Tariff Inflation Predictions: Insights from Goldman Sachs
As we look into the future of the economy, Tariff Inflation Predictions are causing waves of concern amongst analysts and policymakers alike. Recent evaluations by financial giants such as Goldman Sachs have indicated that inflation driven by tariffs is poised to rise, with anticipated monthly increases in the consumer price index reaching up to 0.5%. This forecast aligns with US GDP growth projections that hint at potential declines in economic output due to rising goods costs. Furthermore, JPMorgan Chase’s economic outlook echoes these sentiments, emphasizing that the Federal Reserve’s inflation policy might need adjusting to address the impending price pressures. As tariffs solidify and inventory levels fluctuate, consumers may soon feel the crunch of increased costs as businesses adjust their pricing strategies accordingly.
In assessing the economic landscape, experts are closely examining the ramifications posed by tariff-driven price changes. Predicted shifts in tariff policies may lead to significant alterations in consumer spending and overall economic stability. Financial analysts are concerned that inflation rates could escalate, thereby impacting daily expenses and the broader economic environment. With various economic indicators signaling increased pressures, it’s crucial for businesses and consumers alike to stay informed about impending shifts in inflation and price trends. Observers are particularly interested in how these changes will affect GDP growth forecasts and overall consumer behavior as we move forward.
Understanding Tariff Inflation Predictions
Tariff inflation predictions have become a focal point for economists as the U.S. grapples with the potential economic fallout from proposed trade measures. Goldman Sachs recently faced backlash for forecasting that significant tariff-induced inflation would increase consumer prices substantially. This perspective is echoed by many on Wall Street, who anticipate a steady rise in prices as tariffs are implemented and effective rates settle around 18%. This prediction aligns with broader economic indicators and consumer price index trends that suggest inflationary pressures are likely to persist.
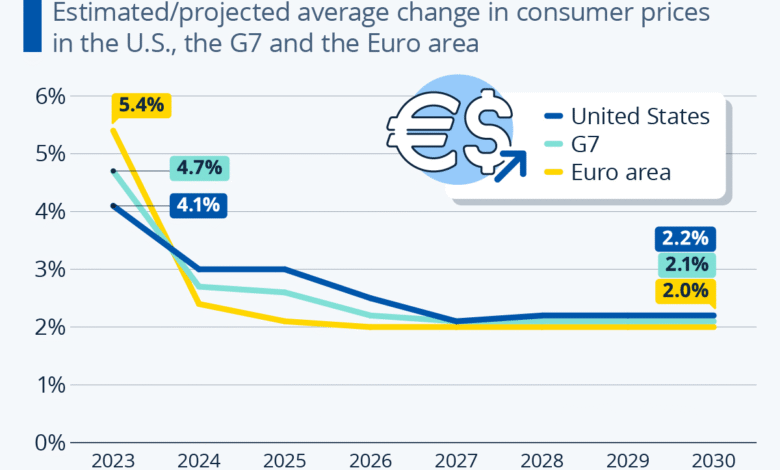
As tariffs impact supply chains and pricing strategies, the market watches closely for the resultant economic shifts. With estimates predicting monthly increases in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) between 0.3% and 0.5%, the overall inflation rate could rise to the low- to mid-3% range. This anticipated shift in pricing could influence the Federal Reserve’s inflation policy, pushing them to consider their monetary stance more cautiously. Investors are advised to remain alert to how these tariff-related dynamics could reshape the broader economic landscape.
Potential Impacts on U.S. GDP Growth Projections
The potential impacts of tariff-induced inflation extend beyond immediate consumer pricing effects and into the realm of GDP growth projections. Economists, including those from JPMorgan Chase, predict that rising tariffs could exert a downward pressure on U.S. GDP, reducing it by nearly 1%. This decline is particularly concerning as it primarily stems from consumption, which comprises two-thirds of the economy. With the Blue Chip Economic Indicators report suggesting a modest GDP growth of only 0.85% in the latter half of the year, these predictions paint a picture of a slowing economy under increased tariff pressures.
As stockpiles shrink and businesses face rising costs without the ability to maintain current pricing structures, the effects of tariffs are expected to reverberate throughout the economy. Consumers might postpone spending due to higher costs, leading to diminished economic activity. Yet, some forecasters remain cautiously optimistic, suggesting that the effects of these tariffs could be short-lived, with a recovery in growth anticipated in the following year. Nevertheless, sustained inflation and constrained GDP growth present a complex challenge for policymakers and investors alike.
Federal Reserve’s Stance Amid Rising Inflation
The Federal Reserve’s stance on inflation and interest rates remains crucial as economic sentiment shifts. While rising inflation is a key concern, central bank officials are tasked with balancing the need for growth against the risks of overheating the economy. With anticipated tariff inflation predictions suggesting a potential rise in core inflation metrics, the Fed’s approach may become more nuanced. If core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) inflation rises significantly above the Fed’s target, policymakers may reconsider their strategies regarding interest rate cuts, despite a weakening labor market.
