Euro Zone Inflation Unchanged at 2.2% – ECB Rate Cuts Ahead
Euro zone inflation has remained steady at 2.2% as of April, a figure that leaves the door open for potential ECB interest rate cuts in the coming months. This constancy contrasts with the expectations of many economists, who had predicted a slight decline to 2.1%. Notably, core inflation, which excludes the more volatile food and energy sectors, revealed a concerning uptrend, rising to 2.7%. Additionally, services inflation also saw a resurgence, increasing to 3.9%, which may indicate growing spending in certain sectors despite broader economic challenges. As the Eurozone grapples with tariff uncertainty and aims for sustainable economic growth, the future trajectory of inflation remains a central concern for policymakers and investors alike.
In the context of the Eurozone’s economic landscape, the persistence of inflation rates poses significant implications for financial policies and market dynamics. With the recent inflation figures stabilizing, central bankers are faced with the crucial task of navigating interest rate adjustments while considering related factors like core inflation and fluctuations in services prices. The ongoing economic performance, evidenced by emerging growth patterns, highlights the interplay between consumer spending and external trade tensions. Moreover, as the European Central Bank weighs potential adjustments, the focus will undoubtedly remain on how geopolitical uncertainties, particularly surrounding tariffs, may influence both inflation and overall market confidence in the Eurozone.
Understanding Euro Zone Inflation Rates in April 2025
In April 2025, Euro zone inflation remained stable at 2.2%, indicating no immediate pressure on consumer prices despite economist expectations of a slight decrease to 2.1%. This steadiness hints at underlying economic trends where inflationary forces are contained, but further analysis of core inflation and services inflation reveals a complex picture. Core inflation, excluding volatile categories like food and energy, has risen to 2.7%, suggesting that consumer demand and spending might be driving prices up in certain sectors of the economy.
The implications of unchanged inflation rates are significant for policymakers at the European Central Bank (ECB). With inflation figures remaining stable, it opens a window for possible interest rate cuts in upcoming ECB meetings. Indeed, the strong performance of services inflation, which increased to 3.9%, could signal that certain sectors are experiencing pricing pressures that might warrant a more nuanced monetary approach. As inflation metrics like these evolve, it’s essential for the ECB to stay vigilant and prepared to respond.
The Role of ECB Interest Rate Cuts in Shaping Eurozone Economic Growth
The European Central Bank (ECB) has been navigating a challenging economic landscape, especially with recent actions to cut interest rates to 2.25%. This move is part of a broader strategy aimed at stimulating economic growth amidst fluctuating inflation rates across the Euro zone. By reducing borrowing costs, the ECB hopes to invigorate consumer spending and investment, ultimately bolstering the economy. However, the recent stability in inflation could complicate further cuts, as the ECB balances growth concerns against inflationary pressures.
Furthermore, the potential for additional rate reductions can significantly influence Eurozone economic growth trajectories. If core inflation rates continue to rise without a corresponding increase in overall inflation, investors and consumers may become more cautious about spending, creating a possible slowdown in economic activity. The ECB’s ability to adapt its strategies to these dynamics will be critical, especially with external factors like tariff uncertainties looming, which could affect both inflation and growth.
Core and Services Inflation Trends: Analyzing Their Impact on the Eurozone
In the latest reports, both core and services inflation have exhibited a notable uptick, with core inflation rising to 2.7% and services inflation reaching 3.9%. These trends are indicative of underlying economic adjustments within the Euro zone, where consumer spending patterns are increasingly influential. Core inflation, which reflects the underlying health of the economy by excluding volatile items, suggests that consumers are willing to spend more, while services inflation highlights growing demand in sectors such as hospitality and travel.
The rise in services inflation can also be attributed, in part, to seasonal factors such as Easter, which historically boosts spending in services-related industries. However, economists caution that such effects may be temporary and could reverse in the subsequent months. This volatility underscores the importance of careful monitoring by the ECB, especially as these figures play a significant role in shaping monetary policy decisions.
Tariff Uncertainty and Inflation Outlook in the Eurozone
Tariff uncertainty poses a significant risk to the inflation outlook within the Eurozone, as highlighted by experts citing potential repercussions from U.S. trade policies. If tariff tensions escalate, Europe could face increased input costs, which would likely translate into higher consumer prices across various sectors. Michael Field, chief equity strategist, expressed that while current inflation figures may seem stable, the precarious nature of trade relationships means that unexpected shifts could emerge.
Such fluctuations in the inflation climate can complicate the ECB’s strategy, as they must navigate both domestic and international pressures to manage interest rates effectively. Policymakers like Christine Lagarde emphasize the importance of being data-dependent, suggesting that upcoming inflation reports and economic data will play a crucial role in future monetary decisions. The interplay between tariff changes and inflation rates could significantly inform the ECB’s trajectory as it works to stabilize the Eurozone economy.
