India Inflation Rate Decreases to 2.10% in June 2023
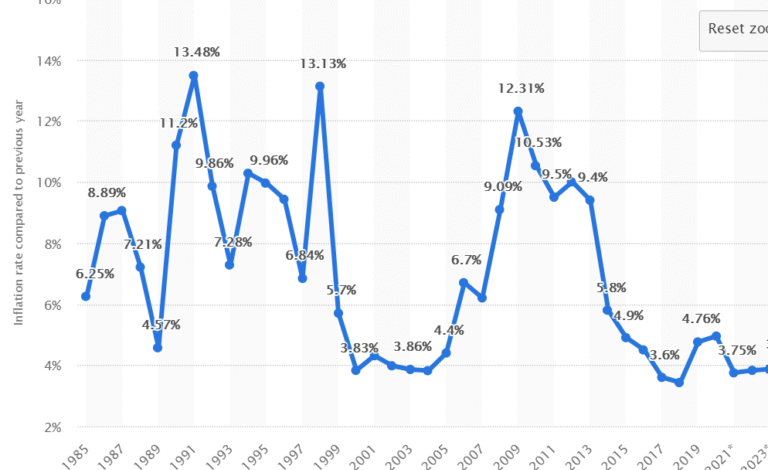
The India inflation rate has recently garnered attention as it continued its decline, registering a surprisingly low consumer inflation rate of 2.10% in June. This marks the lowest inflation level observed in over six years, largely due to a sustained decrease in food prices. Economists had forecasted a higher inflation figure of 2.5%, but the latest data indicates that the consumer price index has now fallen for the eighth consecutive month. This decrease not only offers relief to consumers but also provides the Reserve Bank of India with flexibility to continue easing monetary policies after a significant rate cut earlier this year. The stabilizing inflation rate is expected to bolster economic growth in India, especially with favorable conditions in agricultural production and proactive trade negotiations.
The current economic climate in India has seen a notable shift with the reduction in the inflation rate, often referred to as the cost of living index. Recent reports show consumer price stability, which can significantly impact the household budgeting practices of the population. Additionally, with the Reserve Bank of India poised to adjust interest rates in light of these developments, many are observing how these changes will influence national economic productivity. Furthermore, India’s ongoing discussions regarding international trade agreements could play a crucial role in shaping future inflation trends, especially in relation to food commodity prices. This intricate link between inflation, consumer spending, and trade policies highlights the delicate balance required to foster economic growth.
Understanding India’s Decreasing Inflation Rate
India’s consumer inflation rate fell to a surprising 2.10% in June, demonstrating a continued decline in price levels. This reduction in inflation is attributed to the persistent drop in food prices, which have negatively impacted the consumer price index for the eighth consecutive month. The data suggests that consumers may experience a prolonged period of stabilized prices, making it easier for households to manage their budgets. Furthermore, this lower inflation can bolster consumer confidence, encouraging spending and investment, which is vital for economic growth.
Economists had anticipated a higher inflation rate of 2.5%, but the actual figures present a more favorable outlook. With the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) potentially easing monetary policy further, consumers can expect a more conducive environment for spending. The interplay between food prices and consumer inflation is critical, as ongoing reductions in food price inflation, currently recorded at -1.06%, will support India’s economy in the face of global challenges.
Impact of Food Prices on India’s Inflation Dynamics
Food prices play a substantial role in shaping India’s inflation landscape, especially given that they constitute a significant portion of the consumer price index. As food inflation continues to experience declines, the overall inflation rate benefits from this trend. The Reserve Bank of India’s recent strategies, emphasizing the importance of managing food prices, underscore the reality that stable food supply, influenced by favorable weather conditions, contributes fundamentally to lowering inflation rates.
In June, food inflation turned negative, marking a significant change compared to the previous month’s rate of 0.99%. This continuous decrease can be attributed to enhanced agricultural production, particularly in staple crops such as wheat and pulses, which helps cushion the overall consumer price index. Additionally, the commentary from HSBC emphasizes that adequate food availability will likely keep inflation in check, enabling broader economic benefits such as boosted real wages and increased purchasing power.
