Euro Zone Economy Expands by 0.4% in Q1 2025
The euro zone economy is showing signs of resilience as it recorded an unexpected expansion of 0.4% in the first quarter of 2025, surpassing predictions from economists who had anticipated only a 0.2% growth. This positive shift in euro zone GDP growth reflects a complex interplay of various factors, including the policies of the European Central Bank aimed at stimulating economic expansion in the euro zone. Major players like Germany reported modest gains, while smaller economies, such as Spain and Lithuania, outpaced the larger nations, contributing to the overall vigor of the region’s economic landscape. Despite ongoing concerns regarding global tariff tensions and their potential impact on economic activity, the positive momentum in the euro zone has analysts cautiously optimistic about the future. However, inflation in the euro area remains a pressing issue as the European Central Bank navigates the delicate balance between stimulating growth and managing price stability.
The economic environment of the euro zone, comprising countries that use the euro as their currency, is recently characterized by a surprising uptick in growth rates. The latest statistics reveal that this region experienced an unanticipated increase of 0.4% in its GDP during early 2025, a performance that has raised hopes amidst mixed forecasts by economists. Central to this economic turnaround is the role of the European Central Bank, which has been active in implementing measures designed to foster a robust economic climate. Notably, Germany’s economic contributions, alongside those from peripheral countries like Spain and Italy, demonstrate a diverse growth pattern that reflects the complexities of the European marketplace. As the euro area’s inflation rates hover near the bank’s targets, close monitoring is essential to ensure sustained development against the backdrop of international trade challenges.
An Overview of Euro Zone Economic Performance
The euro zone economy has showcased a resilient growth trajectory, achieving a better-than-expected expansion of 0.4% in the first quarter of 2025. This performance is a significant improvement, particularly when economists had only anticipated a 0.2% growth, reflecting an unexpected strength amidst global uncertainties. Key contributors to this growth include the performance of smaller economies within the euro area, such as Spain and Lithuania, which both reported 0.6% GDP increases, underscoring the vibrant economic expansion in these regions.
Germany’s GDP, while modest at 0.2%, remains a crucial element of the overall euro zone economic health, being the largest economy in the region. France’s contribution at 0.1% further illustrates a mixed performance across member states. As the European Central Bank continues to implement monetary policies aimed at stimulating growth, the contrasting results among euro zone nations highlight the complexity of the bloc’s economic landscape.
Impact of Global Tariff Tensions on Euro Zone Economy
The ongoing global tariff tensions have introduced significant uncertainty into the euro zone economy, affecting expectations for growth in the near future. As per economists, these tariffs, particularly those introduced by the U.S., pose a notable risk to economic expansion, potentially dampening the positive momentum observed in the first quarter. The anticipation of reduced economic activity in response to these tariffs has led analysts like Franziska Palmas to suggest a sharp slowdown in growth over the next six months.
Despite these challenges, it is essential to recognize the strategic measures being taken by the European Central Bank (ECB) to mitigate the impact of tariffs and support the euro zone economy. The ECB’s recent decision to lower interest rates aims to invigorate consumer spending and investment, creating a more favorable economic environment. However, the true test will be whether these efforts can sustain growth amid external pressures.
Analyzing Euro Zone GDP Growth Trends
The euro zone’s GDP growth has displayed fluctuations influenced by various factors, including monetary policies and external economic pressures. The recent growth figures indicate a cautious optimism, with the latest 0.4% increase providing a much-needed boost after a history of subdued performance in recent years. Economic forecasts from the ECB suggest a modest 0.9% growth target for the year, reflecting a cautious outlook in light of potential headwinds ahead.
Furthermore, the ECB’s interventions, particularly the reduction of the deposit facility rate, are crucial in aiming for higher economic activity. These measures appear to be bearing some fruit, but the sustainability of growth remains in question. Policymakers are closely monitoring economic indicators, including the upcoming inflation data release, which could affect future rate decisions and thereby influence GDP growth across the euro zone.
Germany’s Role in Euro Zone Economic Growth
As the largest economy in the euro zone, Germany significantly impacts the overall economic landscape of the region. With a GDP growth of 0.2% in the first quarter of 2025, Germany remains a barometer for the health of the euro area economy. The anticipated fiscal stimulus from the German government is expected to bolster economic activity, although its effects may be felt more strongly in the following year rather than immediately.
Despite facing challenges from trade tensions and inflationary pressures, Germany’s fundamental economic strengths provide a foundation for stability in the euro zone. Analysts underscore that, while growth has been lackluster in the past, strategic policies aimed at enhancing exports and investments could help Germany regain its growth momentum, which is critical for the entire euro zone’s economic recovery efforts.
Inflation Trends in the Euro Area
Inflation in the euro area has increasingly approached the European Central Bank’s target of 2%, indicating underlying pressures on prices despite an environment of modest economic growth. The most recent figures from March 2025 reported an inflation rate of 2.2%, reflecting the ECB’s success in managing inflationary pressures through its monetary policy tools. Such benchmarks contribute to shaping the expectations of both consumers and investors within the region.
However, maintaining inflation at target levels while also promoting economic growth presents a delicate balancing act for the ECB. As global economic conditions evolve, the central bank must navigate potential risks of rising inflation that could hinder the fragile recovery of the euro zone economy, while simultaneously attempting to support GDP growth through liquidity measures.
Projections for Future Euro Zone Economic Expansion
Looking ahead, the euro zone is poised for a mixed economic outlook in 2025, with projections indicating a growth rate of 0.9%. While this rate suggests a slight improvement, there are considerable uncertainties tied to global trade dynamics, particularly concerning U.S. tariffs. Predicting the trajectory of the euro zone economy necessitates close monitoring of these external factors, which will be critical in shaping fiscal and monetary policy responses.
