Climate Change Mortgage: How It Affects Your Credit Score
As the effects of climate change intensify, potential homebuyers must now consider how a climate change mortgage could influence their financial future. With an increase in extreme weather events, lenders are beginning to factor in climate risk assessments and how they may affect mortgage underwriting. This shift has significant implications on credit score impact, leading to potential fluctuations as properties in high-risk areas may face rising foreclosure rates. Moreover, escalating insurance premiums are forcing homeowners to confront tough decisions, making mortgage approval more complex than ever. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for securing a home loan in an environment where climate considerations are becoming integral to the mortgage process.
In the evolving landscape of home financing, it’s essential to recognize how environmental factors are reshaping mortgage agreements. Known colloquially as climate-conscious lending, this approach assesses risks associated with natural disasters, impacting property valuations and homeowner insurance rates. As assessments of climatic threats become standard practice, the influence on borrower eligibility and creditworthiness grows more pronounced. Furthermore, heightened foreclosure probabilities linked to adverse weather events signal a need for buyers to navigate this new territory carefully. Embracing terminology such as eco-sensitive mortgages and risk-adjusted lending practices is essential for understanding the financial implications of residing in climate-prone regions.
Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Mortgage Underwriting
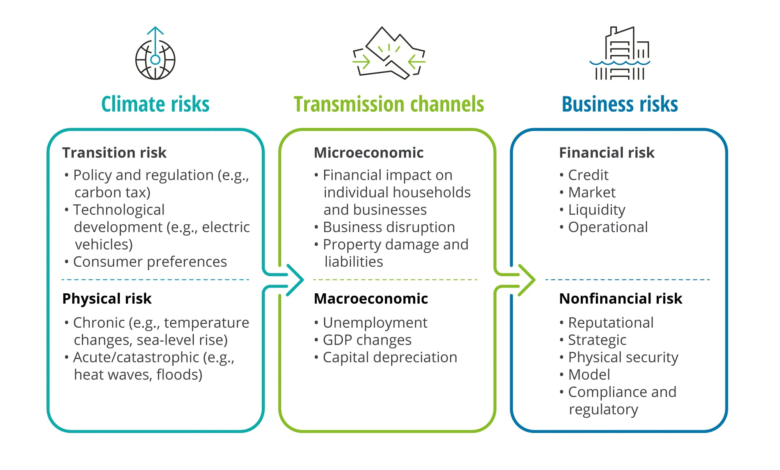
In today’s mortgage landscape, lenders meticulously analyze various factors to assess an applicant’s creditworthiness. Traditionally, the most significant considerations included income, debt, and the value of the collateral property. However, as climate change continues to escalate, its impact is increasingly being integrated into the underwriting process. Lenders are beginning to recognize that the likelihood of climate-related disasters, such as floods and wildfires, can directly influence a property’s value and the borrower’s ability to repay their mortgage. This incorporation of climate risk assessment is crucial, as it may affect the risk profile of both the property and the borrower.
According to recent findings, more and more lenders are beginning to adopt policies that involve a thorough climate risk assessment as part of their mortgage underwriting procedures. These assessments take into account location factors, previous disaster claims, and environmental vulnerabilities, which helps lenders mitigate potential financial losses. Such changes are essential as they could either bolster or hamper a borrower’s credit score, depending on how their property and the risks associated with it are evaluated. For potential homeowners, this evolving mortgage landscape means it is vital to understand how their property’s exposure to climate risk could impact their overall financial future.
The Relationship Between Climate Change and Credit Score
Recent studies have indicated a direct correlation between climate risk and credit scores. When lenders begin factoring in climate rankings during the mortgage approval process, borrowers in high-risk areas may see a decline in their credit scores due to the higher likelihood of foreclosure in case of a climate disaster. Homes in areas prone to flooding, for instance, may face increased scrutiny, leading to potential increases in insurance premiums and, ultimately, the financial burden on borrowers. This could create a challenging environment for buyers looking to secure a mortgage.
As climate change narratives continue to permeate the financial sector, homeowners and potential buyers must remain informed about how their credit scores could be affected. For example, property values in high-risk zones generally produce higher foreclosure rates after severe weather events, which in turn can inflate a borrower’s perceived risk profile. Thus, understanding the implications of climate change on one’s credit score has never been more essential, especially as lenders increasingly emphasize climate risk assessments in their decision-making processes.