The Role of the Reserve Bank of India in Inflation Management
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a key role in managing inflation through its monetary policies. With the recent drop in the consumer inflation rate, RBI has a prime opportunity to soothe its monetary stance further, potentially leading to additional interest rate cuts. The central bank’s previous rate cut of 50 basis points in May demonstrates its commitment to fostering economic growth while keeping inflation under control. This strategy is critical as India looks to stabilize its economy amid global uncertainties.
As the RBI navigates this landscape while keeping a close eye on wages and domestic consumption, the central bank’s policies will directly influence consumers’ purchasing power. By supporting lower interest rates and boosting credit availability, the RBI can further enhance economic activity, crucial as India’s growth rate recently accelerated to 7.4%. In this interconnected system, maintaining sustainable inflation levels is essential for long-term economic prosperity.
India’s Economic Growth Amidst Inflationary Challenges
Despite the challenges posed by inflation, India’s economy has shown substantial resilience, evidenced by its impressive growth rate of 7.4% in the last quarter. This growth can be attributed to various factors, including rising domestic consumption which reflects increased consumer confidence. As inflation continues to decline, consumers are likely to feel empowered to spend more, further stimulating economic activity and potentially leading to a positive cycle of growth.
However, risks remain, particularly concerning global commodity prices and any trade agreements that may impact tariffs. The Indian economy must remain vigilant against external variables that could disrupt this growth trajectory. Nevertheless, the current indicators suggest that if the trend of decreasing inflation persists, India may be well-positioned to maintain strong economic growth for the foreseeable future.
Potential Trade Deals and Their Impact on Inflation
Negotiations for trade deals, particularly with the U.S., play a vital role in shaping India’s economic landscape and managing inflation. With a possible trade agreement looming, India faces the pressures of both export and import tariffs that could significantly impact commodity prices. The administration is keen on ensuring that any deal struck will protect Indian interests in a manner that safeguards inflation levels and boosts economic growth.
The proposed retaliatory tariffs against U.S. imports, as reported earlier, underline India’s commitment to protecting its economy from excessive external pressures. However, successfully negotiating a favorable trade deal could lead to reduced tariffs, which would support the stabilization of prices and enhance supply chains. It is imperative that any outcomes from these negotiations promote a balanced approach to maintaining low inflation while fostering healthy economic relations.
The Future Outlook for Food Inflation in India
Looking ahead, the outlook for food inflation in India appears more favorable, especially in light of recent agricultural advancements and favorable monsoon conditions. The RBI’s insights regarding adequate supply levels suggest that consumers can expect continued stabilization in food prices. This is crucial not only for individuals but also for sustaining lower overall inflation rates, which could remain an average of around 2.5% in the upcoming months.
Moreover, as the Government emphasizes improving agricultural yield and providing better facilities for farmers, the benefits can trickle down to consumers in the form of stable food prices. Such favorable conditions play a dual role by ensuring food security while simultaneously keeping inflation manageable, aligning with the country’s long-term economic goals.
Exploring Consumer Confidence During Low Inflation Periods
The correlation between consumer confidence and inflation cannot be understated. In periods of low inflation, like the current scenario in India, consumer confidence tends to rise as households find their purchasing power effectively preserved. With inflation rates at historical lows, consumers are likely to spend more, thereby boosting economic growth by driving domestic consumption.
Furthermore, consistent low inflation encourages investments as individuals feel more secure in their financial standing. As discussed by economic analysts, enhancing confidence among consumers can reflect positively on sectors such as retail and services, propelling economic activity. This dynamic is critical as India aims to enhance its GDP growth rate in the context of a fluctuating global economy.
Global Factors Affecting India’s Inflation Rate
India’s inflation rate does not operate in isolation but is profoundly influenced by various global factors, including commodity prices and geopolitical tensions. As the country navigates through economic negotiations, particularly around tariffs and imports, these global factors have a direct impact on domestic inflation levels. Rising global prices for essential goods can lead to inflationary pressures locally.
