Trade Deficit Records Major Decrease Amid Lower Imports
A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports, creating a significant imbalance in its trade balance. Recently, the U.S. has seen a dramatic decline in its trade deficit, a development that could have far-reaching implications for the economy. In April, the deficit plummeted by a record amount, largely influenced by a sharp reduction in demand for imports as companies and consumers adjusted to President Trump’s tariffs. The decline in imports, down 16.3%, coincided with a modest rise in exports, which increased by 3%. Understanding the economic impact of trade and how these shifts affect U.S. trade relations is essential for grasping the complexities surrounding the trade deficit and its influence on the global marketplace.
The concept of a trade imbalance reflects the juxtaposition between a nation’s imports and exports, essentially showcasing how much more a country is buying compared to what it is selling abroad. With recent statistics highlighting a significant drop in the U.S. trade deficit, it’s crucial to examine the broader economic landscape affected by these figures. The recent surge in tariffs, spearheaded by President Trump, has prompted consumers and businesses to reconsider their import strategies, leading to a notable decrease in goods entering the country. This shift not only alters the dynamics of economic interactions but also influences relationships with key trading partners such as China and the European Union. Ultimately, the intricacies of trade deficits and balances play a pivotal role in shaping national policies and economic forecasts.
Understanding the Trade Deficit
The trade deficit is an important economic indicator that reflects the balance of trade between a country and its global partners. In April, the U.S. trade deficit witnessed a historic drop, largely due to a significant decrease in imports, which fell by 16.3% to $351 billion. This change in trade dynamics is significant as it indicates ongoing adjustments in U.S. trade relations, especially amid President Trump’s implementation of tariffs aimed at improving the nation’s trade balance. While a trade deficit suggests that a country imports more than it exports, the implications of this economic situation can be multifaceted when considered in context.
Debates surrounding the trade deficit often hinge on perceptions of economic health, with some viewing a deficit as a negative sign while others highlight the benefits of imports on consumer choices and prices. The recent decline in the U.S. trade deficit, shrinking to $61.6 billion, reveals a complex picture of international trade where both imports and exports are experiencing fluctuations. Despite the reduction indicating a potential for improved U.S. trade relations, it is essential to understand the broader economic impact of trade policies and their developments on the global stage.
Impact of President Trump’s Tariffs on Trade Balance
President Trump’s tariffs, introduced with the aim of rebalancing trade, have significantly influenced the flow of imports and exports, leading to fluctuations in the U.S. trade balance. Following the announcement of a 10% tariff on all U.S. imports around “Liberation Day,” there was a marked rush by consumers and businesses to make purchases, resulting in a historic increase in the trade deficit. However, the subsequent drop in imports this April indicates a market adjustment to these trade barriers.
The economic impact of these tariffs goes beyond immediate trade figures. As companies navigate the heightened import costs, they are compelled to adapt their sourcing and pricing strategies, which ultimately can influence consumer behavior and market conditions. Furthermore, while the trade deficit reduction may seem favorable, economic analysts caution that an overemphasis on trade deficits may overlook the potential benefits that imports can have for U.S. consumers and businesses.
The Role of Exports in Trade Relations
Exports play a crucial role in shaping a country’s trade relations and overall economic performance. In April, exports from the U.S. rose by 3%, demonstrating resilience amidst a backdrop of fluctuating import levels. The increase in exports suggests a strengthening economy that continues to engage with global markets, thereby reinforcing relationships with international partners. A diverse export portfolio helps mitigate the risks associated with trade deficits and creates jobs domestically, which is essential for sustaining long-term economic growth.
As U.S. exports expand, especially to critical markets such as China and the European Union, the dynamics of trade balance become increasingly relevant. The ongoing negotiations and dialogues between nations, facilitated by leaders like President Trump, underline the importance of maintaining strong export levels. Strategic management of trade relations can help ensure that the growth of exports balances against imports, ultimately contributing to a more favorable economic landscape.
Economic Considerations Behind Trade Fluctuations
Trade fluctuations often provide insight into the underlying economic landscape and consumer behavior. The significant reduction in the U.S. trade deficit in April can be attributed to various economic factors, including changes in consumer demand and the impact of tariffs. A slowdown in imports can signal changing market dynamics where consumers might prioritize domestic over foreign goods or adjust spending based on new price realities induced by tariff changes. This economic shift is indicative of a responsive market that adapts to policy changes.