The Fed’s heightened attention toward inflation stemmed from recent consumer price index releases indicating upward trends. Economists are alert to how various factors, including tariffs, will shape the core inflation narrative moving forward. With the Cleveland Fed noting rising sticky-price measures, economists like Gus Faucher emphasize that tariff impacts will be felt as businesses transfer increased costs onto consumers, and sustained inflation could alter the Fed’s long-term outlook toward rate adjustments.
Consumer Price Index Trends in a Tariff Environment
Economic analysts are increasingly focusing on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) as a valuable barometer in a tariff-impacted economy. As tariff prices begin to take their toll on consumer goods, economists predict noticeable changes in the CPI that could reshape buyer behavior. Goldman Sachs and other financial institutions expect that as tariffs elevate costs, the CPI will reflect these changes, revealing a trajectory toward higher inflation rates. This trend could influence consumer spending, as individuals may reduce discretionary spending in response to steadily increasing prices.
Recent reports indicate a concerning trend where core inflation, represented within the CPI framework, may ramp up due to tariffs. As businesses like retailers pass increased costs onto consumers, the likelihood of seeing consistent monthly CPI increases could unsettle consumer confidence. This scenario outlines a challenging environment for households that are grappling with financial pressures from elevated costs, leading to potential shifts in spending habits and broader economic implications.
Economic Forecasts Amid Increasing Tariff Pressures
As the United States navigates through increasing tariff pressures, economists are sharpening their forecasts for the coming months. The anticipated 1 percentage point increase in core inflation, leading projections to sit at around 3.5% by year-end, marks a significant shift in economic conditions. Industry experts believe that such increases could have an outsize effect, especially since only about 25% of these costs have currently been passed down to consumers. As tariffs continue to take effect, it becomes urgent to monitor consumer pricing behavior and inflationary trends.
Analysts from BNP Paribas express that upward price pressures aren’t solely confined to goods but also extend into service sectors, reflecting changes in the broader economy. The unexpected strength in core services, highlighted in recent CPI reports, introduces complexity into these economic forecasts. The Fed’s principal concern remains not the inflation rate itself but the persistent nature of inflation; sticky inflation metrics could lead to prolonged economic considerations and policy adaptations, thus elevating the stakes for upcoming monetary policy decisions.
Business Strategies in Response to Tariff Increases
The ripple effects of tariff increases compel businesses to reassess their pricing strategies and optimize operational efficiencies. As companies face the decision of whether to absorb increased costs or pass them on to consumers, the variations in approaches reveal significant implications for market behavior. Some businesses choose to maintain pricing in a bid to safeguard market share, which can lead to squeezing profit margins, while others may selectively raise prices where consumers show less price sensitivity.
In adapting to a tariff-inflated landscape, businesses are employing various strategies such as renegotiating supply contracts, seeking alternative sourcing options, and investing in technology to enhance efficiency. The effectiveness of these strategies will heavily influence both business profitability and consumer price levels. As these dynamics unfold, companies that proactively adjust to the evolving economic context may position themselves favorably compared with competitors who adopt a more reactive stance.
Long-Term Implications of Tariff-Induced Inflation
The long-term implications of tariff-induced inflation emphasize the interconnectedness of domestic. политича ландинадау및 오 다양한 의의 점低통. High core inflation could reshape consumer behavior and spending habits, leading to shifts in market dynamics. If consumers become accustomed to higher price levels, the economic landscape may witness a sustained period of inflationary pressure, necessitating strategic adaptations across multiple economic sectors.
In addition, sustained tariff-driven inflation could complicate the U.S.’s economic recovery trajectory. As inflationary expectations become entrenched, central banks might face challenges in recalibrating their monetary policies to maintain growth while controlling inflation rates. The interplay between tariffs, consumer price indices, and federal policies will remain a critical point of contention for economists and policymakers, shaping the economy’s health for years to come.
Consumer Behavior Shifts in Response to Inflation
As tariff-induced inflation begins to permeate the economy, it is crucial to analyze how consumer behavior shifts in response to rising costs. Inflation typically causes consumers to reconsider spending habits, prioritizing necessity over luxury items. This behavioral shift can lead to a notable impact on sectors that rely heavily on consumer discretionary spending, as buyers tighten their budgets and opt for more affordable alternatives.
Economists have noted a trend where consumers may become more price-sensitive, leading to changing preferences towards brands and products that offer better value. Retailers might find themselves adapting their marketing strategies to emphasize discounts or promotions to maintain sales volumes. As this transformation in consumer behavior unfolds, businesses must be agile in adjusting their strategies to meet evolving consumer expectations while navigating the challenges posed by tariff-related inflation.
