Core Inflation Rate Exceeds Expectations in May 2025
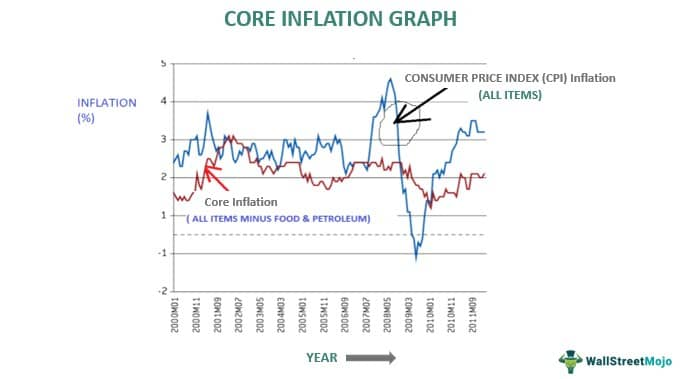
The core inflation rate has captured significant attention lately, especially with its recent rise to 2.7% in May, surpassing analysts’ expectations. This measure, closely monitored by the Federal Reserve, excludes volatile items like food and energy to better gauge underlying inflation trends. The PCE price index, which serves as the Fed’s primary gauge, revealed a modest yet concerning rise in prices, indicating shifts in consumer spending trends that may impact future economic stability. As the Federal Reserve strives to meet its inflation targets of around 2%, these numbers raise important questions about upcoming interest rate decisions. Investors and economists alike are keenly watching these developments, as sluggish consumer income growth poses additional challenges to the broader economic landscape.
A recent spike in the core inflation metric has sparked discussions about its implications for the economy. This vital indicator, which factors out erratic swings from sectors like food and energy, is essential for understanding persistent price stability. Analysts are particularly focused on how the personal consumption expenditures index reflects shifting consumer habits and behaviors. As policymakers navigate these economic signals, the balance between maintaining low rates while countering inflation pressures remains critical. This vital dialogue around inflationary trends signifies a pivotal moment for fiscal planning and strategic economic forecasts.
Understanding the Core Inflation Rate: Current Trends and Implications
The core inflation rate, a vital economic indicator, provides insights into underlying inflation trends by excluding volatile items such as food and energy. As reported in May, the core inflation rate rose to 2.7%, surpassing market expectations. This figure is particularly significant because it reflects the Federal Reserve’s preferred measure of inflation, the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index, which registered a seasonally adjusted increase of 0.2% for the month. Such rises in core inflation can influence the Fed’s monetary policy decisions, affecting interest rates and overall economic stability.
Understanding the dynamics of the core inflation rate is essential for evaluating economic health and making informed decisions. The recent trends indicate a disconnect from the Federal Reserve’s target inflation rate of 2%, a benchmark it hasn’t met since early 2021. This persistent deviation suggests not only inflationary pressures but also highlights broader issues with consumer spending trends, which have shown signs of weakness. As the Fed strives to normalize inflation, analysts closely monitor these developments, recognizing that significant shifts can lead to impactful interest rate decisions in the near future.
Consumer Spending Trends and Inflationary Pressures
Recent economic reports indicate a troubling trend in consumer spending. In May, personal consumption fell by 0.1%, with personal income decreasing even more sharply by 0.4%. These declines suggest a cautious consumer base, which may affect broader economic growth and further complicate the Federal Reserve’s efforts to manage inflation. As consumer spending is a major driver of economic activity, continued weakness in this area could necessitate adjustments in inflation targets and monetary policy.
The interplay between consumer spending trends and inflation is complex. Lower spending could exert downward pressure on prices in the long-term but in the short-term may lead to stagnant growth. If inflation persists above the Fed’s targets—like the reported core inflation at 2.7%—the Fed may be forced to confront the dilemma of raising interest rates to combat inflation without stifling consumer spending further. Balancing these competing priorities remains a crucial task for the Fed, particularly in light of the uncertainty created by fluctuating consumer confidence.
The Federal Reserve’s Inflation Targets and Their Impact
The Fed’s inflation target of 2% is designed to promote price stability and allow for sustained economic growth. However, the persistent rise in the core inflation rate to 2.7% has sparked concern among economists and policymakers alike. This inflation rate, driven by factors such as increasing costs in essential goods and services, shows that the Fed’s strategy has not yet achieved the desired outcomes. Continued monitoring of inflation indicators is essential to determining the need for any recalibration of these targets.
