Actively Managed Bond Funds: A New Investor Strategy
Actively managed bond funds are making waves in the financial arena as investors increasingly gravitate towards safer assets in turbulent market conditions. Amid rising fears of recession, there’s been a marked shift in investor strategies, with many individuals opting for fixed-income ETFs that provide a layer of security. This trend is further amplified by the impressive performance of various actively managed funds that have successfully outperformed their index counterparts in recent evaluations. As bond market trends evolve, these funds offer alternatives to traditional fixed-income investments, allowing for nuanced bond portfolio management that can adapt to changing economic landscapes. With their focus on strategic buying bonds, actively managed bond funds are not just a trend; they’re reshaping how investors approach fixed-income investing today.
When discussing alternative investment options, one can’t overlook the importance of dynamic bond portfolios that adapt to current market conditions. Enhanced core bond funds, along with actively managed fixed-income strategies, are increasingly appealing to investors looking for tailored solutions. The growing interest in these financial products highlights a significant evolution in investor behavior, moving away from conventional passive strategies toward more hands-on approaches in bonds. As the landscape shifts, market participants are placing greater emphasis on nuanced decision-making rather than relying solely on index funds. This transformation marks a pivotal moment for those engaged in the world of bond trading, reflecting a deeper understanding of the complexities inherent in managing fixed-income investments.
The Rise of Actively Managed Bond Funds
In recent years, actively managed bond funds have gained significant traction among investors looking for flexibility and performance in their fixed-income portfolios. This shift suggests that many are reevaluating their strategies, particularly in response to fluctuating interest rates and economic uncertainties. Actively managed funds offer an opportunity for portfolio managers to adjust their holdings based on market conditions, potentially enhancing returns compared to traditional passive strategies.
Notably, the performance of these funds has been impressive during recent market volatility, as highlighted by various reports indicating that a majority of actively managed bond funds outperformed their benchmark indexes in the past year. Investors are increasingly considering strategies that incorporate active management due to the specialized knowledge and agility these funds can provide, particularly in navigating complex bond market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are actively managed bond funds and how do they differ from passive bond funds?
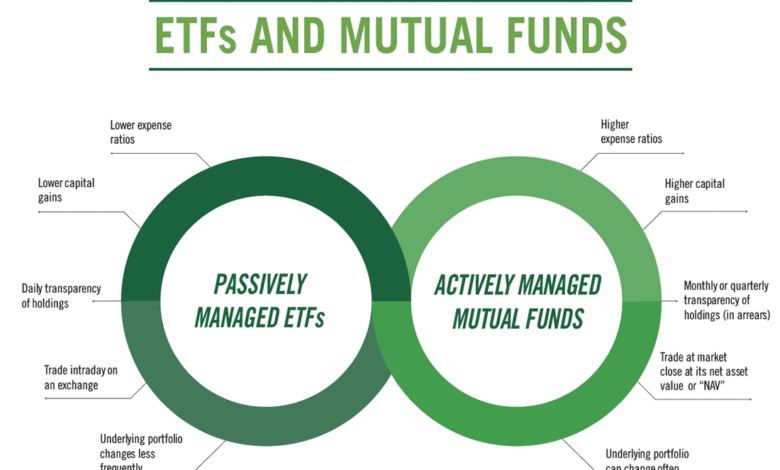
Actively managed bond funds are investment vehicles where portfolio managers make decisions on buying and selling bonds with the goal of outperforming market benchmarks. In contrast, passive bond funds aim to replicate the performance of index benchmarks without active management. This approach allows actively managed bond funds to adapt to changing market conditions, unlike fixed-income ETFs that follow a set index.
Why are investors shifting towards actively managed fixed-income ETFs?
There is a noticeable shift towards actively managed fixed-income ETFs as more investors seek to navigate the complexities of the bond market. Recent performance trends indicate that these actively managed funds have outperformed their passive counterparts, making them attractive options for investors looking for better returns while managing risks associated with fluctuating treasury yields.
What are some strategies for investing in actively managed bond funds?
Investing in actively managed bond funds typically involves strategies that focus on market trends and economic indicators, allowing portfolio managers to make informed decisions. Investors can also look for funds that emphasize bond portfolio management to balance risk and return effectively, particularly in a challenging market environment where traditional methods may not apply.
How have bond market trends affected the performance of actively managed bond funds?
Bond market trends have shown that actively managed bond funds can adapt to fluctuations more adeptly than passive strategies. For instance, during recent market turbulence, many actively managed funds were able to capitalize on market opportunities, resulting in strong performance that outstripped many passive fixed-income ETFs.
What risks should investors consider when choosing actively managed bond funds?
While actively managed bond funds can offer flexibility and potential for higher returns, investors must be aware of the risks involved. Historical data suggests that a substantial percentage of bond fund managers may underperform their benchmarks over the long term. Therefore, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and consider fund manager track records before investing.
How do actively managed bond funds fit into a balanced investment strategy?
Incorporating actively managed bond funds into a balanced investment strategy can enhance portfolio diversification and risk management. Many financial experts, including those at TCW, suggest that combining actively managed bonds with equities can help balance potential volatility, particularly as the traditional model of 60% stocks and 40% bonds gains renewed relevance.
What role do financial advisors play in the growing interest in actively managed bond strategies?
Financial advisors are increasingly advocating for actively managed bond strategies as they tend to feel more comfortable making active decisions with fixed income compared to equities. This professional guidance helps investors navigate the complexities of the bond market, making actively managed bond funds a viable option for achieving financial goals.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Demand for bonds has surged as investors turn to lower-risk options amid market crashes and fears of recession. |
| Increasing popularity of actively managed fixed-income ETFs despite concerns about their long-term performance against passive indexes. |
| Major bond ETFs like iShares Core US Aggregate Bond ETF (AGG), Vanguard’s Total Bond Market ETF (BND), and iShares 20+ Year Treasury Bond ETF (TLT) have seen significant gains. |
| Active bond funds outperformed their index counterparts across several fixed-income categories last year, suggesting a potential shift in strategy. |
| Investments in actively managed enhanced core bond funds have surpassed passive ones, highlighting a change in investor preferences in response to treasury yield fluctuations. |
| Financial advisors are increasingly comfortable making active decisions in fixed income, reinforcing the trend toward actively managed bonds. |
| Despite recent performance improvements, caution is advised as long-term statistics show that many bond fund managers fail to outperform benchmarks consistently. |
Summary
Actively managed bond funds are becoming increasingly prominent as investors seek safety in today’s volatile markets. The shift towards these strategies reflects a growing recognition of their ability to potentially outperform traditional passive options, particularly in uncertain economic conditions. With major ETFs showcasing notable gains, the trend towards active management in fixed income signals a response to evolving market dynamics and investor needs.