Challenges of Sending Humans to Mars: Musk and NASA’s Vision
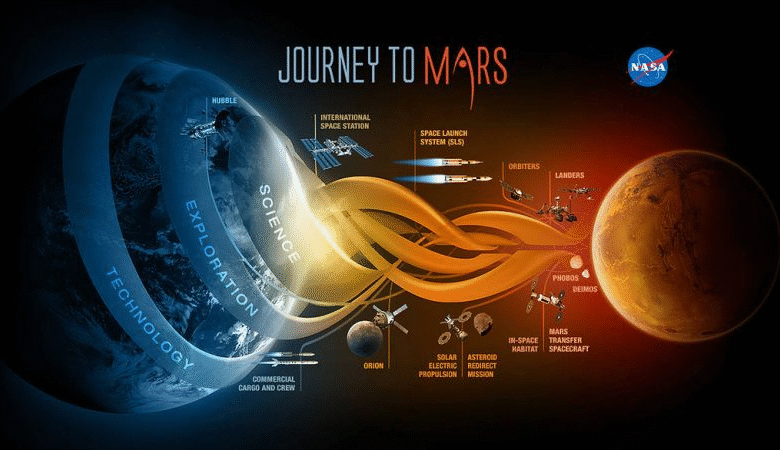
The challenges of sending humans to Mars represent one of the most ambitious endeavors in human history. As visionary tech mogul Elon Musk forges ahead with his dreams of a Mars colony, and NASA aims to achieve manned missions by 2040, both face a myriad of obstacles that could stall their progress. Developing reliable life support systems, dealing with radiation exposure, and creating effective propulsion technologies are just a few of the hurdles that need to be addressed to ensure human life on Mars becomes a reality. Furthermore, the complexities of Mars colonization challenges cannot be underestimated, as they require innovative solutions and international collaboration. As SpaceX’s Starship continues its testing phases, the road to establishing a sustainable human presence on the red planet remains fraught with difficulties but equally ripe with potential breakthroughs.
The quest to establish a human presence on Mars is not only a quest for exploration but also a significant scientific challenge. From the intricate technicalities of human transit to the red planet to the logistical issues of creating a habitable environment, the mission draws considerable attention on a global scale. With the ambitious objectives outlined in both the Elon Musk Mars mission and NASA’s proposed timeline, significant resources and innovations will be required to tackle the obstacles at hand. This sacred pursuit encapsulates humanity’s desire to break barriers and expand our reach beyond Earth, presenting both potential benefits and inherent risks. Through exploring the feasibility of human life on Mars, astronauts may unlock valuable insights about the possibilities of life beyond our own planet.
The Ambitious Goals of Elon Musk’s Mars Mission
Elon Musk’s endeavors to send humans to Mars are fueled by a vision of interplanetary colonization that could redefine the future of humanity. In an age where Earth faces numerous existential threats such as climate change, nuclear warfare, and overpopulation, Musk believes that establishing a sustainable human presence on Mars is essential. His plan, through SpaceX, aims to launch crewed missions as early as 2029, marking a monumental leap toward making Mars an extension of human civilization. The transition from dreams to reality will rely heavily on the success of the SpaceX Starship, a next-generation spacecraft designed for deep-space travel.
Musk’s Mars mission resonates with the greater notion of preserving life beyond Earth, mirroring efforts by other space agencies like NASA, which aims to send astronauts to Mars by 2040. Both objectives highlight a growing recognition of the importance of Martian exploration as a stepping stone for potentially relocating or augmenting human life on the red planet. This interstellar ambition not only reflects humanity’s adventurous spirit but also underscores pressing ethical questions about the future of our species amongst the stars.
NASA’s Vision for Mars Colonization
NASA’s aspiration to reach Mars involves intricate planning and technological advancement that parallels Elon Musk’s timeline yet also reveals contrasting approaches. With the goal of sending humans to Mars by 2040, NASA officials emphasize a methodical process, focusing on understanding the Martian environment, developing life support systems, and ensuring the safety of astronauts during their journey. This ambition is underscored by the Moon to Mars Program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon as a precursor to further deep-space exploration.
The roadmap outlined by NASA highlights the implementation of advanced technologies designed to mitigate the dangers of cosmic radiation, which poses a significant safety challenge during long-term space travel. Enhanced propulsion systems and reliable life support are critical areas of research, reflecting the complexities of not only landing on Mars but sustaining human life there. The collaboration between NASA and private entities like SpaceX may, therefore, become essential in overcoming the numerous challenges associated with Mars colonization.
