Tariff Agreement with China Marks Strategic Decoupling Progress
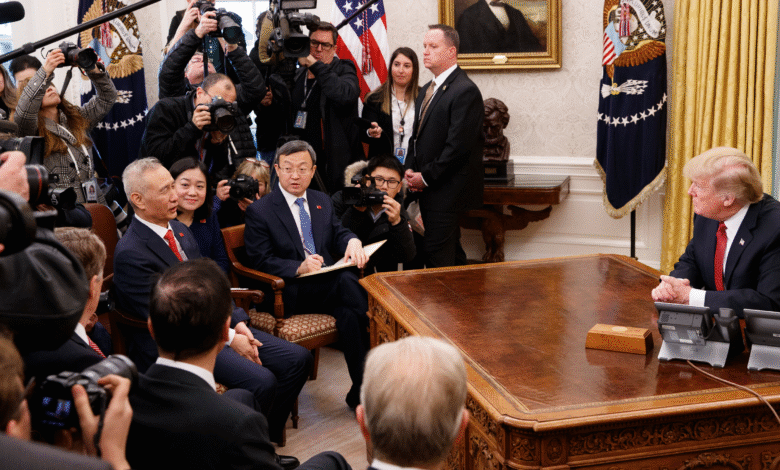
The recent tariff agreement with China has emerged as a significant development in the ongoing conversation about U.S. trade policies and economic strategy. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent has characterized this agreement as a step forward in the country’s efforts for ‘strategic decoupling’ from its main trading partner. While the details of this U.S.-China trade deal remain somewhat ambiguous, it has been confirmed that the previously planned reciprocal tariffs will not proceed, although broad-based tariffs of 10% will remain in place. Bessent emphasized the importance of this agreement in addressing the U.S. trade deficit, which amounted to nearly $440 billion in goods imported from China last year. By enhancing the resilience of U.S. supply chains and reducing reliance on Chinese imports, this tariff arrangement marks a crucial milestone in the quest for economic independence and stability.
In current discussions surrounding international commerce, the notion of a tariff agreement with China reflects broader themes of economic self-sufficiency and trade balance. The recent remarks made by Treasury Secretary Bessent highlight the ongoing efforts to strategically distance the U.S. economy from Chinese trade reliance, especially following disruptions caused by the global pandemic. This trade accord, albeit still lacking in detailed execution plans, indicates a potential shift in U.S. policy, aiming to reduce excessive imports while maintaining essential tariffs on certain goods. As the dialogue surrounding U.S. supply chain reliability and economic resilience evolves, this latest agreement demonstrates the administration’s commitment to fostering a more sustainable trade environment. The emphasis on maintaining strategic trade relationships while decoupling from China is becoming increasingly evident in U.S. trade discourse.
Understanding the New Tariff Agreement with China
The recent tariff agreement with China marks a significant step in reconfiguring U.S. trade policy. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent emphasized that this deal represents progress in the strategic decoupling from China, aiming to reduce reliance on Chinese imports while maintaining a level of economic engagement. The agreement primarily focuses on halting reciprocal tariffs for a defined period, while the existing broad-based 10% duties remain in place. This strategic maneuver acknowledges the need to protect domestic industries while also exploring avenues for cooperation.
Despite the details surrounding the U.S.-China trade deal being sparse, the implications of this tariff agreement are extensive. It signals an ongoing effort to mend supply chain vulnerabilities that were exposed during the pandemic. Bessent highlighted that the trade deficit with China, which stood at nearly $440 billion in 2024, necessitates new strategies that not only aim to stabilize the economy but also prioritize national security concerning essential goods.
Bessent’s Statements on Tariffs and U.S. Supply Chain Decoupling
In his recent statements, Bessent shed light on the rationale behind the U.S. tariff system and its role in the broader context of supply chain decoupling. He articulated that the current U.S. tariffs on imports serve as a tool for bolstering domestic production, specifically in sectors like steel. His perspective emphasizes that while tariffs can create immediate hurdles for international trade, they are instrumental in achieving long-term strategic objectives, which include fostering a robust and resilient U.S. supply chain.
Additionally, Bessent’s commentary reflects an understanding that the approach to tariffs should not be one of complete separation from China but rather a recalibration based on strategic necessities. This notion of strategic decoupling aligns with discussions surrounding the U.S.’s shift to a goods-oriented economy post-pandemic, focusing on creating a more self-sufficient economy while mitigating risks that were highlighted during periods of global disruption.
