China Retail Sales Growth Surges to New Heights in May
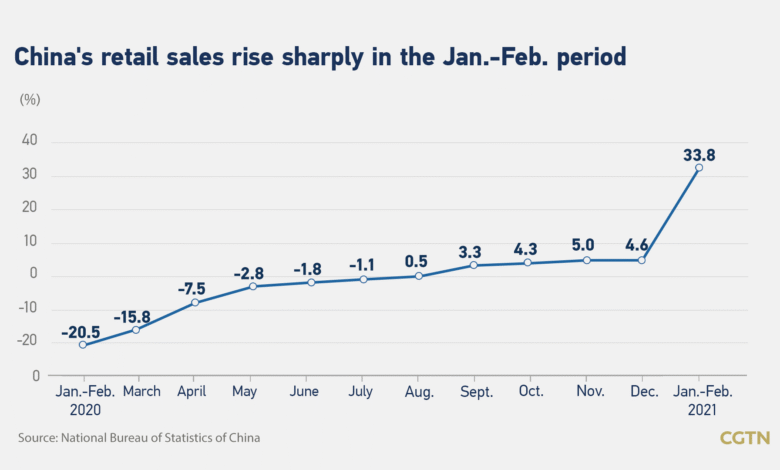
In the latest report on China retail sales growth, figures released for May reveal a remarkable surge of 6.4%, marking the highest increase since December 2023. This impressive performance eclipsed analysts’ predictions, who had anticipated only a 5% rise, and indicated an upward shift from April’s 5.1% growth. The boost in consumer spending comes in the wake of the Labor Day and Dragon Boat festivities, which historically stimulate shopping and expenditure. As China’s economy continues to recover, robust retail sales reflect not only a return in consumer confidence but also suggest potential implications for China trade relations and overall economic stability. Coupled with figures on industrial output and employment rates, this growth narrative paints a comprehensive picture of China’s ongoing economic resilience amid global challenges.
Exploring the dynamics of consumer buying patterns, the recent escalation in retail revenues from China underscores an essential aspect of the nation’s economic landscape. The latest May retail statistics indicate a notable climb, correlating with the resurgence in consumer confidence and heightened spending activities. This surge is critical for understanding China’s broader economic recovery and can also shed light on related sectors such as industrial production and investment trends. Furthermore, the interplay between domestic consumption and international trade dynamics highlights the ongoing transformation within China’s retail sector. Analysts and economists alike are closely monitoring these trends, as they provide crucial insights into the future of China’s economic growth and sustainability.
China Retail Sales Growth: A Surge in Consumer Activity
China’s retail sales in May 2025 experienced a remarkable increase of 6.4% year-on-year, marking the highest growth benchmark since December 2023. This surge is significant as it not only overcame analysts’ predictions of a 5% rise but also reflected an acceleration from the previous month’s growth of 5.1%. The uptick in retail sales can largely be attributed to major holiday periods, such as Labor Day and the Dragon Boat Festival, which traditionally stimulate consumer spending. Shoppers flocked to markets, spurred by government incentives like consumption vouchers, further enhancing the retail landscape in cities such as Shanghai.
The positive momentum in retail sales indicates a gradual recovery in consumer confidence, a crucial element for China’s broader economic recovery. As households showed increased willingness to spend, economic experts are optimistic about the sustained growth of consumer sectors, which could lead to a ripple effect across various industries. Nevertheless, despite these promising indicators in retail, there are parallel challenges with industrial output that must be addressed, as manufacturing remains a cornerstone of China’s economic structure.
Industrial Output Trends: Challenges Amid Retail Growth
In contrast to the notable growth in retail sales, China’s industrial output reported a slower increase of 5.8% year-on-year in May 2025. This figure slightly missed analysts’ expectations set at a 5.9% rise, reflecting potential stress in the manufacturing sector. This disparity suggests that although consumer spending is picking up, the overall industrial activity is not keeping pace, leading to concerns about the sustainability of this economic recovery. Experts believe that the slowdown could be indicative of underlying issues within the supply chain or weaker global demand for manufactured goods.