Forecasting Eurozone Economic Growth Amidst Inflationary Pressure
Preliminary data indicating a 0.4% growth rate for the Eurozone in the first quarter of 2025 has raised optimism about recovery, exceeding forecasts of just 0.2%. This growth, however, must be contextualized within the landscape of stable inflation rates and the ongoing tariff uncertainties affecting trade. Economists predict that while the Eurozone may experience short-term growth, long-term prospects could be stymied by external factors that influence inflation and economic stability.
Moreover, the interconnectedness of regional economies implies that growth in one member state can have ripple effects across the Eurozone. Policymakers will need to ensure that fiscal and monetary policies are aligned to nurture this growth while also mitigating inflationary risks. Attention to emerging economic data will remain critical to ensure that the Eurozone can sustain its momentum amidst fluctuating global economic conditions.
The Impact of Eurozone Inflation on Consumer Spending Habits
With inflation holding at 2.2%, consumer spending habits in the Eurozone may shift in response to perceived economic conditions. As uncertainty prevails, consumers tend to adopt a more cautious approach towards spending, opting to save or delay significant purchases. This behavioral change can slow economic momentum, putting additional pressure on businesses that rely on steady consumer demand. It is essential for companies to remain agile and responsive to these changes in order to sustain profitability.
Furthermore, rising core and services inflation could drive consumers towards more budget-friendly options as they seek to stretch their dollars. Retailers and service providers will need to adapt their offerings to meet changing consumer priorities, focusing on value and affordability. Insights into these consumer shifts will be crucial for businesses seeking to thrive in a potentially evolving inflation landscape.
What Lies Ahead for Eurozone Inflation and the ECB’s Response
As the Eurozone navigates the complexities of inflation data, the prospect of future ECB interest rate cuts remains a vital topic of discussion among economists. The recent stasis in inflation at 2.2% provides some leeway for the ECB to react based on the evolving economic landscape. However, as policymakers like Christine Lagarde have suggested, the ECB will maintain a careful and data-driven approach, ensuring that any decisions are well-informed by the latest economic indicators.
Looking ahead, potential shifts in inflation rates may be influenced by various factors including geopolitical developments and changes in consumer demand. The interplay between domestic economic growth and external trade pressures such as tariffs will likely shape the Eurozone’s inflation outlook. As these dynamics evolve, the ECB’s ability to respond effectively to new data will be critical in maintaining stability in the Eurozone economy.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) Trends in Major Eurozone Economies
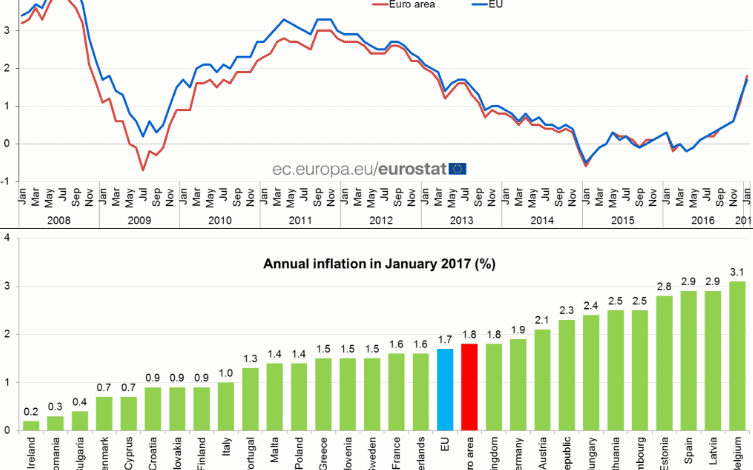
Reporting from major Eurozone economies such as Germany and France reflects diverse inflation experiences that contribute to the overall Eurozone consumer price index. For instance, Germany reported a consumer price rise of 2.2%, which was slightly above expectations, emphasizing a cautious optimism about economic resilience. Conversely, France’s harmonized inflation figures came in at a lower 0.8%, providing a different perspective on consumer price stability across the Eurozone.
These variations illustrate the importance of harmonized data when assessing inflationary trends across member states. As individual economies within the Eurozone may react differently to inflationary pressures, understanding these dynamics becomes crucial for the ECB’s policy framework. Monitoring the interplay of regional inflation rates will enable the central bank to tailor its strategies in a way that supports overall economic stability and growth.
