EU Tariffs Impact on Exports: A Threat to European Goods
The impact of EU tariffs on exports has become a pressing concern for European producers as they navigate the complexities of international trade. With the threat of a 30% import duty imposed by the U.S., businesses from Irish whiskey distilleries to Italian cheese producers are bracing for significant price increases that could cripple their U.S. market presence. The ramifications of such tariffs extend beyond individual businesses, influencing EU trade relations with the U.S. and reshaping the landscape of trade agreements. As companies adapt to these changes, many are reevaluating their supply chains and sales strategies in response to the fluctuating environment marked by Trump’s tariffs on EU goods. The uncertainty surrounding these tariffs not only threatens EU food and beverage exports, but also raises concerns over the long-term relationships between the two economic giants.
The repercussions of tariffs imposed on European goods by the U.S. have sparked intense debate about their influence on international trade dynamics. As EU manufacturers face potential increases in import duties, they are compelled to rethink their export strategies in a shifting economic landscape. Many producers are particularly anxious about how heightened tariffs on products like whiskey and food items would affect consumer prices and their bottom lines. Additionally, the ongoing challenges in EU-U.S. trade relations bring to light the delicate balance needed to foster favorable agreements. This situation presents a critical juncture for European exporters, who must now navigate not only tariffs but also the broader implications of changing market conditions.
Understanding the EU Tariffs Impact on Exports
The recent threat by the Trump administration to impose a 30% tariff on EU imports has sent shockwaves through European exporters. This potential tariff increase could radically alter the landscape of trade between the EU and the U.S., affecting everything from fine wines and spirits to essential food products. For many EU businesses, especially those reliant on exports, the prospect of such high tariffs presents a major challenge, forcing them to reassess their pricing strategies, supply chain logistics, and market targeting. With the U.S. being a crucial market, representing approximately 20-40% of sales for a significant number of EU producers, an increase in import costs could mean drastically reduced competitiveness and sales in one of their most lucrative markets.
June O’Connell’s experience with Skellig Six18 Distillery exemplifies how these tariffs threaten the viability of EU businesses aiming to expand into the American marketplace. She points out that the additional burden from tariffs would not only increase warehouse costs but would also stifle growth potential, as consumers face steeper prices. The wider implication is that these tariffs do not merely affect the exporters; they extend to American consumers who could see limited choices at elevated prices for imported goods. Consequently, this can lead to a ripple effect harming both sides of the Atlantic.
The Broader Impact of Trump Tariffs on EU Goods
The Trump tariffs have raised significant concerns regarding the future of EU goods in the American marketplace, leading to rising apprehensions among exporters. With a baseline 10% tariff already in place, businesses are now bracing for the potential increase to 30% on a broader range of products, including iconic items like Irish whiskey and Italian cheese. Companies, particularly in the food and beverage sector, have voiced their anxiety about how such price hikes will affect consumer behavior. As indicated by industry leaders, any significant uptick in import costs would likely push U.S. prices out of reach for mainstream consumers, leading to reduced sales and profitability for EU exporters.
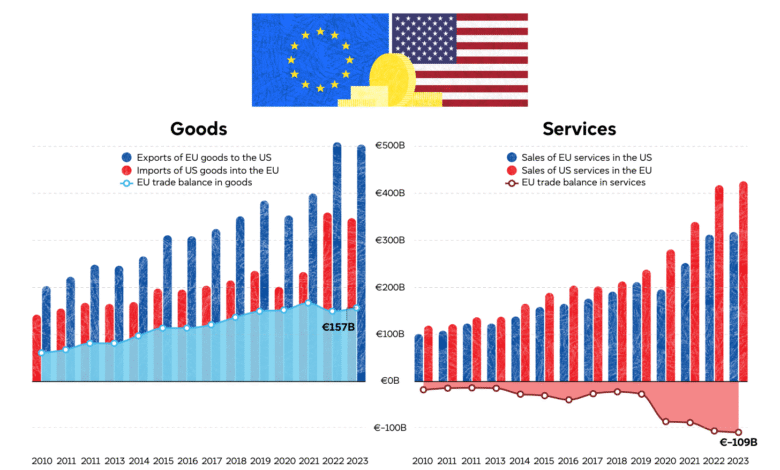
Moreover, the negative repercussions of these tariffs extend beyond price hikes; they directly impact EU trade relations with the U.S. and could lead to retaliatory measures from European governments. The EU’s food and beverage trade with the U.S. stands at nearly €30 billion, a market that could be severely threatened if tariffs escalate further. As producers navigate these turbulent waters, many are forced to rethink their export strategies—not just to retain U.S. customers, but to solidify their overall market presence in the face of potential U.S. restrictions.