Moreover, understanding the economic impact of these trade fluctuations requires a nuanced approach that looks beyond just the trade deficit figures. Economic indicators such as employment rates, inflation, and consumer spending patterns play a vital role in comprehending the broader implications of trade policies. Analysts view such variations in trade balance as opportunities for ongoing dialogue about import-export relationships, navigating the fine line between protecting domestic industries and promoting international trade.
Analyzing Imports and Exports in Today’s Economy
The balance of imports and exports is a key indicator of a nation’s economic health. Recent data showing a significant decline in U.S. imports against a backdrop of rising exports indicates a noteworthy shift in this balance. As imports dropped by 16.3% in April, businesses and consumers appeared to recalibrate their spending habits in response to tariff impacts. This adjustment not only influences the trade deficit but also reflects a strategic move by both industries and consumers to align more closely with national economic policies.
Moreover, the growth in exports serves as a testament to the capabilities and competitiveness of U.S. goods in the global market. The positive export trajectory brings forth opportunities for job creation and economic expansion. As companies engage more in international trade, understanding how imports and exports interrelate can provide a clearer picture of the U.S. economic environment, informing both policy decisions and consumer behaviors moving forward.
The Trade Balance and Its Economic Implications
The trade balance is an intricate aspect of economic policy and performance that informs various stakeholders about the state of the economy. A falling trade deficit, as seen this April, may initially suggest a healthier trade position; however, it is vital to consider the implications this has on economic growth and job creation. Economists argue that while reducing the deficit can be positive, an overreliance on such metrics could detract from the true benefits of maintaining robust trade relationships with global partners.
The smaller trade deficit can provide breathing room for domestic industries, allowing them to innovate and compete more effectively on a global scale. Nevertheless, policymakers must remain vigilant, recognizing that trade relationships are intricate and rooted in mutual benefit. The balance must be struck between protecting local industries and taking advantage of the efficiencies afforded by imports, ensuring that the U.S. continues to thrive economically in a competitive environment.
Current Trends in U.S. Trade Relations
The U.S. trade relations have entered a new phase, influenced by the current political landscape and economic policies surrounding tariffs. With ongoing negotiations aimed at improving trade dynamics, the current trends reflect a push towards greater efficiency and fairness in trade practices. Observing the shifts in the trade deficit alongside the changes in import-export behavior can offer valuable insights into the long-term sustainability of trade relationships between the U.S. and its global partners.
In this context, understanding the importance of U.S. trade relations is paramount as they not only affect economic growth but also bolster global partnerships. The recent communication between President Trump and international leaders highlights the concerted efforts to refine trade agreements that benefit all involved parties. As these trends unfold, it is critical to observe how they will shape future economic policies and influence the overall state of international trade.
Looking Ahead: Future of U.S. Trade Balance
The future of the U.S. trade balance appears to be in a state of flux, driven by complex global economic factors and domestic policy shifts. As industries adapt to new tariff-related challenges, the management of the trade deficit will remain a crucial focus for economic planners. Understanding how the balance of imports and exports will evolve in the coming months is essential for anticipating potential market responses and making informed strategic decisions.
Additionally, ongoing developments in trade relations, particularly concerning key players like China and the European Union, will play a significant role in shaping the future of U.S. trade balance. As tariffs continue to influence trade patterns, companies and consumers alike will need to navigate the changing landscape carefully. Insights into current trends and a proactive approach to trade negotiations will be vital for ensuring that the U.S. maintains a competitive edge on the global stage.
Implications of Trade Policies on Economic Growth
Trade policies enacted by the government have profound implications for economic growth, influencing everything from consumer prices to employment levels. President Trump’s tariffs were designed not only to combat trade deficits but also to encourage the growth of U.S. manufacturing and job creation. However, the ramifications of such policies can be complex, resulting in both positive and negative effects on the economy at large.
As policymakers evaluate the success of these tariffs, it’s important to consider the long-term consequences they may have on international trade relations. The ability to balance protecting American interests while fostering healthy international trade relationships will be pivotal. As global economic conditions shift, the interplay between trade policies and economic growth will continue to evolve, highlighting the need for agile and informed economic strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a trade deficit and how does it affect the trade balance?
A trade deficit occurs when a country’s imports exceed its exports, negatively impacting the trade balance. In April, the U.S. experienced a significant trade deficit reduction due to a sharp decline in imports and a slight increase in exports.
How do imports and exports influence the U.S. trade deficit?