The Relationship Between Inflation and Fiscal Policies in the Eurozone
Fiscal policies within the Eurozone are significantly influenced by inflation dynamics, particularly as central banks like the ECB adjust interest rates in response to economic data. The recent inflation reading of 2.2% highlights the need for EU member states to consider how their fiscal measures can either support or hinder growth. With countries like Germany implementing infrastructure packages, the link between inflation and fiscal response becomes increasingly important.
Furthermore, Eurozone governments may need to take a proactive stance in addressing inflation through targeted fiscal policies aimed at bolstering sectors affected by rising prices. By balancing spending with demand management, fiscal strategies will play a crucial role in stabilizing the economic environment amid uncertainties posed by both inflation and external pressures. As coordination between monetary and fiscal policies improves, the Eurozone can better navigate its inflation challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the Euro zone inflation rate in April 2025, and how does it impact ECB interest rate cuts?
In April 2025, Euro zone inflation remained unchanged at 2.2%. This stability in inflation leaves the European Central Bank (ECB) open to further interest rate cuts, potentially providing economic relief amidst ongoing tariff uncertainties.
How do core inflation and services inflation relate to Euro zone inflation trends?
Core inflation in the Eurozone accelerated to 2.7% in April 2025 from 2.4% in March, while services inflation increased to 3.9% compared to 3.5% previously. These rising inflation metrics are significant indicators, influencing ECB interest rate decisions and the overall inflation outlook.
What factors contribute to Eurozone economic growth despite Euro zone inflation pressures?
Despite Euro zone inflation pressures, recent data suggests a 0.4% economic growth in the first quarter of 2025. This growth can be attributed to resilience in the consumer sector and a rebound in services, though economists caution that tariff uncertainties could disrupt this trend.
How are tariff uncertainties affecting Euro zone inflation and economic policies?
Tariff uncertainties may escalate inflation rates in the Eurozone, potentially complicating the ECB’s policy decisions. Increased tariffs can lead to higher costs for goods and services, adding upward pressure on inflation, which could take the ECB off its path towards further interest rate cuts.
What implications does the Euro zone inflation rate have on ECB policy in 2025?
The Euro zone inflation rate of 2.2% in April 2025 suggests the ECB remains data-dependent in shaping its monetary policy. While recent stability offers an opportunity for interest rate cuts, ongoing economic factors like tariff tensions and core inflation trends necessitate careful monitoring to ensure inflation targets are met.
Will the current Euro zone inflation rate of 2.2% lead to changes in ECB interest rate strategy?
The steady Euro zone inflation rate of 2.2% will likely influence the ECB’s strategy by providing grounds for further interest rate cuts if economic conditions allow. ECB President Christine Lagarde emphasized a cautious approach, highlighting that the central bank’s decisions will be heavily influenced by evolving inflation data.
What role does services inflation play in the current Euro zone inflation landscape?
Services inflation, which rose to 3.9% in April 2025, plays a crucial role in the Euro zone inflation landscape, reflecting consumer demand pressures. It indicates a recovering economy but also heightens inflation concerns that may influence ECB’s upcoming monetary policy decisions.
How is Euro zone inflation affecting consumer purchasing power in 2025?
The Euro zone inflation rate of 2.2% in April 2025 may diminish consumer purchasing power, as persistent inflation tends to erode the value of money. Rising prices can particularly impact essential services, which have seen increased inflation, leading consumers to adjust spending habits.
What does the unchanged Euro zone inflation rate imply for future ECB interest rate adjustments?
The unchanged Euro zone inflation rate suggests a cautious stance for the ECB regarding interest rate adjustments. While the current rate allows for potential cuts, the future direction will depend on ongoing inflation data, economic growth rates, and external factors such as tariff uncertainties.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Euro zone inflation remained unchanged at 2.2% in April. | This figure matched March’s inflation rate, defying forecasts of a decrease to 2.1%. |
| Core inflation increased to 2.7% from 2.4% in March. | Services inflation rose to 3.9%, up from 3.5%. |
| The euro gained value against the USD and GBP post data release. | Bond yields remained stable, with 10-year German bonds rising by around 3 basis points. |
| ECB President Christine Lagarde is optimistic about reaching inflation targets by 2025. | Lagarde noted the ECB’s decisions will heavily rely on ongoing data analysis. |
| Growth in the Euro zone was reported at 0.4% for Q1 2025, exceeding expectations. | Concerns remain over potential impacts from global tariff tensions affecting future growth. |
Summary
Euro zone inflation has remained stable at 2.2% as of April 2025, indicating a steadiness that leaves room for potential interest rate cuts by the European Central Bank (ECB). Despite minor increases in core and services inflation, economists are cautious about future inflation stability due to ongoing tariff uncertainties. Overall, while recent data indicates that the euro zone economy might be on a path of growth, policymakers emphasize a close watch on inflation trends and external economic factors.