Furthermore, with fixed-asset investments also falling short of forecasts at a growth of just 3.7%, the overall industrial outlook appears cautious. The lackluster performance in industrial output could hinder China’s economic recovery trajectory as it relies heavily on robust industrial performance alongside growing consumer expenditure. Stakeholders are thus closely monitoring government policies and potential adjustments aimed at revitalizing industrial growth, which will be crucial for achieving balanced economic expansion.
China’s Economic Recovery: Factors Driving Growth
The recent growth in retail sales amid a slower industrial output reflects the complex dynamics of China’s economic recovery process. As sectors recover at different speeds, consumer spending has emerged as a crucial driver, propelled by pent-up demand and supportive fiscal measures from the government. Analysts suggest that while consumer behavior appears increasingly optimistic, the inconsistencies in industrial output growth highlight the need for a comprehensive strategy to support both consumers and manufacturers. These developments will play a critical role in shaping China’s economic recovery trajectory in the near future.
Additionally, as China seeks to bolster its spending momentum, it must also address challenges related to inflation, rising consumer prices, and international trade dynamics, particularly in the context of ongoing tariff negotiations with the U.S. A careful balance will need to be maintained to ensure that consumer enthusiasm translates into sustainable economic growth, while also fostering a robust industrial sector that can meet both domestic and international market demands.
Understanding May Retail Sales Data in Context
The May retail sales data presents an insightful look into China’s economic environment, showcasing considerable growth that exceeds market expectations. Analysts noted that the growth is indicative of not only a recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic era but also of changing consumer patterns evolving in response to both domestic and international factors. The government’s provision of consumption vouchers has played a significant role in encouraging spending, especially in leisure and hospitality sectors, which had been notably impacted in previous years.
Moreover, the context of this growth is essential, as geopolitical factors such as trade relations influence consumer confidence and market dynamics. Continued resilience in retail sales could signal a turnaround in overall economic sentiment, assuming that sectors such as industrial output can recalibrate in time to support such consumer trends. In the long run, maintaining growth in retail sales may require targeted investments in consumer goods and services, alongside structural reforms aimed at bolstering industrial performance.
The Impact of China Consumer Spending on Economic Stability
Consumer spending has a fundamental impact on the overall health of China’s economy, especially as local demand begins to recover. The 6.4% increase in retail sales suggests that consumers are not only willing to spend but are also responding positively to governmental measures aimed at stimulating economic activity. As consumer confidence builds, spending could drive further economic expansion, reinforcing China’s resilience as it navigates external pressures such as trade conflicts and global economic uncertainty.
However, sustaining this buoyancy in consumer spending requires addressing issues such as consumer price deflation, which has persisted for several months. Policymakers are keenly aware that to fortify consumer confidence, measures must be introduced to mitigate deflationary pressures while also enhancing job creation to further validate increased consumer expenditure. The government’s approach to managing these factors will be critical in shaping the landscape for Chinese consumers in the coming months.
Navigating China Trade Relations and Economic Growth
The complexities of China’s trade relations, particularly with the United States, have significant implications for its economic growth trajectory. The recent tariff deals, which provided temporary relief, have allowed for some normalization in trade flows, albeit still under the shadow of substantial tariff barriers that linger on many products. Growing exports to regions such as Southeast Asia and the EU serve as a testament to China’s attempts at diversifying its trade partnerships, which is essential for mitigating risks associated with dependence on the U.S. market.
Moreover, sustained economic growth will also depend on how effectively China can navigate its trade relations while maintaining stable domestic consumption levels. As exports continue to fluctuate amid adverse international conditions, strengthening internal markets becomes vital. Policymaking efforts that encourage diversification and resilience in trade relations will be pivotal in ensuring that the momentum in retail spending translates into broader economic stability.
Evaluating China’s Economic Forecasts Chapter: Post-Month Adjustment
Looking forward, economists are cautiously optimistic regarding China’s economic forecasts as domestic consumption seems poised to remain robust. The anticipation of GDP growth exceeding 5% in the first half of 2025 is encouraging, but it comes with the expectation that industrial challenges must be addressed simultaneously. Forecasts indicate that while consumer spending is likely to remain strong, industrial output will require concerted efforts to stimulate to support seamless economic growth.
