German Inflation April 2025: Insights and Economic Impact
The recent figures on German inflation for April 2025 reveal a slight dip to 2.2%, a result that has garnered attention in light of its implications for the broader German economic landscape. As Germany grapples with fluctuating GDP growth, which managed a nominal increase of 0.2% in the first quarter, the April inflation rate in Germany raises questions about the efficacy of the European Central Bank’s (ECB) inflation targets. The consumer price index remains a critical indicator, reflecting core inflation Germany’s persistent challenges, especially in the backdrop of rising services inflation which outpaced forecasts. Such economic shifts have led experts to reassess the German economic outlook, considering the ongoing struggles with energy prices and overall consumer sentiment. With scrutiny on the implications for households, businesses, and overall economic policy, this month’s inflation data is pivotal in shaping future strategies for both the ECB and the German government.
In April 2025, the economic situation in Germany took center stage as inflation figures were released, showing a notable decrease that nonetheless surpassed expectations. This April inflation rate revealed significant dynamics within Germany’s economy, which has navigated a precarious path marked by minimal growth and shifting consumer prices. As the European Central Bank evaluates its inflation strategies, the topic of core inflation in Germany and its broader impacts has become increasingly relevant. Observers are keen to see how these developments will influence both domestic policies and the eurozone’s economic stability. With challenges like rising costs in essential services and the ongoing debate over Germany’s economic prospects, the latest statistics provide vital insights into the nation’s financial health.
Understanding German Inflation Trends in April 2025
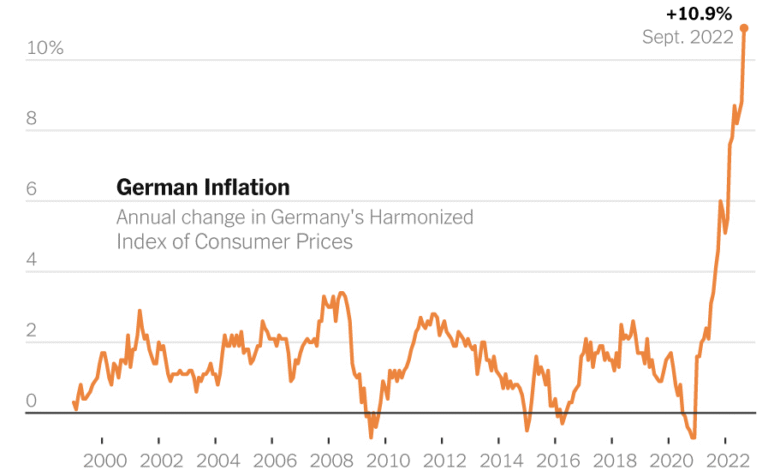
In April 2025, German inflation edged down to 2.2%, reflecting a slight dip from the previous month’s figure of 2.3%. This decline, while a minor relief for consumers, still surpassed many economists’ expectations, who had predicted a figure of only 2.1%. The inflation rate remains closely monitored by financial analysts and is crucially relevant given the ongoing economic stagnation that Germany has been experiencing for nearly two years. The consumer price index highlights these complexities, particularly noting that while overall inflation has eased, core inflation—an indicator often favored by the ECB—actually increased to 2.9%. This raises questions about the resilience of inflationary pressures amid fluctuating energy prices and consumer spending patterns.
The slight dip in inflation is primarily attributed to decreases in food and energy costs; however, services inflation has seen notable resistance, climbing to 3.9% in April. This persistence in services inflation can indicate a broader issue within the German economy regarding wage growth and service sector stability. Economists like Sebastian Becker from Deutsche Bank caution that while overall inflationary trends may appear to align better with the ECB’s target, underlying factors point toward persistently high core inflation rates, which complicate the economic outlook further. Understanding these dynamics is essential for policymakers aiming to implement effective monetary strategies.
The Economic Outlook: What’s Next for Germany?
Looking ahead, Germany’s economic outlook remains uncertain. Despite registering a modest GDP growth of 0.2% in the first quarter of 2025, many experts argue that this is insufficient to break the cycle of stagnation. Continuous fluctuations in GDP from growth to contraction highlight the challenges that the largest economy in Europe is currently facing. Factors such as increased competition from China, rising production costs, and ongoing geopolitical uncertainties, particularly regarding U.S. trade policies, are contributing to a fragile economic framework. For Germany to regain robust growth and stability, it must navigate these complexities effectively and bolster its key economic sectors such as automotive and manufacturing.
Moreover, revisions to Germany’s economic forecasts now predict stagnation throughout 2025, exacerbated by the ramifications of international tariff policies introduced by the U.S. The impact of these tariffs affects not only trade relationships but also internal economic confidence and investment levels. To counter these challenges, the German government has suggested infrastructure investments and adjustments to fiscal policies, in hopes of rejuvenating economic growth. However, analysts remain cautious, noting that while these fiscal measures may provide a longer-term solution, immediate results are crucial to alleviating persistent stagnation.