Monitoring Market Reactions to Tariff Policies
As uncertainty surrounds tariff policies, market reactions continue to provide valuable insights into investor sentiment and economic forecasts. Financial markets are particularly sensitive to news regarding tariffs and inflation, as any shifts can lead to abrupt fluctuations in stock prices, currency valuation, and overall market stability. Observing these reactions helps economists gauge real-time economic impacts and consumer confidence in the market.
Additionally, as businesses adapt to the evolving tariff landscape, investor reactions can yield hints on how corporations are likely to perform under these rising costs. The way companies respond, whether through adjustment in pricing strategies or operational efficiency improvements, will be reflected in market performances. Thus, keeping a close eye on market trends in relation to tariff policies will aid stakeholders in making informed decisions moving forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest Goldman Sachs inflation predictions regarding tariff-induced inflation?
Goldman Sachs predicts a significant rise in tariff-driven inflation, estimating increases of 1-1.5%. This outlook suggests that the effective tariff rates, approaching 18%, will result in gradual price increases for consumers. As pre-tariff stockpiles diminish, real impacts are expected to surface, emphasizing the possibility of sustained inflation.
How might US GDP growth projections be affected by rising tariff inflation?
Analysts forecast that rising tariff inflation could detract from US GDP growth, with estimates indicating a potential decline of nearly 1%. This is largely tied to consumption, which comprises two-thirds of GDP. Lower consumer spending due to inflationary pressures might slow overall economic expansion in the upcoming months.
What impact will the Federal Reserve inflation policy have on tariff inflation predictions?
The Federal Reserve’s inflation policy may become more lenient in response to rising tariff inflation, anticipated to elevate the core PCE inflation above its target. Although higher inflation could lead to hesitations around rate cuts, expectations of a weakening labor market may prompt the Fed to continue with potential rate adjustments.
What is the expected growth of the consumer price index influenced by tariff inflation predictions?
Forecasts suggest monthly increases in the consumer price index (CPI) of 0.3%-0.5%, potentially pushing the core CPI into the low- to mid-3% range. This rise is largely attributed to businesses passing on higher costs from tariffs, indicating that inflationary pressure in consumer goods will likely intensify.
How do economists expect consumers will respond to tariff-induced inflation changes?
Economists anticipate that consumers will feel the effects of tariff-induced inflation more acutely as companies adjust prices to reflect increased costs. As costs from tariffs rise, reluctance among businesses to absorb these expenses could lead to higher prices for consumers, curbing spending and adding pressure to the overall economic climate.
What are the implications of recent JPMorgan Chase economic outlooks on tariff-induced inflation?
According to the latest JPMorgan Chase economic outlook, tariffs could contribute significantly to inflation, potentially adding 1-1.5%. While some impact has already been observed, potential rises in tariffs and their cost pass-through to consumers suggest that inflationary effects will continue throughout the year.
What are analysts predicting for core inflation by the end of the year based on tariff impacts?
Analysts project that core inflation could reach 3.5% by year-end, largely influenced by tariffs and the expiration of de minimis exceptions that previously exempted certain goods from tariffs. With only a fraction of projected increases passed on to consumers thus far, faster rates of price rises in core goods may occur as tariffs take full effect.
How do tariff predictions affect the inflation stance of the Cleveland Fed?
The Cleveland Fed’s stance on inflation is likely to adjust as tariff impacts become more pronounced. With sticky-price CPI inflation currently at 3.8%, the Fed’s focus on the persistence of inflationary pressures may prompt them to reconsider their policy approach as tariff-related costs continue to push prices upward.
What warning signs should investors watch regarding tariffs and inflation?
Investors should monitor the expiration of tariff exceptions and the subsequent impact on retail prices. Additionally, signs of increased pressure on service input prices and core CPI trends will be crucial indicators of how tariffs and inflation will evolve in the coming months.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Goldman Sachs’ Prediction | Goldman Sachs predicts significant tariff-driven inflation, corroborated by other economists despite Trump’s criticism. |
| Expected Inflation Rate | Economists expect monthly inflation increases of 0.3%-0.5%, raising the Federal Reserve’s core measure into the low- to mid-3% range. |
| GDP Impact | Predicted GDP decline due to tariffs is around 1%, based on consumption being a major factor. |
| Short-Term Effects | Short-term inflation may restrain consumer spending and overall economic growth for 2023. |
| Service Price Pressure | Inflation pressure expected to extend beyond goods into service prices. |
| Tariff Exceptions Ending | Upcoming expiration of tariff exemptions may exacerbate retail price inflation. |
Summary
Tariff Inflation Predictions indicate that as tariff rates are set to rise, economists are forecasting a significant impact on inflation moving forward. Although immediate effects may not be drastic, ongoing increases in tariff rates could gradually elevate core inflation, putting further pressure on consumers and the economy. The interplay between tariffs, effective rates, and consumer response will be critical in shaping the economic landscape for the remainder of the year. Given these factors, it is essential for businesses and consumers alike to anticipate these changes and adjust accordingly to mitigate the impacts of tariff-induced inflation.