ECB Interest Rates: Trump’s Tariffs Complicating Future Path
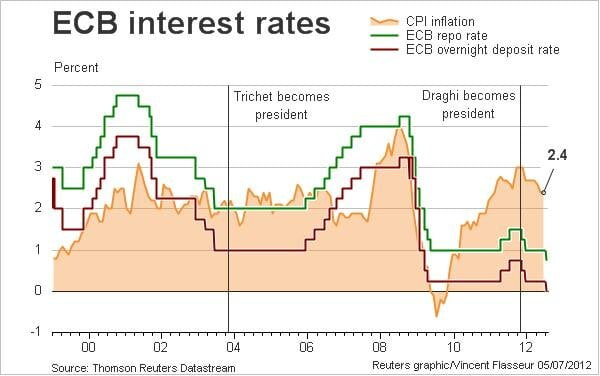
The current landscape of ECB interest rates is increasingly influenced by factors beyond the European economy, particularly U.S. President Donald Trump’s tariffs. Recent comments made by ECB Governing Council member Pierre Wunsch shed light on how these trade policies complicate the path for interest rate decisions in Europe. As Trump imposes new tariffs, including a substantial 25% on foreign automobiles, the implications for inflation impact and overall economic growth become more intricate. With the EU facing potential retaliatory measures, the dynamics surrounding trade agreements and tariffs may significantly sway the European Central Bank’s approach to monetary policy. As the ECB prepares for its next interest rate meeting, understanding the interplay between international trade and local economic conditions becomes crucial.
In examining the European Central Bank’s monetary strategies, the intersection of tariffs and interest rates plays a pivotal role in shaping economic forecasts. Recent tariff measures implemented by the U.S. administration under President Trump are raising concerns about their reverberation across European financial markets. These developments are not merely about immediate consumer prices; they delve deeper into long-term inflation consequences and growth trajectories affected by such trade regulations. As the ECB approaches its annual interest rate evaluation, the influence of external trade barriers on financial stability and economic growth necessitates a comprehensive understanding of global market responses. The evolving trade landscape demands that policymakers maintain a keen eye on how these tariffs may influence European fiscal strategies moving forward.
Impact of Trump Tariffs on ECB Interest Rates
The imposition of tariff policies by U.S. President Donald Trump is creating a ripple effect that complicates the European Central Bank’s (ECB) interest rate decisions. According to Pierre Wunsch, a member of the ECB’s Governing Council, these tariffs threaten to disrupt a carefully charted course towards monetary stability in the eurozone. With the upcoming 25% tariff on cars not produced in the U.S., along with threats of further tariffs on European allies, the implications for economic growth within the Eurozone can be severe. The uncertainty around how European economies will respond to these trade policies leads to a convoluted landscape where predicting future inflation becomes increasingly challenging for the ECB.
As Wunsch highlighted, while they initially had a constructive outlook regarding inflation becoming more predictable by 2025, the introduction of tariffs muddles this forecast. The interplay between these tariffs and ECB interest rates is pivotal, as any hike or cut may now hinge on international relations and trade dynamics rather than just domestic economic indicators.
Moreover, the ECB’s upcoming meeting on April 17 will be crucial in determining how these tariffs collectively influence their decisions. With market analysts suggesting a significant probability of a rate cut, the ECB must also weigh the potential inflationary pressures introduced by Trump’s tariff policies. If these tariffs do indeed contribute to rising prices across the Eurozone, the ECB may find itself trapped between the need to cut rates to stimulate the economy and the reality of increasing inflationary pressures. Thus, the complexity surrounding Trump tariffs adds another layer of difficulty to an already complex decision-making process for the ECB.
Trade Policies and Their Influence on Inflation
Trade policies, including President Trump’s tariffs, play a significant role in shaping inflation rates across Europe. As Wunsch mentions, these tariffs are likely to lead to a detrimental impact on growth, paired with an uncertain inflationary effect. This means businesses may encounter higher costs for imported goods, which could lead to increased prices for consumers. In a global economy interconnected through supply chains, any disruption can create downstream effects that extend well beyond the borders of the United States and directly affect Eurozone economies.
A careful analysis of these trade policies emphasizes the importance of understanding their long-term implications. While there may be short-term spikes in inflation due to the tariffs, it is essential for economists and policymakers to consider how these fluctuations will stabilize over time, especially in a context where the ECB is expected to make crucial interest rate decisions. The increased defense spending and infrastructure investments in Germany, for example, may provide an offsetting effect against potential inflationary pressures from tariffs, illustrating that the outcomes of trade policies are multidimensional.
