germany to adapt and thrive in an uncertain global economy.
Future Projections: Navigating Uncertainty
As we look forward, understanding future projections for the German economy involves navigating a complex landscape filled with uncertainties. Analysts are closely watching global economic trends, particularly U.S.-China relations and emerging markets, to gauge potential impacts on Germany’s growth. Ongoing tariff tensions and trade negotiations will play a significant role in shaping future economic activity, making it essential for businesses to remain adaptable and forward-thinking.
Furthermore, internal economic dynamics such as inflation rates and demographic shifts will also significantly affect the projections for GDP growth. Policymakers and business leaders need to engage in strategic planning that factors in not just immediate challenges but also potential shifts in consumer preferences and market demands over time. By doing so, Germany can position itself to leverage both opportunities and challenges as they arise in this ever-evolving economic landscape.
The Importance of Sustainability in Economic Planning
In light of recent economic challenges, sustainability has emerged as a crucial pillar in Germany’s economic planning. The commitment to climate initiatives and sustainable investments embodies a shift in focusing not just on immediate economic returns but also on long-term viability. As the government prepares to invest significantly in green initiatives, this framework not only aims to bolster economic growth but also address pressing environmental concerns.
Aligning economic strategy with sustainable practices presents opportunities for innovation, job creation, and enhanced competitiveness in the global marketplace. Companies that adopt sustainable protocols may find themselves better positioned to mitigate risks associated with climate change while tapping into the growing demand for eco-friendly products and services. This proactive approach will be vital in ensuring that the economy remains resilient and adaptable to future challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of Germany economy growth?
Germany’s economy has shown a modest growth rate of 0.2% in the first quarter, indicating a fragile recovery amidst ongoing economic challenges. Analysts suggest that while the German GDP growth is in line with expectations, it has been marked by fluctuations between growth and contraction throughout 2023 and 2024.
How is Germany’s GDP growth influencing its economic outlook?
The current GDP growth of Germany is impacting the economic outlook, which has been revised by the government to reflect a stagnation forecast for 2025. This adjustment is largely driven by external factors such as U.S. trade policies and internal challenges like rising costs in key sectors.
What are the challenges affecting Germany’s economy growth?
Germany’s economy is facing numerous challenges affecting its growth, including tensions related to U.S. tariffs, increased competition in the automotive industry from China, and difficulties in housing and infrastructure investments driven by soaring costs.
What is the forecast for inflation rates in Germany amidst economic growth?
While Germany’s economy experiences sluggish growth, inflation rates are nearing the European Central Bank’s target of 2%. Recent reports show a harmonized consumer price index of 2.3% for March, signaling a slight decrease from the previous month and highlighting economic resilience.
How do export challenges impact Germany’s economic growth?
As a country heavily reliant on exports, Germany’s economic growth is significantly impacted by export challenges. Tariff tensions and competition in global markets create uncertainty, influencing the overall stability and growth potential of the German economy.
What roles do consumer expenditure and capital formation play in Germany economic growth?
In the first quarter, increased household final consumption expenditure and capital formation positively contributed to Germany’s economic growth. These factors are crucial as they indicate consumer confidence and investment, essential for driving the country’s GDP growth.
What long-term investments are being considered to promote Germany economy growth?
Germany is contemplating significant long-term investments, including a 500 billion euro fund aimed at enhancing infrastructure and supporting climate initiatives. Such fiscal rule modifications could foster economic stability and growth in the coming years.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Economic Growth Rate | Germany’s economy expanded by 0.2% in the first quarter. |
| Expected Growth | The growth rate aligned with a Reuters poll expectation of 0.2%. |
| GDP Adjustments | The GDP figures were adjusted for price, calendar, and seasonal variations. |
| Growth Attribution | Increases in household consumption and capital formation contributed to growth. |
| Export Dependency | Germany’s economy is heavily reliant on exports, facing challenges from U.S. tariff tensions. |
| Economic Outlook | The German government predicts stagnation in 2025, largely influenced by U.S. trade policies. |
| Sector Challenges | The automotive sector is struggling with increased competition, while housing and infrastructure face rising costs. |
| Positive Developments | A new fiscal rule allows increased defense spending and a 500 billion euro fund for infrastructure. |
| Inflation Rates | Inflation is close to the ECB’s target of 2%, with a CPI of 2.3% in March. |
Summary
Germany economy growth has experienced a modest expansion of 0.2% in the first quarter, indicating a slow but steady recovery amidst various challenges. The economy, highly reliant on exports, continues to grapple with external pressures such as U.S. tariffs and internal sector competition. However, the government’s forward-looking fiscal changes and a focus on infrastructure investment may bolster growth potential in the coming years. Overall, while Germany faces immediate economic hurdles, optimistic developments hint at a possible turnaround.