Federal Reserve Board Members Protection Explained
The protection of Federal Reserve board members has come into sharp focus following a recent Supreme Court ruling that indicates their special status against presidential removal. This landmark decision suggests that while President Donald Trump may have the authority to dismiss members from other federal agency boards, the same power does not extend so easily to Federal Reserve members. Indeed, Jerome Powell, the current Chairman of the Federal Reserve, has asserted that he would not resign even if asked by the president, citing legal protections that guard against such dismissals. The ruling highlights the crucial distinction in conduct regarding constitutional protections for board members and raises questions about the limits of presidential removal powers. As the Supreme Court navigates these complex issues, it is evident that ongoing debates surrounding the independence of Federal Reserve members, similar to protections afforded by the NLRB and MSPB, will continue to unfold in the public eye.
The recent Supreme Court decision illuminates the safeguarding of Federal Reserve governors within the broader context of executive power. In this discussion, the notion of robust safeguards against removal extends beyond just the Federal Reserve, touching on similar protections associated with federal regulatory bodies like the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) and the Merit Systems Protection Board (MSPB). As litigation surrounding the removal powers evolves, it raises essential inquiries regarding the capacities of the president in overseeing these independent entities. The intricacies of these legal interpretations not only emphasize the unique role of the Federal Reserve but also draw parallels with the structures that govern other federal administration members. As such, this topic serves as a critical point of contention in current political and legal spheres.
Understanding the Supreme Court Ruling Impact on Federal Reserve Members
The recent Supreme Court ruling has significant implications for Federal Reserve board members, emphasizing their unique position within the federal framework. By upholding the president’s ability to remove other federal agency members while simultaneously signaling potential protections for Federal Reserve members, the Court hints at a complex interplay between executive powers and legislative safeguards. The majority opinion highlights that while Presidential removal powers are extensive, the Federal Reserve operates under a different set of considerations that may protect its members from arbitrary dismissals.
This distinction, rooted in historical precedents, suggests that the Federal Reserve’s independence is paramount. The majority’s remarks imply that any presidential attempt to dismiss a Federal Reserve member could provoke judicial scrutiny, particularly regarding the foundational principles that govern such independent institutions. Thus, while other federal appointees may face firings without stringent oversight, those within the Federal Reserve may enjoy protections that reinforce the body’s objective of impartial monetary policy free from political pressures.
Jerome Powell’s Statement on Federal Reserve Independence
In response to the Supreme Court’s decision, Jerome Powell, the Chair of the Federal Reserve, explicitly stated that he would not step down if President Trump were to request his resignation. Powell’s assertion not only reflects his allegiance to the Federal Reserve’s independent stance but also underscores the legal protections afforded to its board members against presidential whims. This statement serves to reassure markets and stakeholders that the central bank will remain insulated from political turmoil, promoting economic stability.
Powell’s confidence in the legal framework surrounding the Federal Reserve indicates a broader commitment to maintaining its operational autonomy. By advocating for the board’s protection, Powell highlights the importance of impartiality in economic governance, especially during politically charged periods. This sentiment aligns with the dissenting opinions expressed by Justice Kagan, who firmly supports the notion that Federal Reserve members, much like those at the NLRB and MSPB, deserve protections that prevent removal without just cause.
Presidential Removal Powers and Their Limitations
The Supreme Court’s ruling deftly navigates the complexities of presidential removal powers, reaffirming that the President holds significant authority over executive officers. However, this power is not absolute; it recognizes certain limitations grounded in the Constitution and legal precedents. The majority’s opinion elucidates that while Presidents can generally fire members at will, agencies like the Federal Reserve are structured to resist arbitrary dismissals, fostering a framework where continuity and stability in governance are prioritized.
Within this landscape, understanding the constitutional underpinnings that govern federal appointments becomes crucial. The ruling indicates that while the President wields considerable power, the necessity of safeguarding independent regulatory bodies—like the Federal Reserve—is acknowledged as essential for a balanced democracy. As discussions surrounding executive authority evolve, this case will likely serve as a touchstone for future deliberations on the extent of presidential powers regarding removal and oversight of independent federal entities.