In addition, India’s trade partnerships play a significant role in determining the availability and pricing of goods. The country’s ongoing negotiations to enhance trade agreements, particularly with major economies like the U.S., can significantly influence inflationary trends as favorable terms may lead to lower prices for imports, positively impacting the overall consumer price index.
The Importance of Monetary Policy in Controlling Inflation
Monetary policy is a pivotal tool in controlling inflation, as evidenced by the recent actions of the Reserve Bank of India. By adjusting interest rates and adopting strategies that encourage growth, the RBI can influence inflation rates effectively. Easing monetary policy when inflation is low, as currently seen, allows for a proactive approach that can stimulate economic activity while also maintaining price stability.
The delicate balance between fostering economic growth and controlling inflation necessitates a close watch on various economic indicators. Through careful regulation and responsive fiscal policies, the RBI can steer the economy towards a stability path, ensuring that inflation rates do not spiral out of control as domestic consumption and production levels fluctuate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current India inflation rate for June 2023?
In June 2023, India’s consumer inflation rate registered at 2.10%, continuing its trend of decline and marking a significant drop from previous months.
How does the Reserve Bank of India influence the inflation rate in India?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) influences the inflation rate through its monetary policy, including adjustments to interest rates. With the recent drop in inflation, the RBI has more leeway to potentially ease monetary policy further.
What factors are contributing to the low inflation rate in India?
The low inflation rate in India can be attributed to declining food prices, particularly with food inflation falling to -1.06% in June. Additionally, strong agricultural production and favorable weather conditions play a significant role in maintaining low inflation levels.
How do food prices impact the overall India inflation rate?
Food prices have a substantial impact on the overall India inflation rate since they constitute a significant portion of the consumer price index. The recent decrease in food inflation helps lower the consumer inflation rate, as seen in June 2023.
What is the relationship between India’s inflation rate and economic growth?
There is a complex relationship between India’s inflation rate and economic growth; a lower inflation rate, like the recent 2.10%, can stimulate economic growth by increasing consumer purchasing power and boosting domestic consumption.
Will the negotiations of a trade deal with the U.S. affect India’s inflation rate?
Yes, negotiations for a trade deal with the U.S. could impact India’s inflation rate, as tariffs or trade policies that affect import costs could lead to fluctuations in consumer prices and overall inflation.
How does the food inflation rate affect consumers in India?
The food inflation rate directly affects consumers’ purchasing power; a decline in food inflation, as recorded at -1.06%, means lower grocery bills, enhancing the disposable income available for other expenditures.
What future trends are predicted for the India inflation rate?
Analysts predict that India’s inflation rate will average around 2.5% over the next six months, influenced by favorable agricultural production and a decrease in food prices, helping stabilize the economy.
| Key Points |
|---|
| India’s consumer inflation rate fell to 2.10% in June, below expectations of 2.5%. |
| This marks the eighth consecutive monthly decrease in the consumer price index. |
| Food inflation turned negative at -1.06% in June, down from 0.99% in May. |
| The decline in inflation allows the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) more space to continue easing its monetary policy. |
| RBI predicts inflation could average around 2.5% over the next six months, aided by good agricultural output. |
| A favorable monsoon season is expected to further control inflation and boost consumer purchasing power in the informal sector. |
| India’s economy grew at 7.4% in the last quarter, driven by increased domestic consumption. |
| Concerns remain over weather uncertainties and potential impacts of U.S. tariffs on Indian exports. |
Summary
The India Inflation Rate continues to demonstrate a downward trend, reaching a historic low of 2.10% in June, much lower than economists’ predictions. This sustained decrease is primarily attributed to falling food prices, allowing the Reserve Bank of India greater flexibility to adjust monetary policy in favor of economic growth. While the favorable agricultural conditions and expected continued decline in food inflation are promising, vigilance against external economic pressures such as tariffs and international commodity prices remains crucial for maintaining this positive trajectory.