Spain GDP Growth Surpasses Expectations in 2023
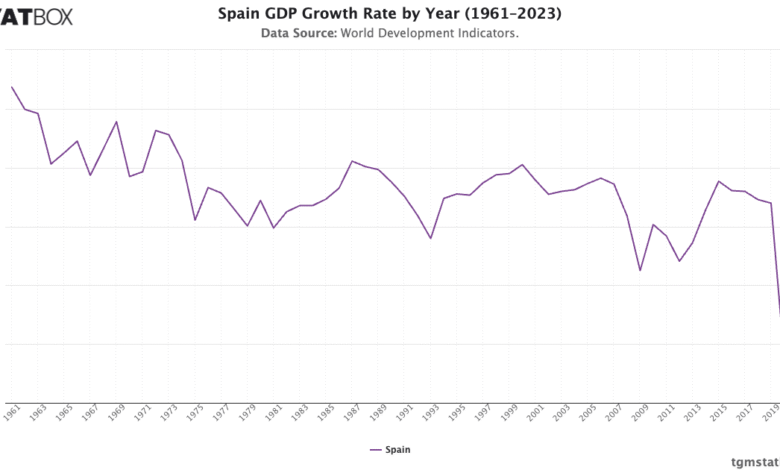
Spain GDP growth has captured the attention of economists and investors alike, with the nation’s economy exceeding expectations during the second quarter, reflecting a robust growth rate of 0.7% against a forecast of 0.6%. As the tourism sector rebounds post-pandemic, Spain emerges as a thriving economic powerhouse, largely driven by increased investment and consumption. With annual GDP growth projected to be 2.5% in 2023, Spain not only surpasses its European counterparts but also ranks as a top destination for foreign investment. Finance Minister Carlos Cuerpo highlights Spain’s unique position as a growth outlier, while acknowledging the role of Next Generation EU funds in bolstering economic stability. However, challenges remain, including the need to balance wages with living costs and address youth unemployment, as Spain navigates its promising economic landscape.
The economic landscape of Spain in 2023 showcases a dynamic interplay of growth indicators, most notably in its gross domestic product expansion. This vibrant southern European nation is not just recovering from the pandemic; it is thriving, propelled by a flourishing tourism sector and a surge in foreign investments. The influx of Next Generation EU funds has significantly contributed to Spain’s strategic investments, enhancing various non-tourism sectors as the country modernizes its economy. Despite facing economic challenges such as political fragmentation and high youth unemployment, Spain continues to attract attention as a premier destination for investors. As the country balances growth with these challenges, it exemplifies a model for recovery in the post-COVID era.
Spain GDP Growth: A Bright Economic Future
Spain’s recent GDP growth has shown remarkable resilience, with the economy expanding by 0.7% in the second quarter of 2023. This growth exceeded expectations, driven largely by robust investment and increased consumer spending. Key sectors contributing to this surge include tourism, which has rebounded significantly post-pandemic, and a burgeoning service industry that encompasses non-tourism services like information technology and financial solutions. As a result, Spain is now seen as a major player on the European economic stage, attracting foreign investment with its potential for continued growth.
The projected annual GDP growth rate of 2.5% for 2023 positions Spain favorably against its European counterparts, with France and Germany lagging behind. This outperformance underscores the effective policies spurred by government initiatives such as the Next Generation EU funds, which aim to stimulate investment in critical sectors. Such strategies reveal Spain’s proactive approach to managing economic challenges while capitalizing on its strengths, ensuring that the nation remains an attractive destination for both tourists and investors alike.
Tourism in Spain: The Economic Engine
Tourism remains a cornerstone of Spain’s economy, contributing roughly 12% to its GDP. The sector has experienced a remarkable resurgence, with an influx of international visitors buoyed by more competitive prices compared to other Western European destinations. This surge in tourism not only supports local businesses but also drives job creation, making it a pivotal area for economic stability in the post-pandemic era. However, the rapid increase in tourist numbers has sparked debates concerning the impact on local communities and cultural heritage.
As the tourism industry evolves, Spain’s government is focusing on sustainable growth, ensuring that while it attracts visitors, it also addresses the needs and concerns of its residents. This dual focus helps in maintaining the delicate balance between economic benefits derived from tourism and the preservation of local culture and environment. Efforts to promote off-peak travel and diversify tourist experiences beyond traditional hotspots are part of a comprehensive strategy to develop a more resilient tourism sector capable of withstanding future shocks.