Core Inflation and ECB Targets: A Balancing Act
As core inflation in Germany increased to 2.9% in April 2025, it has become increasingly clear that this measurement is more significant for the European Central Bank (ECB) than headline inflation rates. The ECB aims to maintain inflation close to its 2% target, and with core inflation exceeding this mark, it raises the question of the effectiveness of the ECB’s monetary policy in managing inflationary pressures. The rise in core inflation suggests that underlying economic factors—not merely fluctuating food and energy prices—are driving price increases across various sectors.
The ECB’s response to these developments will be crucial, as further action may be required to steer core inflation back closer to target rates. Tightening monetary policy could safely rein in inflation but may also risk stifling economic growth that is already under pressure due to various external factors. Thus, the central bank faces a delicate balancing act; it must consider the interplay between stabilizing inflation and fostering an environment conducive to sustainable economic recovery.
Impact of Energy Prices on German Inflation
Energy prices play a pivotal role in influencing inflation trends within Germany. The recent significant drop in energy prices, which fell by 5.4%, contributed positively to an overall easing of consumer inflation in April. While lower energy costs generally signal relief for consumers and businesses alike, the relationship between energy prices and core inflation complicates the broader economic picture. With energy consistently affecting production costs and consumer spending, fluctuations in this sector disproportionately influence overall inflation metrics.
In light of these trends, policymakers must remain vigilant about potential volatility in energy markets, as unexpected spikes can quickly reverse any progress made in stabilizing inflation. Additionally, as the global economy continues to shift towards renewable energy sources, Germany’s energy policies will need to adapt, balancing short-term inflation targets with long-term sustainability goals. This conundrum highlights the complexity of inflation management in the current economic landscape.
Consumer Spending Patterns in Response to Inflation
As inflation rates adjust, consumer spending patterns inevitably shift in response, impacting the economy’s overall health. The slight inflation dip in Germany to 2.2% does not automatically translate to increased consumer confidence or spending. In fact, many consumers remain cautious, particularly in the face of rising core inflation rates that reflect stable price increases in essential services. With many households feeling the strain of higher living costs, discretionary spending may take a backseat, further influencing the economic landscape.
The interplay of consumer sentiment and inflationary pressures highlights the need for effective fiscal policies that encourage spending while also addressing inflation concerns. As household consumption represented a key driver of GDP growth in early 2025, understanding how shifts in consumer behavior—prompted by inflation—can stabilize or destabilize the economy is essential for developed market economies like Germany. Strategies enacted now will be crucial to ensuring that consumer spending can rebound sufficiently to support sustainable economic growth.
The Role of Global Trade in the German Economy
Germany’s position as a leading export economy means that global trade dynamics significantly influence its economic health. Recent tensions, specifically due to U.S. trade policies and tariffs, have contributed to a climate of uncertainty that impacts German exporters. With a reliance on exports, fluctuations in international demand can lead to variations in GDP growth rates and also affect domestic inflation trends as price changes filter through the economy. Thus, a clear understanding of global trade developments is necessary for assessing the overall inflation and economic outlook for Germany.
Moreover, as the German government navigates these challenges, strategic adjustments to trade policies and international relations are crucial. It is essential for Germany to protect and strengthen its trade partnerships, particularly with significant markets like the U.S. and China, where tariffs could adversely affect export volumes. As the 2025 predictions suggest stagnation, fostering favorable trade environments becomes even more pressing to sustain economic momentum and manage inflation effectively.
Fiscal Stimulus and Economic Growth Prospects
In response to persistent economic stagnation, the German government has initiated discussions surrounding fiscal stimulus, including a significant investment fund aimed at infrastructure and climate initiatives. This planned fiscal stimulus, estimated at €500 billion, could potentially galvanize different sectors of the economy, promoting growth and stability in both the short and long term. By redirecting funding toward these essential areas, Germany aims to foster innovation and resilience against economic fluctuations.
However, the impact of such stimulus is highly contingent upon effective implementation and overcoming bureaucratic challenges. Experts warn that without swift and efficient execution, the expected benefits may be slow to materialize. Therefore, the government’s actions and strategies moving forward will be critical in reassessing the broader economic picture. As investment in future-oriented sectors becomes increasingly relevant, stakeholders must remain vigilant to ensure that fiscal changes lead to tangible improvement in economic growth and inflation management.
Investment Landscape for German Enterprises
Amidst the fluctuating economic climate, the investment landscape for German enterprises is being reshaped by both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, the current inflationary environment presents obstacles, particularly the rising costs associated with materials and labor. On the other hand, governmental fiscal initiatives designed to boost infrastructure can provide a much-needed lifeline for companies seeking to innovate and expand. This dichotomy underscores the necessity for businesses to adapt their strategies according to the evolving economic indicators, particularly as they relate to inflation and growth.