The Impact of Strategic Decoupling on US-China Relations
The notion of strategic decoupling from China has far-reaching implications for U.S.-China relations. As Bessent articulated, the objective isn’t to create a complete rift but to redefine the economic interactions between the two countries. This strategic framing allows for a more nuanced approach, facilitating cooperation in vital areas such as public health and drug trafficking, while still addressing the legitimate concerns over supply chain vulnerability and national security.
Moreover, the continued reliance on Chinese goods exacerbates issues regarding trade deficits; hence, balancing decoupling with potential partnerships is critical. By addressing specific industries, like the fentanyl crisis, Bessent illustrates how targeted collaborations could alleviate pressing concerns while promoting mutual benefits. Therefore, as the U.S. navigates this complex landscape, strategic decoupling becomes a pivotal element in redefining its interactions with China.
Strategic Necessity versus Complete Separation from China
Bessent’s insights into the strategic necessity of decoupling from China unveil the complexity of U.S. trade policy. Rather than promoting a complete separation, the focus is on creating a balanced approach that mitigates risks while maintaining essential trade relationships. The emerging sentiment emphasizes that complete economic disengagement is impractical, considering the interdependent nature of global markets. A strategic focus allows for essential goods to be sourced responsibly while enhancing domestic production capabilities.
This measured approach is particularly vital in industries where the U.S. has faced significant vulnerabilities, such as pharmaceuticals and technology. By recognizing which sectors require close scrutiny, U.S. policymakers can create targeted strategies that drive innovation and security without disrupting overall economic stability. This delineation highlights the necessity for continued engagement with China, while firmly addressing areas of strategic concern.
Tariffs and the Future of U.S. Trade Policy
The future of U.S. trade policy will likely be dominated by tariff strategies aimed at reshaping international trade dynamics, particularly with China. Bessent’s statements point towards a framework where tariffs are not merely revenue generators but tools for fostering an economic environment that prioritizes domestic stability and resilience. This perspective is increasingly relevant as national security concerns push policymakers to reconsider existing trade agreements and structures.
As the U.S. navigates its relations with China, the broader implications of tariffs will play a key role in the design of future trade policies. In the context of global supply chain adjustments and inflationary pressures, it becomes crucial to strike a balance between protecting U.S. industries and maintaining competitive trade with international partners. The ongoing discussions surrounding tariffs underscore the need for a comprehensive approach that encompasses both economic strategy and international collaboration.
Navigating the Challenges of Tariffs in a Post-Pandemic World
The challenges posed by tariffs have been accentuated in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Bessent noted that vulnerabilities in the supply chain became alarmingly clear when the transition from a service-oriented economy to one reliant on physical goods resulted in unprecedented inflation levels. Understanding these challenges becomes imperative for policymakers tasked with recalibrating U.S. trade strategies that not only address current issues but also anticipate future crises.
In response to these challenges, the Biden administration seems poised to utilize tariff agreements as strategic tools rather than reactive measures. By integrating insights gained during the pandemic into future trade negotiations, U.S. policymakers can create a more resilient economic framework. The intersection of tariffs with broader economic policy will be essential in ensuring that the U.S. remains competitive in the global market while supporting domestic growth.
The Role of Collaboration in U.S.-China Trade Relations
Bessent’s views on the importance of collaboration highlight a pivotal shift in U.S.-China trade relations. Despite the backdrop of tariffs and strategic decoupling, his outlook underscores a willingness to work with Chinese officials on critical issues like fentanyl trafficking. This cooperative approach signals an understanding that collaboration can lead to significantly positive outcomes, even amidst broader trade tensions.
The emphasis on collaboration reflects a pragmatic recognition of the interconnectedness of global trade issues. As nations grapple with historical trade imbalances and economic dependencies, creating pathways for dialogue and cooperation becomes essential. In this context, Bessent’s comments illustrate a vision for U.S.-China relations that is not solely adversarial but incorporates elements of partnership, particularly in sectors that directly impact public health and safety.
Evolving Economic Strategies in Response to Global Shifts
The response to global economic shifts necessitates a reevaluation of established strategies, as highlighted by Bessent in his discussion on tariffs. With increasing pressures from both domestic and international fronts, the U.S. is compelled to adapt its economic policies to better suit an evolving global landscape. This adaptability reflects a broader understanding that the world economy is not static but dynamic, requiring ongoing assessments and strategic pivots.
In navigating these challenges, the U.S. is increasingly inclined to harness tariffs as a mechanism for not only protecting domestic industries but also as a means to align economic strategies with emerging global realities. By scrutinizing trade relationships and tariffs through this lens, Bessent advocates for a more thoughtful approach that aligns U.S. interests with the complexities of the current global economy.