The Role of Federal Reserve’s Unique Structure
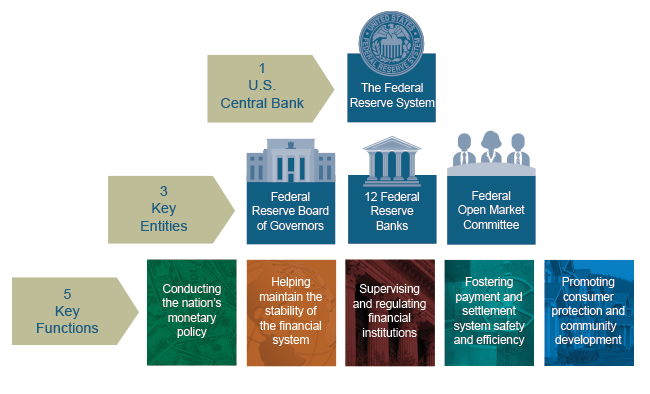
The Federal Reserve’s distinct structure is pivotal to its ability to operate independently, a trait recently emphasized by the Supreme Court’s majority opinion. This quasi-private entity is designed specifically to foster economic stability and unbiased monetary policy, drawing from historical precedents that date back to the First and Second Banks of the United States. The decision to regard the Federal Reserve as uniquely structured suggests that it functions under a different legal regime compared to other federal entities, which could influence its members’ job security.
Such differentiation raises important questions about the democratic accountability of independent agencies. Critics, including dissenting Justices, argue that labeling the Federal Reserve as special could pave the way for inconsistent legal applications, thus undermining the uniform standards established in prior rulings. The tension between preserving an autonomous Federal Reserve while ensuring accountability reflects the intricate balance required in governance where economic decisions affect the entire nation.
Implications for Other Federal Agencies: NLRB and MSPB
The implications of the Supreme Court’s ruling ripple beyond the Federal Reserve, casting a spotlight on the protections afforded to members of other federal agencies, such as the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) and the Merit Systems Protection Board (MSPB). The dissenting opinions underscore the need for legal certainty regarding the job security of individuals within these agencies, particularly when their roles are tied to upholding essential democratic principles in labor relations and civil service. This parallel highlights a broader struggle for independence among federal regulatory bodies.
As the Court navigates the delicate balance between presidential authority and agency autonomy, the future of various boards will remain uncertain. The ruling suggests potential vulnerabilities that may arise if political agendas begin to influence these agencies, threatening their ability to carry out functions vital to ensuring fair labor practices and efficient public service. Thus, the discussions surrounding NLRB and MSPB protections hold significant weight in shaping the operational landscape of federal appointments.
The Dissenting Opinion and Its Significance
Justice Elena Kagan’s dissent provides a compelling counter-narrative to the majority opinion, emphasizing that the Federal Reserve’s independence is akin to that of other bipartisan administrative entities. By arguing that the protections against presidential removal should be uniformly applied, Kagan asserts the importance of maintaining consistent legal standards across federal agencies. Her dissent challenges the majority’s characterization, suggesting that it undermines the very principles the Court should uphold.
Moreover, Kagan’s perspective underscores the need for judicial vigilance when examining the boundaries of executive power. By highlighting the potential consequences of allowing political interference in the Federal Reserve, the dissent serves as a reminder of the vital constitutional principles that safeguard against arbitrary governance. As the future landscape of executive power unfolds, Kagan’s dissent will likely be referenced as a foundational argument for advocating the preservation of checks and balances within the federal structure.
Historical Context of Federal Reserve’s Authority
The Federal Reserve’s authority and the legislative frameworks underpinning it are steeped in rich historical context. Established in the early 20th century, the Fed was created to address the inadequacies of the banking system and provide a more stable monetary environment. Over the decades, it has evolved into a formidable institution with responsibilities that span monetary policy, financial regulation, and economic stability. This historical narrative helps frame the importance of the Supreme Court’s ruling regarding the protective measures for its members.
As the Supreme Court evaluated the relationship between the President’s powers and the Fed’s independence, it drew on this contextual backdrop to understand the institution’s role. The ruling suggests that while the President’s role in executive powers remains significant, it cannot infringe upon the essential functions that the Federal Reserve performs, which are deeply ingrained in the country’s economic well-being. This recognition of historical importance emphasizes the need for maintaining the Fed’s autonomy in a rapidly changing political climate.
Future Challenges for Federal Reserve Governance
As the Supreme Court ruling settles, one must consider the future challenges facing the governance of the Federal Reserve. The intricate balance between maintaining the Fed’s independence while ensuring adequate oversight by the executive branch presents ongoing dilemmas. The ruling reinforces the notion that members of the Federal Reserve Board should enjoy protections akin to those of other independent entities, but it leaves open questions about how these protections will be enacted or challenged by future administrations.