Foreclosure Rates and Climate-Related Risks
Climate change is driving an alarming increase in foreclosure rates nationwide, significantly impacting the housing market. With recent estimates indicating that climate-driven foreclosures could result in bank losses of over $1.21 billion, this statistic represents a notable percentage of total credit losses attributed to foreclosures. The financial implications not only affect lenders but also have secondary repercussions for homeowners caught in the cycle of rising costs tied to climate risks, such as increased insurance premiums and potential property depreciation.
According to the First Street report, homes experiencing flooding during weather catastrophes may see a 40% increase in subsequent foreclosure rates compared to their unaffected neighbors. This trend highlights the urgent need for lenders to adapt their strategies to account for climate-related risks. If they do not, borrowers could find themselves at risk of losing their homes, as many might opt to walk away from properties they can no longer afford due to escalated costs linked to insurance or repairs.
The Influence of Insurance Premium Hikes on Mortgages
Insurance premiums are rising sharply in regions vulnerable to climate-related risks, which has a domino effect on the mortgage market. Homeowners in high-risk areas, particularly coastal regions, are already feeling the pinch of increased insurance premiums, which can soar following severe weather events. This rise can create financial strain, resulting in higher monthly expenses that may affect a homeowner’s ability to repay their mortgage and subsequently impact their credit score.
Moreover, lenders might require additional insurance for properties in flood plains or other designated high-risk areas. Such measures, while intended to protect both lenders and homeowners, may alienate potential buyers who find the overall costs too burdensome. If the trend of rising insurance premiums continues, it could further exacerbate foreclosure rates, negatively impacting the overall housing market and posing a significant risk to lenders who have not adequately adjusted their underwriting models to accommodate these new realities.
The Future of Climate Risk Assessment in Mortgage Markets
Looking ahead, the trend of incorporating climate risk assessment into mortgage lending practices appears to be on the rise. As financial institutions recognize the systemic risks presented by climate change, they are likely to develop more sophisticated underwriting models that incorporate environmental and climate-related data. This shift will mark a critical evolution in how lenders evaluate risk and determine creditworthiness, making it essential for borrowers to stay informed.
By implementing advanced climate risk assessment tools, lenders can gain insights into potential impacts that climate events could have on property valuations and default rates. This proactive approach would not only protect financial institutions from losses but also educate borrowers about the importance of location and property resilience in assessing their mortgage options. In light of the ongoing climate crisis, this forward-thinking strategy could be pivotal in shaping the future stability of the mortgage market.
Adapting to Climate Change: Strategies for Homebuyers
As more lenders adopt climate risk assessments in their mortgage underwriting processes, homebuyers must develop a strategic approach to these changes. A proactive strategy involves researching properties in low-risk areas while simultaneously considering the resilience of the home against potential climate impacts. By prioritizing properties with strong climate resilience features, buyers can minimize future risks and possibly enhance their credit scores in the long run.
Moreover, potential homeowners should take initiative in understanding the financial implications of their insurance needs and the potential for rising premiums linked to climate change. By budgeting for these costs and engaging in discussions with lenders about their policies towards climate-related risks, homebuyers can make informed decisions that protect their financial future. Ultimately, being prepared to navigate the evolving landscape of climate change can position buyers for success in securing a mortgage that aligns with both their financial goals and environmental responsibility.
The Role of Financial Institutions in Addressing Climate Change Risks
Financial institutions play a pivotal role in mitigating the impacts of climate change on the mortgage sector. By adopting new underwriting practices that take into account climate risk assessments, lenders can reduce exposure to potential losses stemming from natural disasters. Moreover, they are in a unique position to educate borrowers about the realities of climate risks associated with their property, thus enabling them to make better financial decisions regarding homeownership while keeping an eye on potential credit score impacts.
Moreover, these institutions also have the responsibility to advocate for policy changes within the industry that prioritize sustainable practices and responsible lending protocols. By promoting awareness of the financial implications that extreme weather events can have on borrowers, lenders can champion a more resilient housing market that benefits both consumers and financial institutions alike. This collaborative approach will lead to a more sustainable integration of climate considerations into the mortgage landscape.