Failure to meet inflation targets can lead to a paradigm shift in economic policy. If inflation remains above the target, as seen with the recent PCE price index data, the Federal Reserve may have to consider more aggressive measures to align with its goals. This includes potential interest rate increases, which could further dampen consumer spending and slow down economic growth. As markets respond to the complexities of inflation and the Fed’s policy paths, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for investors and consumers alike.
Interest Rate Decisions Amid Rising Inflation Rates
Recent economic data has presented the Federal Reserve with a challenging scenario regarding interest rate decisions. With the core inflation rate climbing higher than expected, the Fed must evaluate its current strategies to curb inflation while also fostering economic growth. The market’s subdued reaction to the latest inflation figures suggests uncertainty about future rate hikes and highlights the delicate balance the Fed is attempting to maintain. Some officials advocate for potentially lowering interest rates if inflation reduces to manageable levels, underscoring the complex relationship between interest rates and inflation.
As the Federal Reserve considers its next moves, the implications of rising interest rates on the economy cannot be overlooked. Higher rates could strain consumer spending, further impacting growth and income levels. Conversely, maintaining lower interest rates could exacerbate inflationary pressures, keeping the core inflation rate above acceptable thresholds. Therefore, the Fed’s future interest rate decisions will hinge on incoming data regarding consumer behavior and broader economic conditions, shaping the landscape of the U.S. economy.
Analyzing the PCE Price Index and its Significance
The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index serves as a crucial gauge of inflation trends in the American economy. By tracking changes in the prices of goods and services purchased by households, the PCE index helps the Federal Reserve make informed decisions about monetary policy. The slight increase of 0.1% reported recently has raised eyebrows, as it suggests inflationary pressures are building, straying from the Fed’s established targets. Such developments prompt economists to reassess consumer behavior and spending habits, as these factors fundamentally influence the PCE index.
Analyzing the PCE price index can provide valuable insights into underlying economic conditions. For instance, the exclusion of food and energy from core inflation readings helps isolate more stable prices, yet it also highlights the bigger picture of economic activity. With core inflation now at 2.7%, the Fed faces increasing scrutiny about its management of inflation and interest rates. Economists and financial analysts closely monitor changes in the PCE index, as it serves as a foundational element in the Fed’s strategy to achieve balanced economic growth while maintaining price stability.
The Road Ahead: Potential Outcomes of Current Economic Trends
As the Federal Reserve grapples with rising core inflation and fluctuating consumer spending trends, the road ahead appears fraught with challenges. The recent uptick in the core inflation rate to 2.7% and the sluggish growth in consumer spending necessitate a careful assessment of future monetary policy decisions. Analysts predict that if inflationary pressures continue to mount, the Fed may be compelled to tighten policies further, potentially impacting interest rates and economic growth. The interconnectedness of these elements creates a complex landscape that requires thoughtful, nuanced approaches.
Looking ahead, policymakers must navigate the precarious balance between promoting growth and controlling inflation. With the Fed’s inflation target of 2% feeling increasingly distant, public perception of the economy’s health will be influenced by the Fed’s actions. Consumer confidence, spending habits, and inflation expectations are all factors that may shape the U.S. economy’s trajectory. Ultimately, stakeholders across various sectors must remain vigilant as they anticipate the Fed’s decisions in response to evolving economic conditions.
Inflation Expectations and Their Role in Economic Forecasting
Inflation expectations play a pivotal role in economic forecasting and can significantly influence consumer behavior and spending trends. With recent inflation data indicating a core rate of 2.7%, expectations regarding future inflation can affect the decisions made by both consumers and investors. If consumers anticipate continued inflationary trends, they may adjust their spending habits accordingly, potentially exacerbating the very inflation the Federal Reserve aims to control. The psychology of inflation expectations creates a dynamic that can complicate policy efficacy.
Moreover, accurate predictions of inflation expectations are crucial for the Federal Reserve when setting monetary policy. If inflation is expected to rise, the Fed may opt for preemptive interest rate hikes to mitigate potential adverse effects on the economy. Conversely, consistent signals of weak consumer spending could indicate a need for more accommodative policies to spur growth. Understanding these interconnected factors is essential for evaluating the Fed’s strategy and the overall health of the economy.
