Belt and Road Initiative: China’s Drive for Development
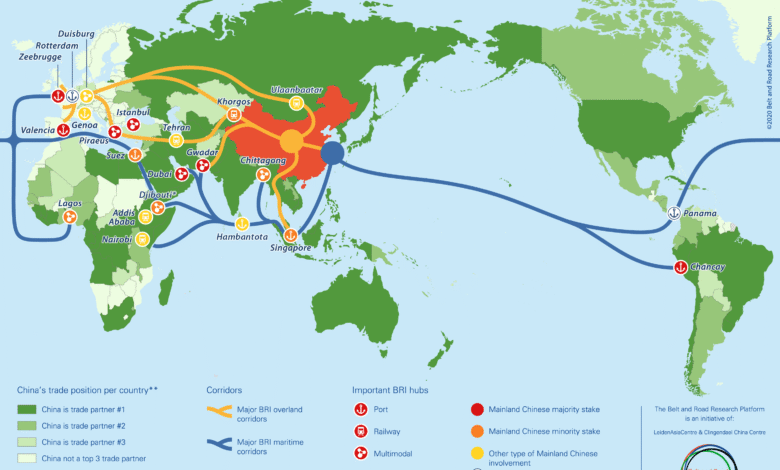
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), launched by China in 2013, is a bold vision for enhancing global connectivity through expansive infrastructure development. This ambitious program aims to create an extensive network of trade routes, linking Asia with Europe and Africa, thereby fostering economic growth and collaboration among participating nations. With the support of institutions like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), which provides critical infrastructure loans to developing countries, China is effectively shaping global development trends in its favor. The BRI not only underscores China’s strategic economic policies but also positions the country as a key player in financing essential development projects worldwide. As the global landscape evolves, initiatives like the BRI are increasingly pivotal in determining the trajectories of international cooperation and investment.
Referred to as the Silk Road Economic Belt, the BRI encompasses a multitude of infrastructure projects aimed at revitalizing trade routes across continents. This initiative is part of China’s broader strategy to expand its economic influence and engage with emerging markets through various development programs. The initiative facilitates large-scale investments in transportation, energy, and digital infrastructure, supported by the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, which plays a crucial role in providing necessary funding. By connecting nations through enhanced trade links, the BRI not only encourages regional economic integration but also elevates China’s status within the global economy. Ultimately, such efforts highlight the importance of sustainable economic policies in propelling forward the development aspirations of countries involved in these partnerships.
The Role of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank in Global Development
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) plays a pivotal role in supporting developing nations through its extensive infrastructure loans. As one of the primary financial institutions backed by Beijing, the AIIB focuses on addressing the significant infrastructure gaps in Asia and beyond. Established in 2016, the AIIB has rapidly gained recognition as a vital player in global development efforts, especially in light of decreasing support for traditional Western-led financial systems like the World Bank and IMF. With a focus on critical projects such as transportation, water supply, and energy, the AIIB’s initiatives are essential to fueling sustainable economic growth in underdeveloped regions.
Furthermore, the AIIB complements initiatives like China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aims to enhance connectivity across nations by constructing infrastructure that links Asia with Europe and Africa. The strategic partnership between the AIIB and the BRI underscores China’s commitment to fostering open regionalism and collaboration among countries. By funding key projects that align with both the AIIB’s goals and the broader objectives of the BRI, China not only strengthens its influence in developing countries but also establishes itself as a global economic leader.
Strengthening Synergy between AIIB and Belt and Road Initiative
In recent comments, Premier Li Qiang emphasized the need for the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank to enhance its synergy with the Belt and Road Initiative. He called for the bank to focus more on facilitating partnerships between Asian nations and promoting economic connections that transcend borders. This synergy is vital, as it allows the AIIB to leverage its financial capabilities in alignment with China’s broader development strategies. By directing resources towards projects that resonate with the BRI’s vision, the AIIB can significantly contribute to the realization of enhanced trade routes and transportation networks.
Emphasizing his views during the ASEAN-China-GCC Economic Forum, Li pointed out that strengthening cooperation among Asian countries is essential in the current geopolitical climate. With the U.S. reducing its support for international finance organizations, the AIIB’s role becomes even more pronounced as it steps in to fill the void. By increasing support for the BRI, the AIIB not only promotes infrastructure development but also positions itself at the forefront of global development, encouraging deeper engagement between Asia and the rest of the world. This collaborative approach is expected to foster economic resilience and stability across the region.
China’s Economic Policies and Development Programs
China’s economic policies have increasingly oriented towards enhancing its global influence through development programs. The Belt and Road Initiative stands out as a flagship effort aimed at expanding trade connectivity and infrastructure development across nations. Today, with a focus on poverty alleviation and sustainable development, the BRI aligns closely with global goals, such as the United Nations’ 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda. This strategic focus not only reinforces China’s economic policies but also contributes to its long-term vision of establishing stronger international ties.