Challenges of Sending Humans to Mars
The challenges of sending humans to Mars are multifaceted, encompassing technical, biological, and psychological hurdles that need to be addressed before a successful manned mission can take place. One of the foremost challenges involves navigating the perilous radiation environment in deep space. Cosmic radiation poses a substantial risk to astronaut health over extended durations, potentially leading to severe health issues like cancer or acute radiation sickness. Furthermore, the spacing of resupply missions between Earth and Mars necessitates innovative solutions to support human life independently on the Martian surface.
Moreover, the complexity of the Mars landing itself cannot be understated. The delicate balance of velocity and gravitational pull requires meticulous planning and precision technology to ensure the safety of landing crews. With SpaceX’s Starship and NASA’s planned missions, extensive testing and simulations are crucial to developing effective landing protocols. Every aspect, from crew training to spacecraft reliability, plays a significant role in overcoming these inherent challenges of reaching and residing on Mars.
SpaceX Starship: The Key to Mars Exploration
SpaceX’s Starship program represents one of the most ambitious aerospace projects in history, aimed at making missions to Mars a feasible reality. This fully reusable spacecraft is designed to carry large payloads and numerous astronauts, making it essential for the colonization of Mars. The recent test flights have provided valuable data but also highlighted the challenges inherent in developing such a complex vehicle. For instance, the recent explosion of the Starship after its eighth test flight underscores the risks involved in this groundbreaking attempt to refine reusable rocket technology.
The capabilities of the Starship will be pivotal not only for the Mars mission but also for its role in future exploration of outer space. Its design will enable it to transport supplies and equipment necessary for establishing a human settlement on Mars. Ultimately, the success of Starship will determine the feasibility of reaching Musk’s vision of a self-sustaining city on the Red Planet, making it a focal point in the quest for human life on Mars.
Mars Colonization: Ethical Considerations and Responsibilities
As humanity sets its sights on Mars, ethical considerations become paramount, particularly concerning Mars colonization. The notion of claiming another planet raises significant questions around planetary protection and the potential implications for any existing microbial life on Mars. Scientists emphasize the importance of not contaminating Mars with Earth-origin microbes during manned missions, highlighting ethical responsibilities towards preserving the potential native Martian ecosystems. This challenge necessitates rigorous protocols and discussions within the scientific community to ensure responsible exploration.
Additionally, there are moral implications in deciding who gets to participate in the exploration and eventual colonization of Mars. The selection process for astronauts and future colonists may inadvertently perpetuate societal biases, raising concerns about equity in access to extraterrestrial opportunities. Discussions surrounding diversity and inclusion in the context of Mars missions underscore the importance of approaching this new frontier with awareness and sensitivity to humanity’s collective identity.
Prompting Global Collaboration in Space Exploration
The ambitious goals of sending humans to Mars have the potential to unite countries and institutions in a shared vision for space exploration. As multiple nations, including China and Russia, express their desire to establish human presence on Mars, collaboration could lead to accelerated advancements in technology and shared knowledge necessary for overcoming the challenges of interplanetary travel. Global partnerships may prove key in pooling resources, talent, and innovative ideas to tackle both the technical challenges and the ethical implications of colonizing another planet.
Furthermore, fostering international cooperation in space endeavors could help mitigate competition and conflict on Earth, highlighting a collective aspiration for peaceful exploration. By working together, countries can share the vast research and development costs associated with such ambitious missions, ultimately producing a more robust approach to Mars exploration. This collaborative framework could lay the groundwork not only for successful missions to Mars but also for future explorations beyond our solar system.
Potential Benefits of Human Presence on Mars
Establishing a human presence on Mars holds potential benefits that extend beyond scientific discovery. As humanity confronts pressing challenges on Earth, Mars could serve as a new frontier for habitation, offering solutions to overpopulation and resource depletion. The exploration and eventual colonization of Mars could foster technological advancements that may also benefit life on Earth, including innovations in sustainability, agriculture, and energy production. Such technological leaps could ultimately contribute to a more sustainable future for our home planet.
Moreover, setting up a human civilization on Mars could stimulate global interest in STEM fields, inspiring future generations to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. By making space exploration a focal point of human achievement, we can spark a renewed commitment to education and research that addresses both terrestrial and extraterrestrial challenges. This shift may invigorate global collaboration and inspire breakthroughs essential for both Mars colonization and addressing the issues facing humankind.
The Science Behind Mars Missions
The science behind missions to Mars is grounded in the desire to uncover the Red Planet’s past and understand its potential for supporting human life. Research into the geological composition of Mars, along with studies of its atmosphere and climate, plays a crucial role in informing future missions. Understanding what conditions existed when Mars had liquid water is essential for assessing its habitability, and the findings from rovers and orbiters continue to shape our expectations of what human explorers may find.