Long-term Implications of the U.S.-China Trade Deal
The long-term implications of the recent U.S.-China trade deal will likely shape the future landscape of international trade. As Bessent articulated, the notion of strategic decoupling from China is not merely about immediate economic gains but about positioning the U.S. for long-term resilience and competitiveness. The careful balancing of tariffs and trade agreements will be essential as the U.S. strives to protect its interests while navigating its relationship with one of its largest trading partners.
Furthermore, the success of this trade deal may hinge on the U.S.’s ability to shift its economic paradigm from one heavily dependent on Chinese imports to a more self-sufficient approach that also maintains strategic collaborations. This may involve investing in domestic production capabilities and building supply chain resilience. Ultimately, the outcome of these negotiations could redefine not only U.S.-China relations but also set a precedent for how nations globally approach trade agreements in an increasingly interdependent world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the tariff agreement with China according to Bessent’s statements on tariffs?
According to Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, the tariff agreement with China marks progress in the U.S.’s strategic decoupling from China. This agreement signifies an important step towards reducing dependence on Chinese imports while maintaining some tariffs for specific goods.
How does the tariff agreement with China affect U.S. supply chain decoupling?
The tariff agreement with China is viewed as a crucial part of the U.S. supply chain decoupling strategy. By halting reciprocal tariffs while retaining broad-based duties, the U.S. aims to enhance domestic resilience in supply chains disrupted during the pandemic.
What are the main components of the recent tariff agreement with China?
The recent tariff agreement with China involves a 90-day suspension of planned tariff hikes, with existing broad tariffs remaining in place. Specific industry tariffs, particularly a notable 20% fee on fentanyl-related products, will not be disrupted.
Why does Bessent emphasize strategic decoupling from China rather than complete separation?
Bessent emphasizes strategic decoupling from China to address critical supply chain vulnerabilities without completely severing trade ties. This approach seeks to focus on strategic necessities and reduce reliance on Chinese goods while still facilitating trade where suitable.
What is the impact of U.S. tariffs on imports from China following the trade deal?
Following the trade deal, the impact of U.S. tariffs on imports from China includes the continuation of a 10% duty on broad categories of goods while halting additional reciprocal tariffs. This aims to strike a balance between protecting domestic industries and maintaining necessary imports.
How does Bessent’s view on the tariff agreement relate to the future of U.S.-China trade relations?
Bessent’s view on the tariff agreement suggests a cautious optimism regarding U.S.-China trade relations, indicating that while the U.S. does not seek complete separation, it aims for a more strategic and resilient approach to future engagements and collaborations, especially concerning issues like fentanyl.
What challenges does the U.S. face in achieving supply chain decoupling from China?
The U.S. faces several challenges in achieving supply chain decoupling from China, including establishing domestic alternatives for imported goods and addressing the significant trade deficit, which stood at approximately $440 billion in 2024.
What role do tariffs play in enhancing U.S. economic resilience according to Bessent?
Tariffs play a critical role in enhancing U.S. economic resilience by protecting key domestic industries, such as steel production, and creating a framework to manage imports strategically while addressing vulnerabilities revealed during global disruptions like the pandemic.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Trade Agreement Significance | Represents progress in strategic decoupling from China as stated by Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent. |
| Reciprocal Tariffs | Reciprocal tariffs will be halted, but broad-based 10% duties remain in place. |
| U.S.-China Trade Deficit | U.S. imported nearly $440 billion from China in 2024, highlighting a significant trade deficit. |
| Supply Chain Resilience | Bessent emphasized the need for more resilient U.S. supply chains post-pandemic. |
| Tariffs and Domestic Production | Tariffs aimed to support increased domestic steel production and manage industry-specific tariffs. |
| Fentanyl Tariffs | Includes a 20% fee linked to fentanyl; positive collaborations with China on fentanyl issues. |
| Future Discussions | Next discussions with China may occur in the coming weeks, focusing on supply chain and tariffs. |
Summary
The tariff agreement with China marks a significant step forward in the ongoing strategic decoupling between the two economies. As outlined by Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, this agreement aims to reduce U.S. dependence on Chinese imports while acknowledging the complexities and gradual nature of this transition. With tariffs being adjusted and specific measures in place to support domestic industries, the U.S. is not seeking complete decoupling but rather a strategic alignment based on national necessities. The positive engagement regarding collaborative efforts on fentanyl further underscores the potential for constructive discussions moving forward.