In this context, ongoing assessment of economic indicators will be vital for policymakers to ensure that consumer spending aligns with industrial capabilities. Should the government implement effective measures to foster growth across all fronts, we may witness a solidified path toward sustained recovery, enabling China to not only achieve its short-term objectives but also lay a foundation for long-term stability in both consumer and industrial sectors.
The Role of Fixed-Asset Investment in China’s Growth Strategy
Fixed-asset investment figures reveal a critical dimension of China’s growth strategy, as this metric typically reflects the health of infrastructure and production capacity. In May 2025, the year-to-date growth rate of 3.7% came in below expectations, highlighting the necessity for renewed focus on stimulating investments that could elevate industrial output. This stagnation poses risks, as inadequate investments have the potential to hinder trade relations and the overall economic recovery, particularly as global markets continue to evolve.
To invigorate fixed-asset investment, Beijing may need to adopt approaches that not only incentivize private investment but also facilitate public investment in key sectors. Investing in infrastructure projects that elevate productivity could be beneficial, and if executed well, these strategies may contribute significantly to comprehensive economic recovery. Addressing the shortfalls in investment will be key to supporting the broader economic framework that underpins retail and industrial sectors.
The Future of China’s Economy: Balancing Growth with Challenges
As China moves into the latter half of 2025, navigating the path of economic recovery will hinge upon balancing the dual narratives of growth in consumer spending against the challenges posed by sluggish industrial output. The current retail sales surge offers hope, but it’s essential that growth is not merely an isolated phenomenon, rather, a signal of broader economic stabilization. Key indicators like unemployment rates can further provide insights into the resilience of the labor market and consumer behavior.
Ultimately, China’s economic future will involve intricate interactions between domestic consumption, industrial growth, and external trade dynamics. Policymakers must strategically address the challenges illuminated through recent data, ensuring that each sector contributes to a stable and thriving economic environment. With careful navigation through these complexities, China has the potential not only to recover but to emerge even stronger as it fosters a balanced and prosperous economic ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contributed to the recent growth in China retail sales?
China retail sales growth in May was primarily driven by the Labor Day and Dragon Boat holidays, leading to a significant increase of 6.4% year-on-year. This surge surpassed analysts’ expectations and was indicative of a recovering consumer spending environment.
How do May retail sales data reflect China’s economic recovery?
The May retail sales data, which showed a 6.4% increase, suggests a positive trajectory in China’s economic recovery following previous downturns. This growth indicates enhanced consumer confidence and spending, partly stimulated by government initiatives like consumption vouchers.
How does China’s industrial output growth relate to retail sales growth?
While retail sales growth reached a remarkable 6.4%, China’s industrial output growth slowed to 5.8% in May. This contrast highlights that despite robust retail performance, industrial activities are facing challenges, possibly affecting overall economic balance.
What is the significance of China consumer spending trends in retail sales growth?
Trends in China consumer spending significantly impact retail sales growth. The latest figures indicate a rebound in consumer confidence, with increased spending reflected in the 6.4% growth rate for May, signaling potential sustainability in economic recovery.
How might recent trade relations affect China retail sales growth?
Recent trade relations, including a truce in tariff disputes with the U.S., may provide temporary relief for China’s exports, indirectly benefiting retail sales growth by bolstering employment and consumer disposable income, thereby enhancing consumer spending.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Retail Sales Growth | 6.4% year-on-year growth in May, surpassing the expected 5%. This is the fastest increase since December 2023. |
| Industrial Output Growth | Slowed to 5.8% year-on-year, slightly below the expected 5.9%. |
| Unemployment Rate | Urban unemployment rate fell to 5.0%, the lowest since November. |
| Fixed-Asset Investment | Grew by 3.7% year-to-date, below the forecast of 3.9%. |
| Consumer Prices | Consumer prices fell by 0.1% year-on-year, continuing a four-month decline. |
Summary
China retail sales growth in May 2025 marked a significant turnaround, showcasing a 6.4% increase from the previous year, the fastest rate since late 2023. This surge was propelled by the country’s holiday seasons and defied analyst expectations. Despite the positive retail performance, industrial output growth fell short of forecasts, highlighting ongoing challenges within the Chinese economy, including sluggish domestic demand and deflation concerns. However, the lower unemployment rate and resilient export data indicate that China is on a path towards recovery, making this an essential time for monitoring economic trends.