Additionally, foreign investments remain a crucial factor for the German economy. In recent years, foreign direct investments (FDIs) have begun to see some fluctuations, potentially influenced by global market perceptions of economic stability. With Germany’s GDP growth currently inching upward, now could be an opportune time for international investors to consider lucrative opportunities in key sectors that cater to future trends. However, corporate resilience is essential to capitalize on these opportunities effectively.
The Importance of Monitoring Economic Indicators
As the economic landscape evolves, regularly monitoring critical economic indicators becomes paramount for forecasting and decision-making processes. For Germany, key metrics such as GDP growth rates, inflation rates, and core inflation are essential data points that help in crafting sound fiscal and monetary policies. Understanding these indicators allows businesses, analysts, and policymakers to evaluate current trends and make informed decisions that can avert deeper economic troubles.
Through comprehensive analysis of these economic indicators, stakeholders can identify potential risks before they escalate and align strategies accordingly. As Germany grapples with the dual challenges of inflation and stagnation, an informed approach toward interpreting these trends will become increasingly important in determining the nation’s economic trajectory for the remainder of 2025 and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the German inflation rate for April 2025 and how does it compare to previous months?
In April 2025, the German inflation rate dipped to 2.2%, slightly easing from the 2.3% reported in March. This figure was above economists’ expectations of 2.1%, reflecting ongoing challenges in the German economic outlook.
How does the April inflation rate in Germany affect the European Central Bank (ECB) inflation targets?
The German inflation rate of 2.2% in April 2025 is approaching the ECB’s inflation target of 2%. However, the core inflation, which rose to 2.9%, suggests persistent inflationary pressures that the ECB must consider in its policy decisions.
What are the implications of the April inflation data for Germany’s GDP growth?
The April 2025 inflation data suggests a complex economic landscape. While a 2.2% inflation rate might seem favorable, it is coupled with a modest GDP growth of 0.2% in the first quarter, indicating that the German economy is still grappling with sluggishness despite slight recovery.
How has core inflation in Germany changed in April 2025?
In April 2025, Germany’s core inflation increased to 2.9% from 2.6% in March, marking a significant rise. This uptick highlights underlying inflation pressures, diverging from the overall decline in consumer inflation, and presents a challenge for the ECB in achieving its inflation targets.
What are the challenges facing Germany’s economic outlook despite a slight increase in GDP?
Germany’s economic outlook remains challenged due to prolonged stagnation, as demonstrated by fluctuating GDP growth and ongoing competition from international markets, particularly in industries like automotive. Additionally, external factors, including tariffs, further impact the economic stability.
What sectors are contributing to inflation in Germany as of April 2025?
As of April 2025, services inflation surged to 3.9%, contributing significantly to the overall inflation rate in Germany, while energy prices fell. This indicates that while consumer prices are stabilizing, certain sectors exhibit stronger inflationary trends.
How does the current state of inflation in Germany relate to past economic performance?
Current inflation levels, such as the 2.2% rate in April 2025, indicate a recovery phase for Germany from the economic disruptions experienced in 2023 and 2024. However, the increase in core inflation suggests that underlying economic strengths must be addressed to sustain growth.
What fiscal changes are taking place in Germany that may influence future inflation?
Recent alterations to Germany’s debt brake rule may enable enhanced infrastructure and defense spending, possibly stimulating economic growth and influencing inflation rates in the foreseeable future, as these measures are implemented.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| German Inflation Rate | 2.2% in April 2025; fell slightly from March’s 2.3%, exceeding economist forecasts of 2.1%. |
| Core Inflation | Rose to 2.9%, up from 2.6% in March, indicating persistent inflation pressures. |
| Services Inflation | Increased to 3.9%, showing underlying price pressures in the services sector. |
| Energy Prices | Dropped significantly by 5.4%, contributing to the overall inflation rate decline. |
| Economic Growth | Economy grew by 0.2% in Q1 2025, indicating slow recovery from previous stagnation. |
| Challenges Facing Economy | Struggles with competition, trade tension with the U.S., and ongoing effects of tariffs. |
| Fiscal Policies | New debt rules could spur spending, but implementation remains critical. |
| Future Outlook | Economic forecasts indicate stagnation with potential for long-term growth improve. |
Summary
German inflation for April 2025 has dipped to 2.2%, deviating slightly from expectations and marking an intriguing development in the economic landscape. Despite positive indicators in GDP growth, challenges remain, particularly in inflationary pressures and external trade dynamics. The persistent rise in core inflation signals ongoing pressures that could impact future monetary policy decisions. Overall, while Germany’s economy shows signs of recovery, the outlook remains cautious due to global influences and internal economic adjustments.