Navigating the Mortgage Market Amid Climate Uncertainty
As climate change continues to pose challenges to the mortgage market, navigating these complexities demands careful consideration from all stakeholders, including lenders, borrowers, and insurers. With the ongoing rise in severe weather patterns, identifying properties that pose lower climate risks can protect borrowers from adverse financial outcomes. Homebuyers must conduct thorough research, weighing factors such as insurance costs and potential property value fluctuations related to climate conditions.
In this evolving market, borrowers who understand the influence of climate risk on their credit scores and overall financial health will be better positioned to secure favorable mortgage terms. In addition, lenders that prioritize transparency regarding the impact of climate risks on property values will foster greater trust and collaboration, ultimately leading to a more resilient mortgage market capable of weathering the uncertainties posed by climate change.
The Importance of Climate Awareness in Real Estate Decisions
In an era defined by climate change, awareness of environmental factors is crucial for anyone making real estate decisions. The willingness to consider potential climate risks—such as rising sea levels, increased flooding, and extreme weather—will not only impact purchase decisions but also influence future financial stability through factors such as insurance costs and mortgage terms. Homebuyers need to approach their search with a comprehensive understanding of how these elements could affect their long-term financial goals.
Real estate agents, lenders, and buyers alike must foster open conversations about the importance of climate awareness in property selection. By working collaboratively, stakeholders can develop methods to educate prospective homeowners about the nature of climate risk assessments that lenders are beginning to implement. This education is essential for ensuring responsible lending practices and for instilling a sense of resilience within communities that are increasingly vulnerable to the effects of climate change.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does climate change impact mortgage underwriting processes?
Climate change significantly affects mortgage underwriting processes as lenders are beginning to include climate risk assessments in their evaluations. Rising risks from natural disasters, such as flooding and wildfires, can influence a borrower’s credit score and overall creditworthiness. This change may result in stricter lending conditions or higher interest rates for properties located in high-risk areas.
What is the relationship between climate change and credit score impact for mortgage applicants?
The credit score impact for mortgage applicants is increasingly tied to climate risk assessments. If a property is deemed high-risk due to climate change factors, lenders may adjust the credit score impact. This can lead to either decreased credit scores, affecting loan approval odds, or improved scores if effective mitigation strategies are in place.
Are foreclosure rates influenced by climate change risks?
Yes, foreclosure rates are influenced by climate change risks. Properties damaged by climate-related events, such as floods, face approximately a 40% increase in foreclosure rates compared to unaffected homes. With projections suggesting that climate-driven foreclosures could rise dramatically, this presents a significant risk to lenders.
How do insurance premiums relate to climate change mortgages?
Insurance premiums are closely linked to climate change mortgages, especially in high-risk areas prone to natural disasters. As extreme weather events become more frequent, insurers are raising premiums, which can put additional financial strain on homeowners and potentially lead to higher foreclosure rates.
What role do lenders play in climate risk assessments for mortgages?
Lenders play a crucial role in climate risk assessments for mortgages by evaluating potential climate impacts on property values and borrower creditworthiness. As the mortgage market adapts, lenders may start incorporating climate-related factors into their underwriting decisions to mitigate risks associated with climate change.
Will climate change affect future mortgage lending practices?
Yes, climate change is expected to significantly affect future mortgage lending practices. As lenders recognize the systemic financial risk tied to climate change, they may adjust their underwriting criteria to account for climate risks, potentially influencing loan availability and conditions for borrowers.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Climate-driven Foreclosures | Projected bank losses of $1.21 billion this year due to climate-driven foreclosures, accounting for 6.7% of total foreclosure credit losses. |
| Impact on Credit Scores | Lenders integrating climate risk into underwriting could cause fluctuations in consumers’ credit scores based on property risk. |
| Rising Disaster Costs | The annual costs from climate-related disasters have increased by 1,580% over the past 40 years. |
Summary
Climate change mortgage is rapidly emerging as a critical factor influencing mortgage underwriting and homeowners’ financial stability. As lenders increasingly recognize the risks posed by climate change, prospective borrowers must be aware of how these evolving standards may affect their credit scores and overall mortgage eligibility. With significant increases in climate-related foreclosures and disaster costs, understanding the implications of climate risks on mortgage markets is essential for both consumers and financial institutions.