McDonald’s New Drinks: Testing Exciting Beverages Soon
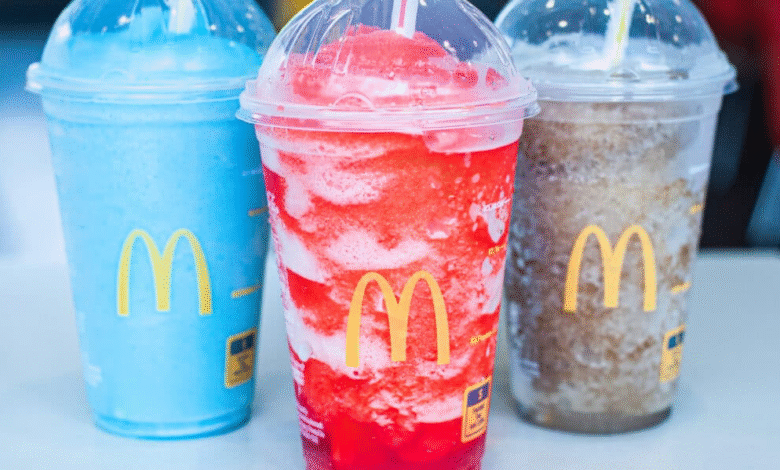

Exciting news is bubbling at McDonald’s with the launch of their new drinks, featuring a delightful assortment of coffee drinks, refreshers, and flavored sodas that are set to tantalize taste buds in over 500 restaurants. These innovative beverages, inspired by their recent CosMc’s spinoff, aim to captivate an audience eager for colorful and refreshing options. As fast-food beverage trends shift towards engaging flavors and playful presentations, McDonald’s is strategically positioning itself to cater to Gen Z drink preferences. From the refreshing Strawberry Watermelon Refresher to the creamy Vanilla Cold Brew, there’s something for every palate in this revamped drink lineup. This venture not only addresses the growing demand for vibrant beverages but also reaffirms McDonald’s commitment to enhancing the customer experience through exciting drink choices.
In a bold new initiative, McDonald’s is gearing up to unveil an array of refreshing beverages designed to attract attention in the fast-food landscape. This includes various beverage innovations such as aromatic coffee concoctions, vibrant refreshments, and flavorful sodas, showcasing a keen awareness of evolving consumer tastes, particularly among younger drinkers. Inspired by the now-closed CosMc’s brand, these fresh drink options aim to fuel excitement and draw customers looking for a delightful break during their day. As consumer preferences shift toward dynamic and visually appealing options, McDonald’s seeks to enhance its seasonal beverage selections, aligning with contemporary trends and catering to the cravings of a diverse audience.
Exploring McDonald’s New Drinks: A Fresh Take on Coffee and Refreshers
McDonald’s commitment to innovation is evident as they prepare to launch a range of new drinks in over 500 restaurants, bringing a much-anticipated twist to their beverage lineup. This includes enticing options like Creamy Vanilla Cold Brew and Toasted Vanilla Frappe, which are designed to cater to the taste preferences of their younger audience, notably Gen Z. These beverages not only highlight McDonald’s ongoing evolution in its beverage offerings but also demonstrate an understanding of current fast-food beverage trends that favor unique, flavorful concoctions.
The introduction of flavored sodas like Sprite Lunar Splash is an exciting development that adds a fun dimension to the traditional soda lineup. McDonald’s flavored sodas are expected to be attractively colorful and refreshing, making them perfect additions for customers seeking a delightful afternoon refreshment. By expanding their drink portfolio in this way, McDonald’s aims to create more occasions for customers to enjoy their food, thus enhancing the overall customer experience.
Gen Z Drink Preferences: How McDonald’s is Adapting
Understanding Gen Z drink preferences is crucial as they represent a significant segment of fast-food consumers. McDonald’s is keenly aware that this generation values not only flavor but also the visual appeal of beverages. The introduction of bright, colorful options reflects a strategy to engage younger audiences who seek fun and Instagram-worthy drinks. For instance, the Strawberry Watermelon Refresher is expected to be both refreshing and vibrant, appealing directly to Gen Z’s desire for aesthetically pleasing beverages.
Moreover, McDonald’s move to test out these innovative drinks aligns with trends indicating that younger consumers are more inclined to explore adventurous drink offerings rather than standard fare. As fast-food chains compete for this demographic, McDonald’s aims to position itself as a leader in beverage innovation. This response to Gen Z drink preferences is a strategic effort to revitalize their brand and attract a new customer base while maintaining relevance in an ever-competitive market.