Furthermore, the evolving political landscape necessitates a reassessment of the legal frameworks that govern such independent bodies. Stakeholders must remain vigilant to preserve the integrity of institutions like the Federal Reserve, especially in times when the intersection of politics and economic policy becomes increasingly fraught. The challenges ahead will require thoughtful dialogue and interpretation of the ruling to ensure that the Federal Reserve can continue to perform its critical roles without undue influence from political entities.
The Supreme Court’s Broader Implications for Executive Branch
The Supreme Court’s decision regarding the Federal Reserve board members is not just a pivotal moment for the Fed itself but also presents broader implications for the executive branch as a whole. By affirming the need for special protections for certain federal agencies, the Court is charting the course for how executive powers may be limited in specific contexts. This ruling sets a precedent that could influence how future courts interpret presidential authority in relation to other quasi-autonomous federal agencies.
As policymakers and legal scholars analyze the ruling, it is clear that the balance between political authority and institutional independence will be a cornerstone of future legal debates. The implications of this ruling extend beyond immediate challenges faced by the Federal Reserve, creating benchmarks for how similar cases will be adjudicated moving forward. This landscape will require constant vigilance from both the judicial system and federal agency leadership to ensure that established protections remain intact.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Supreme Court’s ruling on Federal Reserve board members protection?
The Supreme Court has indicated that Federal Reserve board members enjoy special protection against presidential removal, suggesting that any attempt by a president to fire them would encounter significant legal challenges. This ruling highlights the unique status of the Federal Reserve within federal entities.
How does presidential removal power affect Federal Reserve members?
According to the recent Supreme Court ruling, while presidents have broad removal powers over federal officials, Federal Reserve members are likely to be protected under constitutional principles that restrict their removal without just cause.
What did Jerome Powell’s statement mean for Federal Reserve board members protection?
Jerome Powell, the Federal Reserve Chairman, affirmed he would not resign if asked by President Trump, underscoring the legal protections that prevent arbitrary dismissal of Federal Reserve board members.
How does the ruling impact other federal agencies like NLRB and MSPB?
The Supreme Court ruling primarily affects the Federal Reserve’s board members, suggesting their protections differ from those of members of other federal agencies, such as the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) and the Merit Systems Protection Board (MSPB), who have faced termination challenges.
What legal precedents support Federal Reserve members protection from presidential removal?
The Supreme Court ruling referenced historical precedents that uphold for-cause removal protections for Federal Reserve members, implying a strong constitutional basis for their protection against arbitrary dismissals by the president.
What are the implications of a Federal Reserve board member being fired?
While the Supreme Court’s ruling does not explicitly prevent a presidential firing of Federal Reserve board members, it signals that such actions would likely be met with judicial scrutiny and resistance, reinforcing their protected status.
What views were expressed in Justice Kagan’s dissent regarding Federal Reserve members protection?
Justice Elena Kagan’s dissent emphasized that Federal Reserve board members are legally safeguarded against being fired without just cause, arguing for the independence of the Federal Reserve akin to other bipartisan federal agencies.
How do bipartisan administrative bodies relate to Federal Reserve members protection?
The dissenting opinion in the Supreme Court highlighted that the independence of the Federal Reserve shares core principles with other bipartisan administrative bodies like the NLRB and MSPB, suggesting a broader interpretation of protections for such entities.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Supreme Court Ruling | The Supreme Court suggests Federal Reserve board members have special protection against removal by the president. |
| Majority vs. Dissent | The decision was made with six conservative justices in favor and three liberal justices dissenting. |
| Presidential Power | While psident Trump can fire, the court indicates any effort will face legal resistance, hinting at constitutional protections. |
| Jerome Powell’s Position | Jerome Powell, the Fed chairman, affirms he wouldn’t resign if asked by Trump, noting legal protections. |
| Legal Implications | The dissent argues that the independence of the Federal Reserve is akin to other federal boards, advocating for consistent legal standards. |
Summary
The topic of Federal Reserve board members protection addresses the legal intricacies involved in the ability of a president to remove members from the board. The recent Supreme Court ruling indicates that while President Trump maintains the power to fire members from other federal agencies, Federal Reserve board members enjoy a degree of protective insulation from such executive actions. This protection is rooted in historical precedent and constitutional interpretation. The dissenting opinions underline the importance of maintaining the independence of the Federal Reserve, reinforcing the argument for consistent application of legal standards across similar governmental entities.