Moreover, the emergence of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank complements these economic policies by offering infrastructure loans to developing countries. By strategically investing in essential sectors like transportation and energy, China aims to raise living standards in partner nations while simultaneously unlocking economic potential. These initiatives reflect a comprehensive approach to development that encapsulates infrastructure, trade partnerships, and regional cooperation, solidifying China’s position as an essential player in global economics.
Challenges Faced by the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
Despite the growing influence of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, it faces several challenges that could hinder its effectiveness in global development. One of the primary concerns is the perception of ‘debt diplomacy,’ where developing nations taking loans from the AIIB might find themselves in unsustainable debt situations. Critics argue that while these loans are intended to enhance infrastructure, they often disproportionately benefit Chinese firms, raising questions about the genuine intentions behind such investments. Addressing these concerns is crucial for the AIIB to maintain credibility and foster a more equitable international finance environment.
Additionally, the AIIB must navigate geopolitical tensions, particularly with Western nations wary of China’s expanding influence. The institution’s decisions and policies are often scrutinized in light of the broader U.S.-China rivalry. To mitigate these challenges, the AIIB needs to enhance transparency and demonstrate accountability in how it operates and allocates funds. Building trust with member nations and fostering genuine partnerships will be integral to ensuring the AIIB’s long-term success in promoting infrastructure development across the globe.
Exploring the Future of the Belt and Road Initiative
The future of the Belt and Road Initiative is poised for significant evolution as China continues to assert its role in global affairs. With Premier Li Qiang’s recent calls for intensified cooperation through the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, it’s clear that BRI will persist as a cornerstone of China’s foreign economic policy. The initiative is expected to adapt to the changing geopolitical landscape, incorporating more sustainable practices and addressing previous criticisms regarding debt sustainability and local community benefits.
As the BRI evolves, it will likely integrate projects that contribute to environmental sustainability and social equity, aligning with the goals of global development initiatives. Collaboration with international organizations and alignment with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals could further enhance the BRI’s narrative as a truly collaborative project that benefits all parties involved. By focusing on quality over quantity in its investments, China aims to create lasting partnerships that yield mutual benefits, ultimately reshaping global infrastructure narratives.
The Impact of Geopolitical Changes on Infrastructure Financing
Geopolitical changes significantly influence the landscape of infrastructure financing, particularly for organizations like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank. As the U.S. steps back from its traditional role in global economic governance, opportunities arise for China to expand its reach through the AIIB and the Belt and Road Initiative. This shift presents a chance for developing nations to reassess their financial partnerships and potentially shift towards more favorable terms offered by Chinese-backed investments.
However, these geopolitical dynamics also introduce challenges. Nations must navigate the intricacies of new alliances and the potential long-term implications of relying on Chinese financing. Therefore, a delicate balance between pursuing necessary infrastructure projects and ensuring sovereignty and sustainable debt levels is imperative. The response of the global community to these shifts will shape the future of international development and infrastructure investment.
The Role of Infrastructure Loans in Economic Development
Infrastructure loans provided by the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank are fundamental to fostering economic development in emerging markets. These loans facilitate the construction of vital infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and utilities, that are instrumental in enhancing trade efficiency and improving quality of life. The AIIB’s focus on infrastructure financing aligns with broader economic policy goals, promoting not just immediate development, but also long-term economic stability and growth. By investing in essential projects, the AIIB enables countries to unlock potential growth avenues tied to better connectivity and resource accessibility.
Additionally, infrastructure loans play a crucial role in creating jobs and boosting local economies. They spur private sector investment and encourage foreign partnerships, as better infrastructure attracts more businesses and facilitates trade. As nations experience these economic benefits, the long-term vision of sustainable growth becomes attainable. The responsible and strategic deployment of infrastructure loans underscores a commitment not only to immediate economic needs but also to a vision that aligns with global development objectives.
Aligning Global Development Goals with China’s Initiatives
Aligning global development goals with China’s initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative and the operations of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank is essential for fostering a cooperative international environment. By ensuring that projects funded by the AIIB align with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), China can demonstrate its commitment to global welfare and responsibility alongside its strategic economic interests. This alignment not only bolsters China’s image but also provides developing nations with much-needed resources to tackle pressing challenges like poverty, education, and healthcare.
Furthermore, the integration of sustainability practices within these initiatives is crucial for gaining the support of both domestic and international stakeholders. By prioritizing projects that further environmental and social equity goals, China can build stronger partnerships and a more positive global reputation. The engagement of international organizations in collaborative projects will also enhance transparency and reduce skepticism surrounding Chinese development initiatives, ultimately contributing to a more balanced economic landscape.