Competitive Edge: McDonald’s vs. Beverage-Focused Chains
As the landscape of fast food continues to evolve, McDonald’s is recognizing the necessity of adapting its beverage offerings to maintain a competitive edge against beverage-focused chains like Dutch Bros and Swig. These competitors have successfully tapped into the demand for personalized and unique drink experiences, attracting a younger clientele. By introducing new drinks inspired by the now-defunct CosMc’s, McDonald’s is not only enhancing its beverage selection but also reclaiming its position in the market as a go-to destination for exciting drink options.
The strategic decision to focus on new coffee drinks and refreshing sodas reflects McDonald’s understanding of the importance of versatility in its beverage program. With declining sales figures in recent months, the chain is keen to draw visitors back through its doors by providing enticing drink options that cater to contemporary tastes. By investing in their drink lineup, McDonald’s aims to recreate the excitement once generated by CosMc’s and ultimately attract consumers looking for innovative and flavorful fast-food beverages.
The Future of Fast-Food Beverage Trends at McDonald’s
The future of fast-food beverage trends is bright for McDonald’s as they embark on this new initiative to expand their drink offerings. With a focus on creative combinations and signature flavors like the Popping Tropic Refresher, the brand is poised to capture the interest of both loyal customers and curious new ones. This testing phase serves as a valuable opportunity for McDonald’s to gather feedback and fine-tune their offerings, aligning with current consumer demands for refreshing, flavorful drinks.
Additionally, the emphasis on colorful, vibrant beverages aligns perfectly with overarching trends in the fast-food industry. Customers are increasingly seeking out not just taste but also an enjoyable visual experience when choosing beverages. With the right mix of creativity and market research, McDonald’s is on track to redefine what it means to enjoy drinks at fast-food establishments, potentially setting new benchmarks for the industry.
McDonald’s Flavored Sodas: A New Era of Refreshment
McDonald’s venture into flavored sodas marks a significant step forward in their beverage innovation strategy. Introducing options like Sprite Lunar Splash showcases an exciting blend of flavors that are designed to cater to the modern consumer’s palate. This move not only highlights McDonald’s willingness to experiment with bold flavors but also reflects a growing trend in the fast-food industry where beverages play a central role in attracting customers.
The inclusion of flavored sodas within their drink lineup is also a response to a broader industry shift towards more customizable drink options. As competitors ramp up their own offerings, McDonald’s need to remain competitive in this space means adapting to customer preferences and trends. This repositioning towards fun and flavorful beverages aims to encourage more consumers to consider McDonald’s not only for their iconic meals but also for refreshing and exciting drink choices.
Innovative Coffee Options: McDonald’s Gets Creative
McDonald’s new coffee offerings, which include the Creamy Vanilla Cold Brew and Toasted Vanilla Frappe, indicate a creative approach to re-engage coffee lovers. These drinks showcase McDonald’s commitment to providing flavorful, high-quality options that can rival those available at specialty coffee shops. By elevating their coffee selection, McDonald’s aims to appeal to a growing segment of consumers who expect more from their fast-food coffee experience.
Incorporating unique flavors and modern twists on traditional coffee drinks places McDonald’s in a strong position to attract a more diverse customer base. By experimenting with different combinations and textures, these new options offer consumers a refreshingly new take on coffee that goes beyond the ordinary. This focus on innovation not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reinforces McDonald’s reputation as a dynamic player in the beverage market.
Responding to Consumer Feedback: The Role of Testing New Drinks
Testing new drinks across select locations allows McDonald’s to effectively gauge which beverages resonate most with their customers. This consumer-centric approach enables the company to adapt and refine their offerings based on direct feedback, creating drinks that genuinely satisfy consumer preferences. It reflects a strategic decision to prioritize customer experience while minimizing risks associated with launching new products in a saturated market.
As they test various drink options, McDonald’s can gather invaluable data that informs not only future product launches but also broader marketing strategies. Understanding what flavors and styles appeal to their audience will be essential in navigating the competitive landscape. This methodical approach to beverage experimentation positions McDonald’s well as they strive to enhance customer engagement and drive sales in a challenging economic environment.
The Impact of Social Media on Drink Trends at McDonald’s
Social media has played a pivotal role in shaping drink trends, particularly among younger consumers who often share their beverage experiences online. McDonald’s is keenly aware of this influence and is strategically using colorful and inventive drinks to generate buzz across platforms like Instagram and TikTok. By introducing vibrant drinks that are visually appealing, McDonald’s aims to capture the attention of social media users, thereby creating organic marketing opportunities as customers share their experiences.
The vibrant colors and imaginative flavors of new drinks will likely encourage consumers to showcase their beverages on social media, driving further interest and engagement with the McDonald’s brand. This dynamic interplay between drink trends and social media advocacy is crucial for McDonald’s as they seek to reenergize their image and reach higher numbers of Gen Z consumers who value unique and shareable experiences.