Imports and exports are crucial in determining the trade deficit. Recently, the U.S. trade deficit fell as imports dropped by 16.3%, while exports grew by 3%, resulting in a deficit of $61.6 billion, well below expectations.
What is the economic impact of trade deficits on the U.S. economy?
Trade deficits can have complex economic impacts, as seen when the U.S. deficit shrank in April. While some view a deficit as negative, economists argue that increased imports have often benefited American consumers and businesses.
How have President Trump’s tariffs affected U.S. trade relations and the trade deficit?
President Trump’s tariffs were initially aimed at reducing the trade deficit by imposing duties on imports. However, the recent drop in the deficit suggests that the tariffs led to a change in consumer behavior, reducing imports ahead of his proposed trade measures.
What sectors or countries contribute most to the U.S. trade deficit?
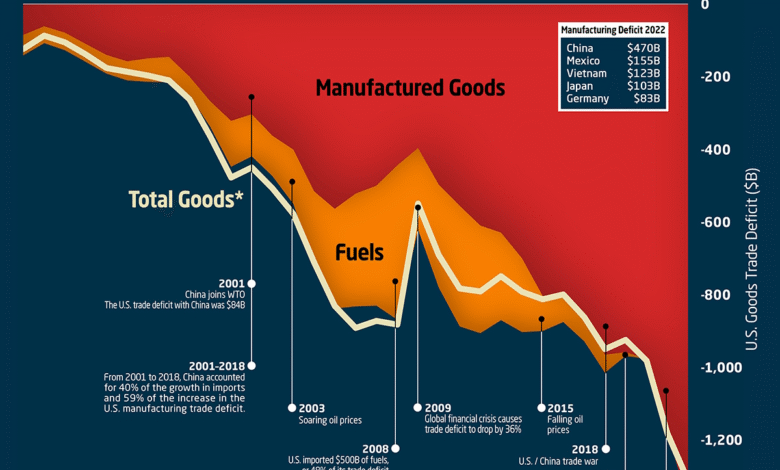
The largest contributions to the U.S. trade deficit have recently come from China, the European Union, and Vietnam, with China alone accounting for a deficit of $19.7 billion in April.
Can the trade deficit be interpreted as a sign of economic weakness?
Not necessarily. While a trade deficit implies more imports than exports, it can also indicate strong domestic demand. The recent trade balance changes highlight that although the trade deficit fell, it does not automatically signify economic weakness.
What should we expect for future U.S. trade relations in light of recent trade deficit changes?
Future U.S. trade relations may see further negotiations, as President Trump indicated ongoing discussions with China. The evolving trade balance will be influenced by these diplomatic efforts and changes in import-export dynamics.
Are there specific products that heavily influence the U.S. trade deficit?
Yes, certain goods significantly influence the U.S. trade deficit. For instance, the report indicated that machinery, electronics, and consumer items are often large components of the imports contributing to the overall trade deficit.
What are reciprocal tariffs and how do they relate to the trade deficit?
Reciprocal tariffs are imposed to counterbalance unfair trade practices. They were discussed by President Trump as part of an initiative to reduce the trade deficit, though their impact is still unfolding as trade talks continue.
How do fluctuations in the trade deficit affect U.S. consumers?
Fluctuations in the trade deficit can directly affect consumers by influencing prices, product availability, and the overall economy. A lower trade deficit, as seen in April, might lead to more favorable trade conditions and pricing for consumers.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Record Trade Deficit Decrease | The U.S. trade deficit fell to $61.6 billion in April, the largest decrease on record. |
| Sharp Decline in Imports | Imports fell by 16.3%, dropping to $351 billion. |
| Increase in Exports | Exports rose by 3% during the same period. |
| Impact of Tariffs | Trade negotiations and tariffs introduced by Trump influenced import behavior. |
| Not Uniformly Positive | A decreasing trade deficit might suggest positive news, but economists urge caution. |
| Year-to-Date Trends | The deficit increased by 65.7% from the same period in 2024. |
| Largest Imbalances | The largest trade imbalance was with China, standing at $19.7 billion. |
Summary
Trade Deficit has become a pivotal topic in U.S. economic discussions, especially following the significant drop observed in April 2025. The record decrease in the trade deficit signifies fluctuating import and export dynamics, primarily influenced by recent tariff implementations and trade negotiations. While the lowering of the trade deficit typically carries a positive connotation, it is essential to consider the underlying complexities, including rising deficit rates compared to previous years and varied impacts on different economies involved.