Challenges for EU Food and Beverage Exports
The EU food and beverage sector has traditionally been one of the most dynamic components of transatlantic trade. However, recent tariff threats from the Trump administration pose standalone challenges for companies exporting goods, like wines, cheeses, and spirits. With tariffs already impacting profit margins, small and medium-sized enterprises find themselves at a crossroads, as they navigate market unpredictability while trying to sustain their presence in the U.S. This situation is complicated further by the intricacies of pricing, with producers facing the daunting task of adjusting their cost structures to absorb additional tariffs without losing competitiveness.
For example, Attilio Zenetti, from the Zanetti cheese company, highlights the unprecedented volatility that tariff-related developments have introduced to strategic planning. The combination of a weaker dollar has already led to a significant increase in retail prices in the U.S.; any further tariff imposition could result in cascading price hikes that might deter consumers from purchasing EU products. The fear is palpable—not just in lost revenue, but also in the potential that unchecked tariffs might undermine the hard-won relationships EU exporters have built with American customers over decades.
Understanding Import Tariffs on Whiskey and Other Spirits
Import tariffs on whiskey and other spirits from the EU have become hotly contested topics amid current trade discussions. The proposed increase to a 30% tariff represents a substantial barrier for many distilleries that rely heavily on American consumers. The U.S. market holds significant promise, especially for Irish and Scotch whiskies, where demand has been growing steadily over recent years. However, as distillers like Franck Choisne from Combier illustrate, navigating tariff landscapes is not only about safeguarding profits but also about ensuring that the core essence of their brands can be maintained amidst price instability.
The potential tariff increase is not just an abstract threat; it represents a tangible risk of diminishing sales volumes and altering the competitive dynamic within a lucrative market. Companies facing these rising costs must weigh their options carefully, which could include strategic shifts in pricing, sourcing, and even exploring new market opportunities outside of the U.S. The competitive landscape is brutal, and as distillers look for ways to ensure survival, the coherent management of tariff impacts on their operations becomes a key factor in defining their longer-term strategic resilience.
Negotiating EU Trade Relations with the U.S.
The ongoing tariff disputes have escalated concerns regarding the stability of EU trade relations with the U.S. Over the past year, the unpredictability surrounding tariff announcements has left many exporters in a state of limbo, trying to predict and prepare for the next move from Washington. While some businesses are seeking avenues to mitigate the effects, the challenge remains that trade relations are being placed under immense strain. The call for a more equitable trading relationship has never been more pronounced, yet negotiations frequently stumble over competing nationalistic interests and the complexities of existing trade agreements.
For many European industries, particularly the food and beverage sectors, the possibility of reaching a zero-tariff agreement with the U.S. could not only stabilize current relations but foster an environment of growth and mutual benefit. The EU’s vast trade surplus with the U.S. has compelled U.S. negotiators to seek concessions in various areas, but many EU producers are apprehensive about being backed into more unfavorable terms. Therefore, as negotiations unfold, it is essential for stakeholders on both sides of the Atlantic to recognize the vital importance of sustaining a balanced and productive trading relationship.
Uncertainty in Transatlantic Trade due to Tariff Dynamics
The current fluctuations in tariff policies create an environment of uncertainty for exporters on both sides of the Atlantic. Frequent changes in imposed tariffs, especially by the Trump administration, have left businesses scrambling to respond to shifting economic conditions. As companies like Skellig Six18 Distillery have shared, the challenges of contending with tariff-induced price hikes means that they must remain agile—pivoting quickly to adapt to new realities. This unpredictability stifles innovation and often results in manufacturers choosing to halt growth strategies due to the fear of increasing operational costs.
Additionally, this cloud of uncertainty affects consumer confidence as prices rise and product availability declines. For many EU goods, navigating this complex landscape requires not only a deep understanding of market demand but also agility in supply chain management. The rightsizing of operations to accommodate fluctuating import tariffs demands that businesses be prepared for both immediate challenges and long-term pressures, making strategic clarity more elusive than ever in current transatlantic trade relations.
The Role of Currency Fluctuations in Tariff Impact
Currency fluctuations significantly play into the larger narrative surrounding import tariffs. A weaker U.S. dollar has heightened costs for American importers, making EU goods less competitive even before tariffs are considered. As companies like Combier Distillery report, combined effects of currency instability and rising tariffs can lead to a staggering increase in final retail prices in the U.S., which could result in drastic sales declines. Understanding the intertwined relationships between currency dynamics and tariff impacts is crucial for EU exporters, who must strategize based on currency valuations to maintain their market position.
The challenge lies not simply in absorbing the impacts of tariffs but also in negotiating a favorable currency environment that can support pricing strategies. For many manufacturers, hedging against currency volatility becomes essential, as these fluctuations can directly influence consumer demand and purchasing behavior. Hence, in an era of rising import tariffs, grasping currency trends is as critical as negotiating favorable trade conditions, ensuring that EU exporters remain competitive in a challenging and dynamic landscape.