The Aftermath of Inflation Data: Financial Market Reactions
The release of inflation data invariably impacts financial markets, and the recent reports are no exception. The core inflation rate rise to 2.7% prompted a mixed response among investors, reflecting uncertainty regarding future interest rate adjustments. While some market participants anticipated a potential rate cut to stimulate economic activity, the inflation numbers have raised apprehensions about the Fed’s capability to manage pricing pressures effectively. This uncertainty can create volatility in stock and bond markets as investors recalibrate their expectations in response to economic indicators.
Market reactions to inflation data are often characterized by rapid shifts, and the mixed signals seen post-report suggest that traders are divided in their outlook. Factors such as consumer spending trends and the PCE price index significantly influence investor sentiment. A better understanding of how the Fed might interpret these latest figures and their potential implications for monetary policy is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the current economic environment. As such, staying informed about inflation data and related policy reactions is imperative for making sound financial decisions.
Navigating Economic Uncertainty: A Conclusion on Current Trends
In conclusion, the current economic landscape is shaped by rising core inflation rates and diminishing consumer spending. With the Fed’s core inflation rate climbing to 2.7%, expectations are high for policy shifts that may influence interest rates and overall economic growth. Policymakers face the challenge of incentivizing consumer spending without allowing inflation to spiral out of control. The road ahead may be uncertain, but comprehending these dynamics will be key to navigating future economic conditions.
Additionally, ongoing analysis of consumer behaviors, inflation targets, and responses from the Federal Reserve will be essential for predicting economic trends. Stakeholders must remain vigilant as they adjust their strategies in this ever-evolving environment. The interplay between inflation data and interest rates will undoubtedly shape the economic future, influencing both consumer and investor confidence as the Fed continues to tread the line between growth and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the core inflation rate and why is it significant for the Federal Reserve?
The core inflation rate measures the change in prices of goods and services, excluding food and energy. It is significant for the Federal Reserve as it reflects underlying inflation trends and helps guide interest rate decisions, aiming to stabilize prices around the Fed’s 2% inflation target.
How does the PCE price index influence the Federal Reserve’s inflation targets?
The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index is the Federal Reserve’s preferred measure of inflation, tracking changes in the prices faced by consumers. It influences inflation targets by providing critical data that informs the Fed’s monetary policy and interest rate decisions.
What do recent changes in consumer spending trends signify in relation to the core inflation rate?
Recent changes in consumer spending trends, such as a drop of 0.1% reported in May, can impact the core inflation rate. Decreased consumer spending may indicate weaker demand, which can dampen inflation pressures and affect the Federal Reserve’s ability to meet its inflation targets.
How did the core inflation rate perform against estimates in May 2025?
In May 2025, the core inflation rate rose to 2.7%, exceeding estimates of 2.6%. This increase, along with the PCE price index rising by 0.1%, suggests persistent inflationary pressures despite overall sluggish economic indicators.
What implications does a rising core inflation rate have for interest rate decisions by the Federal Reserve?
A rising core inflation rate can prompt the Federal Reserve to consider adjusting interest rates to steer inflation closer to its 2% target. If inflation pressures remain high, the Fed may maintain or increase rates; conversely, subdued inflation could lead to potential interest rate cuts.
Why has the Federal Reserve not met its inflation target since early 2021?
The Federal Reserve has struggled to meet its inflation target of 2% primarily due to fluctuating consumer spending trends, ongoing economic disruptions, and varying inflationary pressures, with recent data showing a core inflation rate that exceeds expectations yet reflects underlying economic vulnerabilities.
What does the term ‘core PCE’ refer to in the context of inflation?
Core PCE refers to the core Personal Consumption Expenditures price index, which measures the price changes of core goods and services by excluding food and energy prices. It serves as a crucial indicator for the Federal Reserve’s assessment of underlying inflation trends.
| Indicator | May 2025 | Expected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Inflation Rate (Excl. Food & Energy) | 2.7% | 2.6% (estimate)’}]},{ | Consumer Spending Change | -0.1% | N/A |
Summary
The core inflation rate, which rose to 2.7% in May 2025, indicates significant trends in the economy’s inflation landscape. This increase, surpassing expectations, emphasizes the Federal Reserve’s ongoing struggle to maintain its target inflation rate of 2%—a level it hasn’t reached since early 2021. With sinking consumer spending and personal income, the figures suggest challenging economic conditions that may influence future monetary policy decisions and interest rates.