Foreign Investment in Spain: A Rising Star
Spain has successfully positioned itself as a leading destination for foreign direct investment (FDI), now ranking the fourth most attractive country for investors in the European Union. This appeal is partially driven by government initiatives that streamline the investment process and enhance the business environment. With China committing to invest approximately 11 billion euros in Spain by 2025, it is evident that international stakeholders are increasingly recognizing the economic potential of Spain, especially in sectors like renewable energy and technology.
The influx of foreign capital is crucial for Spain’s economic resilience, providing much-needed resources for innovation, job creation, and sustainable development. It also plays a significant role in bolstering the tourism sector by improving infrastructure and services, fostering a more favorable landscape for both existing businesses and new entrants. As Spain continues to attract FDI, it enhances its capacities to compete on a global scale, paving the way for sustained economic growth.
Economic Challenges Facing Spain in 2023
Despite its favorable growth trajectory, Spain faces several economic challenges that could impede its progress. Issues like high youth unemployment, currently the highest in the EU, pose significant risks to social stability and long-term economic health. Additionally, rising living costs are putting pressure on wages, which need to be addressed to maintain consumer spending and investment levels. These challenges highlight the importance of responsive economic policies that prioritize not just growth, but also the quality of life for Spanish citizens.
Moreover, Spain’s fragmented political landscape complicates the implementation of cohesive strategies to tackle these obstacles. To ensure sustainable growth, policymakers must navigate the intricacies of economic reforms while balancing political interests. Addressing these challenges effectively will be crucial for Spain to maintain its momentum and avoid potential pitfalls that could derail its economic gains.
Next Generation EU Funds: Building a Stronger Spain
The European Union’s Next Generation EU funds represent a powerful tool for Spain as it aims to recover and modernize its economy post-pandemic. With 163 billion euros available through grants and loans, these funds are earmarked for strategic investments in essential sectors, including renewable energy and technology. By utilizing these resources wisely, Spain can enhance its infrastructure, invest in workforce development, and accelerate its transition toward a sustainable economy.
Spain’s proactive approach in tapping into these funds signifies a commitment to innovation and resilience. The focus on non-tourism service exports funded through these initiatives is key to reducing overreliance on traditional sectors and diversifying the economy. By facilitating investments in green energy and digital transformation, Spain is not only preparing for future challenges but is also setting itself up as a leader in the EU’s recovery efforts, showcasing a model of economic adaptability.
The Role of Immigration in Spain’s Economic Landscape
Immigration has notably influenced Spain’s labor market dynamics, contributing significantly to job creation in recent years. With plans to welcome nearly a million migrants over the next three years, Spain is embracing immigration as a vital strategy to bolster its workforce amidst aging population concerns and high unemployment rates. This influx is expected to invigorate various sectors, providing a much-needed boost to economic activity and enhancing overall productivity.
As other EU nations tighten their borders, Spain’s open immigration policies demonstrate a forward-thinking approach. This strategy not only aims to fill labor shortages but also reflects inclusivity and diversity in the workforce. With immigration accounting for 90% of the growth in Spain’s labor force since 2021, it underscores the importance of integrating new workers into the economy to maintain momentum and support Spain’s economic growth trajectory.
Spain’s Energy Sector Transformation: A Path Forward
Spain has made significant strides in transforming its energy sector, particularly through investments in renewable energy sources. With a focus on sustainability, the country has prioritized green energy initiatives, which have insulated it from some of the volatility seen in global energy markets. These efforts align with the EU’s broader green agenda and reflect Spain’s commitment to reducing its carbon footprint while also ensuring energy security.
The low energy costs, bolstered by renewable energy investments since the 2000s, have positioned Spain to navigate the broader European energy crisis resulting from geopolitical tensions. This strategic advantage not only supports domestic businesses but also enhances Spain’s attractiveness to foreign investors looking for stability in energy costs. As Spain continues to innovate within its energy sector, it stands poised to lead in the transition towards a more sustainable future.
Revitalizing Non-Tourism Service Exports in Spain
As Spain’s economy diversifies, the growth of non-tourism service exports has become increasingly vital. Recent developments show that the service sector is now exporting nearly 100 billion euros, surpassing tourism in terms of revenue generation. This transformation underscores the modernization of the Spanish economy, where sectors such as IT, consulting, and financial services are blooming, necessitating skilled labor and innovative practices.
Encouraging investments in non-tourism services creates a more resilient economy capable of weathering disruptions in traditional sectors. By focusing on enhancing service exports, particularly in technology and green services, Spain can improve its competitive edge in the global marketplace. This strategic pivot not only supports job creation but also lays a foundation for sustainable growth and economic diversification.