Strategizing Supply Chain Shifts due to Tariff Threats
In light of mounting tariff threats, many EU businesses are considering significant shifts in their supply chains to mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs. Ideal solutions often involve relocating production centers closer to the target market to avoid tariffs altogether, which may mitigate financial strains. However, such decisions carry implications for job security back in the EU and require complex re-evaluations of existing operations, with manufacturers needing to navigate what it means for their overall brand integrity.
Companies faced with impending tariff adjustments have increasingly explored relocating assembly or production operations to the U.K., where existing trade agreements allow for lower tariffs. By strategically moving parts of the supply chain, businesses hope to shield themselves from the risks associated with high U.S. import tariffs. However, this action brings its own complexities, such as establishing new regulatory compliance and ensuring quality control. Ultimately, finding the most feasible routes to continue exporting while managing costs becomes critical in the ever-evolving landscape of EU trade relations.
Long-Term Strategies for EU Exporters under Tariff Pressure
While current tariffs create immediate challenges, EU exporters are tasked with envisioning long-term strategies that ensure resilience. Focusing on diversifying markets, both in the U.S. and globally, can mitigate risks associated with reliance on any single market. As seen with producers like Skellig Six18, investing in new regions such as Asia and Latin America becomes essential not just for survival but for fostering future growth. Building a brand presence in emerging markets can provide a hedge against the turbulence coming from U.S. tariff uncertainties.
Developing long-term relationships with partners overseas also enhances stability, providing a safety net should tariffs close certain avenues in the U.S. Companies must prioritize understanding the diverse cultural and regulatory environments of new markets, allowing them to tailor their products and marketing approaches accordingly. The evolution of successful trade strategies amid changing economic landscapes can ultimately define export success in the face of price pressures and potential market instability stemming from tariffs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the effects of Trump tariffs on EU exports?
The Trump tariffs on EU exports have significantly increased import costs, particularly with a 10% baseline tariff already in place. A proposed 30% tariff would further exacerbate price increases, jeopardizing sales and profit margins for many EU businesses and leading to reduced competitiveness in the U.S. market.
How do EU tariffs impact the food and beverage sector?
EU tariffs have considerable implications for the food and beverage sector, notably affecting products like wine, whiskey, and cheese. The uncertainty surrounding tariffs deters EU producers from adequately strategizing their market entries, resulting in inflated prices for U.S. consumers and reduced sales volumes for EU exporters.
What might be the impact of tariffs on EU goods entering the U.S.?
The impact of tariffs on EU goods entering the U.S. could lead to increased retail prices for consumers and potential declines in demand, particularly for unique EU products such as Irish whiskey and Italian cheeses. This is especially pertinent with a looming threat of a 30% tariff, which could drastically impede business operations.
What are the concerns regarding import tariffs on whiskey?
Import tariffs on whiskey create substantial concerns for EU distillers, as an increase to 30% would likely trigger a significant price hike, affecting their competitiveness in the U.S. This could lead to a steep reduction in export volumes, damaging longstanding market relationships and increasing costs for American consumers.
How do EU trade relations with the US affect export tariffs?
EU trade relations with the U.S. are strained by tariff discussions, especially with the current tensions arising from Trump’s proposed tariffs. These strained relations complicate negotiations and could lead to retaliatory measures, trapping exporters in a cycle of increased costs and barriers that ultimately hinder trade.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact of Tariffs | EU exporters fear a 30% U.S. import tariff could drive prices unsustainably high, severely impacting sales. |
| Shifting Supply Chains | Some manufacturers are relocating supply chains to the U.S. or other regions, but this is not feasible for all due to specific product regulations. |
| Price Increases | Tariffs combined with a weaker U.S. dollar could increase consumer prices by up to 50%, limiting demand for EU products. |
| Economic Uncertainty | Unpredictable tariff announcements from the U.S. administration have created significant uncertainty for EU businesses. |
| Strategic Responses | EU manufacturers are exploring new markets outside the U.S. but this transition is resource-intensive and can take years. |
Summary
The impact of EU tariffs on exports has raised significant concerns among European producers, with a potential 30% tariff threatening to cripple sales in the U.S. market. As businesses like Skellig Six18 and Combier Distillery face rising costs and market uncertainties due to erratic tariff policies, many are exploring alternative strategies such as supply chain relocations and expanding into new global markets. However, these measures require time and resources, and the inherent costs associated with higher tariffs are likely to deter business growth in the meantime. The ongoing situation prompts a critical need for balanced trade negotiations to mitigate the adverse effects on EU exports.