Looking Forward: What Lies Ahead for McDonald’s Beverage Strategy
As McDonald’s embarks on testing new drinks, their beverage strategy looks to the future with anticipation. The current focus on innovative coffee drinks and exciting refreshers indicates a commitment to evolving customer tastes. This proactive approach will allow McDonald’s to remain relevant in an industry where consumer preferences are continuously shifting, particularly among younger demographics.
Looking ahead, McDonald’s is likely to delve deeper into broader beverage trends, exploring options that not only taste great but also meet the demand for healthier or more sustainable choices. By staying ahead of these trends, McDonald’s can position itself as a leader in the fast-food beverage market, ensuring that they not only meet but exceed consumer expectations in the ever-changing landscape of beverage consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
What new drink options will McDonald’s be testing this summer?
McDonald’s is set to test a variety of new drinks this summer, including coffee drinks like Creamy Vanilla Cold Brew, refreshing options like Strawberry Watermelon Refresher, and flavored sodas such as Sprite Lunar Splash. These drinks are inspired by their former CosMc’s brand and aim to attract younger consumers who enjoy fun and colorful beverages.
How will McDonald’s new drinks cater to Gen Z drink preferences?
The new drink lineup at McDonald’s is designed to cater to Gen Z drink preferences by offering cold, flavorful, and visually appealing beverages. By introducing items like the Toasted Vanilla Frappe and Popping Tropic Refresher, McDonald’s aims to resonate with younger consumers looking for unique refreshment options.
Where can consumers find McDonald’s new coffee drinks and refreshers?
McDonald’s new coffee drinks and refreshers will initially be tested in over 500 restaurants located in Wisconsin, Colorado, and surrounding areas. This rollout will help the chain gather feedback on customer preferences before potentially expanding the offerings to more locations.
What is the significance of McDonald’s focus on flavored sodas in their drink lineup?
McDonald’s focus on flavored sodas in their new drink lineup reflects current fast-food beverage trends, as many chains are introducing fun and colorful drinks to attract consumers. By offering flavored sodas like Sprite Lunar Splash, McDonald’s aims to enhance its appeal and compete with beverage trends popular among younger generations.
Why did McDonald’s close CosMc’s and how does this relate to their new drinks?
McDonald’s closed CosMc’s to refocus its beverage innovation back to its primary restaurants. The lessons learned from CosMc’s are now being applied to McDonald’s new drinks initiative, allowing the chain to experiment with unique coffee drinks and refreshers that resonate with consumer preferences.
When can customers expect to try McDonald’s new refreshers and flavored sodas?
Customers can expect to try McDonald’s new refreshers and flavored sodas later this summer, as the testing begins in select locations. This initiative will help McDonald’s gauge consumer interest and potentially roll out these innovative drinks across more outlets based on feedback.
How do McDonald’s new drinks fit into the competitive fast-food beverage landscape?
McDonald’s new drinks, including coffee and refreshers, aim to enhance the chain’s competitiveness against beverage-focused chains like Dutch Bros and Swig. By expanding their drink offerings, McDonald’s seeks to draw in more customers looking for personalized and enjoyable beverage experiences.
What inspired McDonald’s to develop new beverage options like their refreshers?
The development of new beverage options like McDonald’s refreshers was inspired by the growing trend among younger consumers, particularly Gen Z, who favor fun, colorful drinks over traditional fast-food beverages. This direction reflects McDonald’s intent to adapt to changing consumer tastes and preferences.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| McDonald’s Test New Drinks | McDonald’s is testing new coffee drinks, refreshers, and flavored sodas at over 500 restaurants. |
| Locations for Testing | The tests will take place in Wisconsin, Colorado, and nearby areas. |
| Target Audience | The initiative aims to attract younger consumers, particularly Gen Z. |
| Competitive Landscape | McDonald’s seeks to enhance competitiveness against chains focusing on personalized drinks. |
| New Drink Lineup | Options include Creamy Vanilla Cold Brew, Strawberry Watermelon Refresher, and more. |
| Background | The tests follow the closure of CosMc’s, a spinoff focused on drinks and snacks. |
| Market Trends | There is growing demand for colorful and flavorful drinks among consumers. |
Summary
McDonald’s new drinks initiative signifies a strategic move to redefine its beverage offerings. By testing a range of bold and refreshing beverages at over 500 locations, McDonald’s aims to cater to the evolving tastes of its younger customers, particularly Gen Z. This new drink lineup not only enhances its competitive edge against specialized beverage chains but also reflects a broader trend in the fast-food industry focusing on vibrant and innovative drink options. As the fast-food giant embraces this new direction, customers can look forward to exciting choices that align with contemporary beverage preferences.