Building Stronger Relationships through the Belt and Road Initiative
The Belt and Road Initiative serves as a powerful tool for China to foster deeper relationships with countries across Asia and beyond. By investing in infrastructure projects and offering financial support through institutions like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, China is creating a network of interdependencies that can facilitate stronger economic ties and mutual benefits. These relationships not only enhance trade but also promote cultural exchange and influence, contributing to a more interconnected global community.
As countries participate in the BRI, they potentially gain not only infrastructure enhancements but also bolster their political and economic alignment with China. Over time, such collaborations can yield significant geopolitical advantages for both China and its partners. However, it is essential for these relationships to focus on equitable benefits to avoid criticisms related to neocolonialism and exploitative practices. Fostering transparency and ensuring the participation of local stakeholders will be crucial in building long-lasting and fruitful partnerships.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Belt and Road Initiative?
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a global development strategy launched by China in 2013 aimed at enhancing infrastructure connectivity across Asia, Europe, and Africa. Through this initiative, China seeks to foster economic cooperation by developing transportation networks, promoting trade, and encouraging investment in infrastructure projects globally.
How does the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank support the Belt and Road Initiative?
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) plays a crucial role in supporting the Belt and Road Initiative by providing infrastructure loans to developing countries. These loans are used for projects such as water supply, transportation, and energy that are essential for enhancing regional connectivity and development, aligning with China’s broader economic policies.
What are the benefits of the Belt and Road Initiative for developing countries?
The Belt and Road Initiative offers numerous benefits for developing countries, including access to much-needed infrastructure loans, which can improve transportation networks, utilities, and overall economic growth. Additionally, these projects may attract foreign investment and enhance trade relations, ultimately fostering global development.
What criticisms are associated with the Belt and Road Initiative?
Critics of the Belt and Road Initiative argue that it can lead to high debt levels in developing nations, as many projects are funded through loans from China. Furthermore, there are concerns that the primary beneficiaries are often Chinese companies, particularly state-owned enterprises, rather than the host countries themselves.
How does the Belt and Road Initiative relate to China’s economic policies?
The Belt and Road Initiative is a key component of China’s economic policies, aimed at expanding its influence globally. By investing in infrastructure development across various regions, China intends to create new markets for its goods, enhance trade routes, and solidify economic ties with participating countries, thus promoting its development goals.
What role does the AIIB play in global development initiatives?
The AIIB, in alignment with the Belt and Road Initiative, plays a significant role in global development by financing infrastructure projects in developing countries. It provides a platform for countries to collaborate on economic growth while addressing pressing infrastructure needs, thus enhancing overall global development.
How does the Belt and Road Initiative fit into the Global Development Initiative introduced by China?
The Belt and Road Initiative complements the Global Development Initiative (GDI), which was introduced by China to promote poverty alleviation, public health, and food security as part of its commitment to the UN’s 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. Together, these initiatives reflect China’s strategy to lead in global development and enhance its soft power internationally.
What challenges does the Belt and Road Initiative face in its implementation?
The Belt and Road Initiative faces several challenges, including geopolitical tensions, concerns over debt sustainability in partner countries, and accusations of creating neo-colonial dependencies. Additionally, project delays and varying governance standards across different regions can hinder effective implementation.
Can the Belt and Road Initiative help combat global poverty?
The Belt and Road Initiative has the potential to help combat global poverty by increasing investment in infrastructure and facilitating economic opportunities in developing nations. However, success largely depends on equitable project execution and ensuring that local populations benefit from the increased connectivity and investment.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Chinese Premier Li Qiang’s speech emphasizes AIIB’s role in enhancing Belt and Road Initiative support. | U.S. support for Western-led institutions like IMF and World Bank is decreasing. |
| The Belt and Road Initiative was launched by China in 2013 to increase global influence through infrastructure development. | AIIB finances infrastructure projects in developing countries, focusing on transportation and water supply. |
| Premier Li called for synergy between AIIB and Belt and Road and Global Development Initiative. | China is leveraging U.S. policies to strengthen its regional and global initiatives. |
| Critics argue China’s projects lead to debt for developing nations while benefiting Chinese state-owned enterprises. | AIIB has approved $8.4 billion in financing, totaling over $60 billion since inception in 2016. |
| Zou Jiayi, former finance minister, will become AIIB president in January 2026. | AIIB now has 110 members, with significant participation from UK, France, and Germany. |
Summary
The Belt and Road Initiative is a key strategy for China aimed at improving global connections through extensive infrastructure development. Premier Li Qiang has highlighted the importance of enhancing the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank’s role in supporting this initiative during fluctuating global dynamics. This focus on the Belt and Road Initiative underscores China’s ambition to increase its influence while addressing challenges in international finance and development. As the AIIB continues to grow and support various projects, the implications for global economic relations become increasingly significant.