Further complicating this landscape are retaliatory measures and the potential shifts in exchange rates that could arise from these tariffs. If the Euro strengthens in relation to the U.S. dollar, it could mitigate some of the inflationary pressures by making imports cheaper, yet this scenario remains highly speculative. Hence, policymakers must balance these external trade influences with internal economic conditions when formulating fiscal and monetary strategies. The emphasis should be on fostering stability and predictability to mitigate the adverse effects of volatile trade policies, ensuring that the Eurozone can navigate these challenges without derailing its broader economic recovery.
Future Predictions for ECB Interest Rate Decisions
Looking ahead, the European Central Bank faces a complex decision-making process regarding interest rates, particularly in the aftermath of new tariffs imposed by the Trump administration. As Wunsch noted, the ECB is keeping its options open concerning future interest rate cuts, hikes, or potential pauses. This approach reflects a growing awareness that external factors, particularly international trade dynamics, are significantly shaping the economic landscape. The upcoming ECB meeting on April 17 is viewed as critical, potentially coinciding with the implementation of these tariffs, putting the governing council in a bind regarding their policy trajectory.
The expectations for ECB rate decisions are notably influenced by the current market sentiment, suggesting a 79% likelihood of a rate cut post-tariff implementation. However, there is a growing recognition that reactive measures may not suffice if tariffs lead to persistent inflationary trends. Thus, the ECB’s challenge will lie in not only responding to immediate market pressures but also in anticipating long-term economic impacts stemming from these tariffs.
Furthermore, Wunsch’s remarks about the importance of considering trade policies underscore the necessity for the ECB to adopt a comprehensive and long-term perspective on inflation and growth. With fiscal policies in Europe undergoing transformative changes, particularly in Germany, the potential for these reforms to counterbalance the impacts of tariffs cannot be overlooked. Policymakers must remain vigilant in assessing how these dynamics can create a positive feedback loop that supports the Eurozone’s broader economic goals, thus ensuring they are prepared to make informed decisions that consider both domestic stability and the vagaries of international trade.
The Role of Fiscal Policy in Countering Tariff Impacts
In the light of Trump’s tariffs, the role of fiscal policy becomes increasingly critical in shaping the economic environment within Europe. As Wunsch pointed out, Germany’s recent policy changes—including a constitutional amendment allowing for increased defense spending and establishing a significant €500 billion infrastructure fund—represent a proactive approach to mitigating the negative impacts of U.S. tariffs. These fiscal expansions can inject liquidity into the economy, potentially supporting consumer and business confidence amidst uncertainty in international trade.
The collaborative nature of fiscal interventions at the national level could serve to bolster the effectiveness of ECB monetary policy, offering a dual-pronged approach to addressing the challenges posed by tariffs. By empowering government spending, countries can help cushion their economies against the unpredictability that trade disruptions introduce, thus supporting overall economic stability in a volatile global market.
Additionally, the uncertainty surrounding tariff impacts positions fiscal policy as a tool that can be leveraged to enhance resilience among member states in the Eurozone. As discussions around counteracting the burdens imposed by tariffs evolve, the syncing of fiscal policies across EU nations with the ECB’s monetary strategies will become paramount. By doing so, European leaders can place themselves in a favorable position, equipped to face any adverse consequences stemming from international trade dynamics while laying the groundwork for sustainable growth. This strategic alignment will be essential in offsetting any inflationary challenges that tariff policies may present.
Navigating Uncertainty: ECB’s Options Moving Forward
As the European Central Bank contemplates its paths forward amidst tumultuous U.S. trade policies, the significance of having multiple options becomes clear. Wunsch’s open stance regarding interest rates—signaling flexibility to cut, pause, or even hike—reflects an acute awareness of the unpredictability in economic reactions to tariffs. Given the current atmosphere of high uncertainty, the ability to pivot based on real-time data will be crucial in maintaining economic stability and preventing inflation from spiraling out of control. These decisions will ultimately need to account for both internal economic indicators and external trade relationships.
Moreover, the ECB must maintain vigilance with respect to how these developments might alter investor sentiment or consumer behavior. Such factors could have a cascading effect on inflation trajectories and overall economic performance. The priority, therefore, lies in fostering communication and transparency around policy decisions, all while remaining adaptable to shifts caused by external factors such as Trump’s tariffs and resulting trade tensions. Only through a comprehensive understanding of these interwoven dynamics can the ECB successfully navigate the challenges presented by current global trade policies.