Spain’s Economic Outlook: Optimism Amidst Challenges
The overall outlook for Spain’s economy remains optimistic as it continues to demonstrate strong growth metrics while forging ahead with significant reforms. The collaboration between government initiatives, foreign investment, and a resilient tourism sector presents a dynamic economic environment. Despite facing hurdles such as youth unemployment and rising costs, the robust GDP growth indicates a commitment to overcome these barriers with ingenuity.
Looking forward, Spain’s ability to strike a balance between leveraging its strengths and addressing its challenges will define its economic landscape. The strategic utilization of Next Generation EU funds, combined with a focus on sustainable practices and innovation, positions Spain not only as an emerging leader within the EU but also as a case study in effective economic management during turbulence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are driving Spain’s GDP growth in 2023?
Spain’s GDP growth in 2023 is significantly driven by robust consumer spending and substantial investments, particularly in non-tourism sectors. The booming tourism industry also contributes greatly, alongside foreign investments that continue to enhance Spain’s economic landscape.
How does tourism impact Spain’s GDP growth?
Tourism in Spain is a vital component of the economy, accounting for about 12% of the GDP. The post-pandemic rebound in tourism, combined with competitive pricing compared to other Western European destinations, is fueling GDP growth and job creation.
In what ways are EU Next Generation funds affecting Spain’s GDP growth?
The Next Generation EU funds are poised to significantly support Spain’s GDP growth by providing 163 billion euros for investment in sectors like renewable energy and technology, bolstering economic modernization and enhancing resilience against external shocks.
What challenges does Spain face despite its GDP growth?
Despite positive GDP growth, Spain faces challenges such as high youth unemployment, rising living costs, and the need for improved wage growth. Additionally, maintaining investment rates and managing public debt remain critical issues for the Spanish economy.
What role does foreign investment play in Spain’s economic growth?
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in Spain’s economic growth, positioning the country as the fourth most attractive investment destination in the EU. Significant investments, such as China’s planned 11 billion euros by 2025, are expected to bolster Spain’s GDP and drive job creation.
How is the Spanish economy performing compared to its European neighbors in 2023?
In 2023, Spain’s economy is outpacing its European neighbors, with a projected GDP growth of 2.5% compared to much lower growth rates in countries like France (0.6%), Germany (0%), and Italy (0.7%), highlighting Spain’s economic resilience.
What is the significance of immigration for Spain’s GDP growth?
Immigration significantly contributes to Spain’s GDP growth, with around 90% of the increase in the labor force since 2021 coming from immigrants. This influx supports job creation and helps to address labor shortages in various sectors, enhancing overall economic activity.
What are the expected long-term effects of investments in renewable energy on Spain’s GDP growth?
Investments in renewable energy are expected to yield long-term benefits for Spain’s GDP growth by reducing energy costs and enhancing sustainability. The strategic allocation of EU funds into green energy initiatives aims to strengthen Spain’s economy against future energy crises.
How might changes in international trade policies affect Spain’s GDP growth?
Changes in international trade policies could significantly impact Spain’s GDP growth, particularly given the country’s reliance on exports. Increased tariffs or trade barriers could pose challenges, affecting the competitiveness of Spanish goods in global markets.
What is the outlook for Spain’s GDP growth in the coming years?
The outlook for Spain’s GDP growth remains positive, driven by strong consumption, tourism recovery, and foreign investment, although ongoing challenges such as wage growth and political stability will require ongoing attention to ensure sustained economic progress.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Spain’s GDP grew 0.7% in Q2, surpassing the 0.6% forecast. |
| The growth is driven by investment, consumption, and tourism. |
| Spain is leading economic growth in the eurozone with a forecasted annual GDP increase of 2.5%. |
| Spain’s economy is bolstered by non-tourism services, exports, and EU recovery funds. |
| Challenges include maintaining wage growth, climate change, and high youth unemployment. |
| Tourism accounts for about 12% of Spain’s GDP, experiencing a strong post-pandemic rebound. |
| Spain plans to welcome nearly a million immigrants to support job creation. |
| The country is the second-largest beneficiary of the EU’s Next Generation EU funds. |
| Foreign investment remains strong, with China planning significant investments in Spain. |
Summary
Spain GDP growth has been remarkable, showcasing an impressive 0.7% growth in the second quarter, surpassing expectations. This growth is primarily fueled by strong consumer and investment activities, coupled with a flourishing tourism sector. As Spain continues to outperform its European counterparts, its economic strategies focusing on diverse sectors and immigration are essential for sustaining this momentum. Furthermore, the strategic use of EU recovery funds positions Spain favorably, even while facing challenges such as youth unemployment and rising costs of living. Overall, the growth trend suggests a vibrant future for Spain’s economy.