Additionally, the ECB will be updating its forecasts in June, with many experts keenly watching for signals about potential shifts in monetary policy based on the evolving economic landscape. As policymakers deliberate on how best to navigate these challenges, ensuring sustainable economic expansion in the euro zone remains a top priority.
The Role of the European Central Bank in Stimulating Growth
The European Central Bank plays a pivotal role in stimulating growth within the euro zone, particularly as economic conditions fluctuate. Recently, the ECB has sought to lower interest rates to incentivize borrowing and spending, which are critical in fostering economic recovery. These actions underscore the central bank’s commitment to addressing inflation while simultaneously spurring economic activity across member states.
Moreover, the ECB’s forward-looking approach includes assessing economic indicators to guide their monetary policy decisions effectively. By monitoring growth trends and inflation data, the ECB aims to create a balanced economic environment, which is essential for the long-term stability and growth of the euro zone economy. Such proactive measures are vital as the bloc navigates through current headwinds, especially those arising from external trade pressures.
Southern European Economies and Their Growth Contributions
The performance of southern European economies has been commendable, with countries like Spain and Lithuania leading the growth charge within the euro zone. Their reported GDP increases of 0.6% in the first quarter demonstrate a significant departure from previous years marked by economic struggles. This shift not only enhances the overall economic picture of the euro zone but also highlights the potential for regional growth through diversification of economic activities.
These southern economies, often characterized by recovering tourism and improved consumer spending, serve as vital components in the economic expansion narrative. As they continue to build momentum, the contributions from these nations could prove crucial in bolstering the overall growth figures for the euro zone, countering challenges posed by larger economies and external market forces.
Challenges Facing the Euro Zone Economy
Despite recent growth figures, the euro zone economy faces several challenges that could undermine its recovery efforts. High inflation rates and trade tensions with key partners like the United States create an environment of uncertainty that complicates fiscal planning. The potential impacts of these tariffs could hinder export growth, which is critical for several euro zone countries.
Additionally, the varied performances among euro zone member states highlight economic disparities that could become more pronounced in the face of external shocks. Countries reliant on exports may find themselves particularly vulnerable, emphasizing the need for coordinated policy efforts to support balance and resilience in the region. Such challenges necessitate vigilance from both policymakers and economic stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the latest euro zone GDP growth and how does it compare to previous quarters?
The latest data shows that the euro zone economy expanded by 0.4% in the first quarter of 2025, which is stronger than the expected 0.2% growth. This follows a revised growth of 0.2% in the last quarter of 2024, indicating a slight improvement in the euro zone GDP growth trend.
How is the European Central Bank influencing the euro zone economy?
The European Central Bank (ECB) has been actively cutting interest rates to stimulate the euro zone economy. The ECB recently lowered its deposit facility rate to 2.25%, down from highs of 4% in mid-2023, aiming to boost economic expansion in the euro zone amidst ongoing challenges.
What factors are affecting economic expansion in the euro zone?
Economic expansion in the euro zone is currently influenced by global tariff tensions, particularly U.S. tariffs, which are expected to dampen growth in the coming months. Additionally, fiscal stimulus measures in Germany are anticipated to provide some support, but their impact may mostly be felt next year.
How is Germany’s economic growth impacting the overall euro zone economy?
Germany’s economic growth, which rose by 0.2% in the first quarter of 2025, plays a crucial role in the overall euro zone economy as it is the largest economy in the region. Its growth impacts collective euro zone GDP figures and is crucial for stability and confidence in the euro area.
What is the current inflation rate in the euro area and how does it relate to ECB targets?
As of March 2025, inflation in the euro area stood at 2.2%, which is close to the European Central Bank’s target of 2%. The ECB is closely monitoring inflation trends as they influence monetary policy decisions affecting the euro zone economy.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Euro Zone Growth Rate | The euro zone economy expanded by 0.4% in Q1 2025, surpassing the 0.2% forecasted by economists. |
| Germany and France GDP | Germany’s GDP rose by 0.2% and France’s by 0.1% in the same period. |
| Southern European Economies | Spain and Lithuania saw GDP growth of 0.6%, while Italy’s economic output increased by 0.3%. |
| Ireland’s Growth | Ireland’s economy grew by 3.2% in Q1, reflecting its volatile GDP due to multinational influence. |
| Future Growth Concerns | Expected growth slowdown as US tariffs imposed in April are anticipated to affect economic activity. |
| European Central Bank (ECB) Actions | ECB has reduced interest rates to boost growth; current deposit rate is 2.25%. |
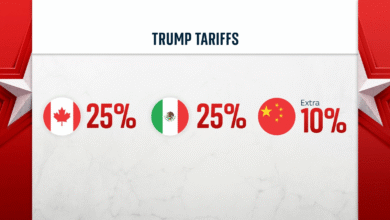
| US Tariff Impact | 20% blanket trade tariffs from the US on the EU, which may affect euro zone economic performance. |
| Economic Sentiment | Economic sentiment in the euro zone fell in April, the lowest since December 2024, despite the recent growth. |
| Inflation Rates | Inflation in the euro zone neared the ECB’s target, recorded at 2.2% in March 2025. |
Summary
The euro zone economy has demonstrated resilience with a robust 0.4% growth in the first quarter of 2025, exceeding expectations amid global trade uncertainties. Despite this positive momentum, concerns loom regarding the impact of U.S. tariffs on growth in the coming months. The economic climate remains delicate, with the European Central Bank actively attempting to stimulate the economy through reduced interest rates, while inflation rates are approaching target levels. The EU’s trade relationship with the U.S. will be a critical factor influencing the euro zone economy’s trajectory moving forward.