Additionally, scientific endeavors on Mars can provide insights into Earth’s own history and evolutionary biology. As researchers draw parallels between the early Earth and Mars, the quest for knowledge about the universe’s past could illuminate critical questions about life’s origins. This connection between planetary science and astrobiology underscores the intrinsic link between our exploration endeavours and our understanding of our own planet, making the pursuit of Mars colonization all the more significant.
Future of Space Travel: Lessons from Mars Exploration
The future of space travel is poised for transformation, drawing lessons from current endeavors focused on Mars exploration. As both private and public entities invest in technologies and strategies to reach Mars, they are simultaneously paving the way for potential missions beyond our neighboring planet. The insights gained from missions targeting Mars will likely inform strategies for interstellar travel, as engineers and scientists learn to overcome the challenges of long-duration spaceflight and human health in outer space.
Moreover, the collaborative spirit of Mars missions will likely inspire future projects aimed at exploring more distant reaches of the universe. By fostering a culture of cooperation and innovation, humanity may position itself for renewed explorations of the cosmos that extend far beyond our solar system. As we invest in reaching Mars, we inadvertently prepare for the next steps in becoming a multi-planetary species, making the lessons learned during these missions invaluable for our interstellar future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the major challenges of sending humans to Mars according to NASA and SpaceX?
The major challenges of sending humans to Mars, as highlighted by NASA and SpaceX, include addressing the complicated Mars landing problem, ensuring reliable life support systems, improving propulsion capabilities, and managing the severe radiation environment in space. These technical hurdles must be overcome for a successful human mission to Mars.
How does Elon Musk plan to tackle the challenges of sending humans to Mars with SpaceX Starship?
Elon Musk’s plan to tackle the challenges of sending humans to Mars revolves around the SpaceX Starship, the tallest and most powerful rocket ever built. Starship aims to provide the required thrust and reliability for deep space missions, and its ongoing test flights are crucial to refining the technology needed for safe landings and sustainable human life on Mars.
What are some Mars colonization challenges that humanity must address?
Mars colonization challenges include creating sustainable life support systems, dealing with the psychological impacts of isolation, ensuring safe transportation to and from Mars, and developing habitats that can withstand the planet’s harsh environment. Each of these challenges needs careful consideration to facilitate long-term human life on Mars.
What technical issues does NASA face in sending humans to Mars by 2040?
NASA faces several technical issues in sending humans to Mars by 2040, including improving propulsion technology for faster travel, developing reliable systems to provide life support in the Martian environment, and overcoming the risks presented by radiation exposure during transit. These challenges make the Mars 2040 mission ambitious.
Why is human life on Mars considered essential by Elon Musk?
Elon Musk considers human life on Mars essential for preserving humanity in the face of threats on Earth, including natural disasters and conflicts. Establishing a human presence on Mars could serve as a safeguard for the future of humanity, creating a backup for life in case of catastrophic events on our planet.
How does the Mars landing problem impact missions planned by Elon Musk and NASA?
The Mars landing problem significantly impacts missions planned by Elon Musk and NASA, as it involves overcoming precise technical challenges such as ensuring a safe descent through the Martian atmosphere and executing a successful landing on the planet’s surface. These factors are critical for the successful establishment of human life on Mars.
What role does radiation play in the challenges of sending humans to Mars?
Radiation poses a severe challenge in sending humans to Mars, as astronauts would be exposed to higher levels of cosmic radiation during transit and on the Martian surface. This risk necessitates designing effective shielding and protective measures to ensure astronauts’ safety, making it a primary concern for both NASA and SpaceX.
What advancements are needed for SpaceX Starship to overcome challenges of Mars exploration?
Advancements needed for SpaceX Starship to overcome the challenges of Mars exploration include improvements in propulsion technology, enhanced safety features for human spaceflight, and the ability to conduct successful recovery of both the Starship and its boosters. These innovations are crucial for ensuring reliable travel to Mars and supporting human life on the planet.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Goal | Sending humans to Mars by 2029 (Musk) and 2040 (NASA) with interest from China by 2038. |
| Importance | Preserves humanity from Earth’s threats; scientific exploration for life. |
| Challenges | Technical issues: radiation, life support, reliability, and propulsion advancements needed. |
| Rocket Technology | SpaceX’s Starship is critical; recent test flights show both progress and setbacks. |
| Research Stations | Mars Desert Research Station provides insights into life on Mars. |
Summary
The challenges of sending humans to Mars are profound and multifaceted, requiring significant advancements in technology, safety measures, and overall mission planning. As Elon Musk and NASA aim for ambitious timelines with the vision of establishing a human presence on Mars, they must navigate complex obstacles such as radiation exposure, life support systems, and ensuring the reliability of their spacecraft. These challenges, intertwined with the aspirations of international space agencies, highlight the importance of continued research and innovation in making interplanetary life a reality.