Long-term Inflation Considerations in Light of Trade Uncertainties
A crucial aspect of the ECB’s strategy moving forward involves taking into account long-term inflation impacts amidst varying trade policies. Wunsch emphasized the need to adopt a long-term perspective on inflation rather than fixating merely on immediate results. The influence of tariffs on prices might set off short-term elevations, yet understanding the enduring impacts needs a more nuanced approach that considers how these inflationary pressures might stabilize in the face of evolving fiscal policies. By integrating this long-term view, the ECB can better navigate its strategies to ensure economic resilience.
Additionally, this long-term outlook encourages policymakers to explore innovative avenues for mitigating potential adverse effects from tariffs. It necessitates collaborative dialogues among EC member nations, ensuring that inflationary trends offer an opportunity for collective action. By recognizing that the immediate impact of trade policies can become more manageable through coordinated fiscal efforts, the ECB can promote stability within the eurozone and alleviate concerns about heightened inflation driven by tariffs. Ultimately, a holistic approach may yield more favorable outcomes rooted in economic cooperation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do Trump tariffs impact ECB interest rates?
Trump’s tariffs introduce complexities to the European Central Bank (ECB) interest rates by potentially slowing growth and creating inflationary pressures. According to ECB’s member Pierre Wunsch, these tariffs complicate the previously predictable rate path.
What is the current outlook for ECB interest rates amid changing trade policies?
The ECB interest rate outlook remains uncertain due to evolving trade policies, including Trump’s tariffs. As these tariffs could have inflationary effects, they may influence the ECB’s decisions when they meet on April 17.
Will inflation impact ECB interest rates as a result of tariffs?
Yes, the inflation impact from Trump’s tariffs could lead to adjustments in ECB interest rates. Wunsch mentioned that if tariffs increase inflation, the ECB may need to reconsider its rate decisions, although the exact impacts are uncertain.
What role do fiscal policies play in relation to ECB interest rates and tariffs?
Fiscal policies, like those introduced in Germany, could mitigate some impacts of Trump’s tariffs on ECB interest rates by stimulating growth, potentially offsetting inflationary pressures and thereby affecting rate decisions.
How likely is the ECB to cut interest rates given the current situation with tariffs?
Current market expectations suggest a 79% probability of a 25-basis-point cut in the ECB interest rates. However, the final decision will depend on the assessment of tariffs’ impacts and overall economic conditions.
What factors will influence the ECB’s next interest rate decision?
Factors influencing the ECB’s next interest rate decision include the effects of Trump’s tariffs on inflation and growth, recent fiscal policy changes in Europe, and overall market conditions leading up to the April 17 meeting.
Can the ECB increase interest rates despite existing tariffs?
While Pierre Wunsch noted that the chances of an increase in ECB interest rates are limited, he acknowledged that a pause in rate cuts may be plausible depending on how tariffs affect the economy and inflation.
What is the time frame for observing the impact of tariffs on ECB interest rates?
The impact of tariffs on ECB interest rates may take time to fully materialize. Wunsch emphasizes looking at long-term inflation implications rather than immediate effects, suggesting a medium-term perspective for evaluation.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Trump’s Tariff Announcements | Imposed a 25% tariff on cars not made in the U.S. and threatened higher tariffs on the EU and Canada. |
| Impact on ECB Interest Rates | Wunsch notes that tariffs complicate the ECB’s ability to set interest rates, affecting growth and inflation. |
| Market Expectations | Currently a 79% chance of a 25 basis-point cut in ECB’s interest rates expected in April. |
| Uncertainty in Effects | The ultimate impact of tariffs depends on both retaliatory actions and exchange rate responses. |
| Fiscal Policy Adjustments | Germany’s constitutional change allows for increased spending that could counteract tariff impacts. |
| Long-term Perspective on Inflation | Wunsch advises considering long-term inflation impacts rather than focusing solely on immediate results. |
Summary
ECB interest rates are under pressure due to the complex situation created by U.S. tariffs, as highlighted by Pierre Wunsch. The interplay between tariffs, growth, and inflation necessitates careful consideration as the ECB approaches its next rate decision in April. While immediate reductions may be anticipated, the ECB remains adaptable to future changes in trade and fiscal policies that could influence the economic landscape.