Federal Reserve Inflation Predictions: What to Expect in 2025
The Federal Reserve inflation predictions signal a troubling trend for the economy, with estimates suggesting inflation could surpass 3% this year. Amid these forecasts, the core personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index is expected to rise to 3.1% by 2025, reflecting greater anxiety surrounding economic policy and geopolitical tensions. Considerable shifts in inflation rate 2025 are anticipated, spurred by the impacts of Trump trade policies and global market instability. Moreover, interest rate forecasts indicate that the Fed may reduce its benchmark rate to combat inflationary pressures, even as economic growth predictions remain bleak. As central bank officials adapt their strategies, understanding these inflation predictions becomes paramount for investors and consumers alike.
When discussing the anticipated trajectory of inflation, it is crucial to consider the central bank’s forecasts regarding rising price levels, particularly those set forth by the Federal Reserve. Current estimates portray a landscape where the core PCE, a critical economic barometer, is projected to climb significantly by 2025, amidst concerns over tariff policies enacted during Trump’s administration. As experts analyze the potential implications of these economic indicators, including a slowdown in growth and shifts in interest rates, they underscore the complexity of navigating today’s volatile financial environment. The dynamic interplay of inflation expectations and government policies will play a continued role in shaping market sentiments in the coming years.
Federal Reserve Inflation Predictions for 2025
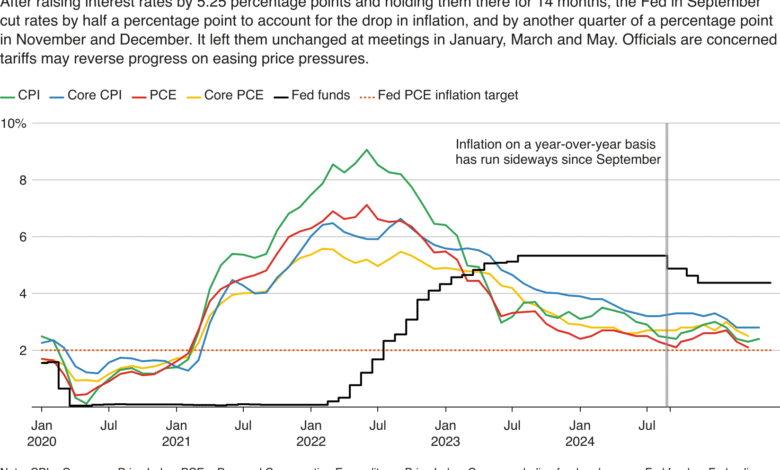
The Federal Reserve’s latest inflation predictions indicate a significant increase, with forecasts suggesting the core personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index may rise to 3.1% in 2025. This projection is notably higher than the earlier estimate of 2.8% made in March, reflecting the central bank’s response to evolving economic conditions. Analysts are particularly focused on these figures as they provide insights into the inflation rate dynamics shaped by various factors, including shifts in trade policies and global economic stability.
This anticipated rise in the inflation rate is contrasted by the PCE price index recorded at 2.1% in April, its lowest since February 2021. Fed officials argue that the core PCE is a more accurate gauge of underlying inflation trends, discounting volatile food and energy prices. However, persistent geopolitical tensions, such as the ongoing conflict in the Middle East, may complicate these predictions. If oil prices surge as a result of geopolitical instability, it could hinder the Fed’s efforts to maintain stable inflation rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Federal Reserve inflation predictions for 2025?
The Federal Reserve predicts that the core PCE price index will rise to 3.1% in 2025, higher than the previous forecast of 2.8%. This prediction reflects concerns about inflation driven by geopolitical risks and trade policies.
How does the Federal Reserve’s inflation rate forecast affect interest rate forecasts?
According to the Federal Reserve’s inflation rate forecast, which projects a core PCE of 3.1% by 2025, interest rate forecasts indicate a potential decline of the benchmark lending rate to 3.9% by the end of that year, suggesting potential rate cuts in response to inflation pressures.
What role do Trump trade policies play in the Federal Reserve’s inflation predictions?
Trump’s trade policies are influencing the Federal Reserve’s inflation predictions by contributing to increased tariffs, which Fed officials believe could drive inflation higher. This uncertainty complicates their monetary policy decisions.
What are the expected economic growth predictions from the Federal Reserve?
The Federal Reserve expects the U.S. economy’s gross domestic product to grow at a slower pace of 1.4% this year, down from an earlier prediction of 1.7%. This slowdown can impact inflation and interest rate strategies.
How might the geopolitical risks affect Federal Reserve inflation predictions?
Geopolitical risks, such as the ongoing conflict between Israel and Iran, could exacerbate inflationary pressures, influencing the Federal Reserve’s inflation predictions and decisions on interest rates.
What does the Federal Reserve’s dot plot indicate about future interest rate changes?
The Federal Reserve’s dot plot indicates officials foresee the benchmark lending rate declining to a target range of 3.75% to 4% by the end of 2025, signaling two potential rate reductions later this year.
How does the core PCE price index serve as an indicator of long-term inflation trends?
The core PCE price index, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, is used by the Federal Reserve as a preferred measure for long-term inflation trends. It is currently predicted to rise to 3.1% by 2025, reflecting underlying inflationary pressures.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The Federal Reserve anticipates inflation to rise above 3% this year due to geopolitical risks and trade policies. |
| Core PCE price index is expected to increase to 3.1% in 2025, up from 2.8% forecasted in March. |
| April’s recorded inflation was 2.1%, the lowest since February 2021; core PCE is at 2.5%. |
| GDP growth is predicted to slow to 1.4% this year, down from previous expectations of 1.7%. |
| Concerns over tariffs causing inflation have made Fed officials hesitant to cut interest rates. |
| The conflict in the Middle East could further complicate the Fed’s ability to manage inflation and growth. |
| The Federal Reserve projects a decline in benchmark lending rate to 3.9% by the end of 2025, with two cuts possibly this year. |
| Seven out of 19 participants prefer to keep rates unchanged this year, indicating a more cautious approach. |
Summary
Federal Reserve inflation predictions suggest that inflation is expected to exceed 3% this year, driven by geopolitical uncertainties and trade policies. Analysts and Fed officials are closely monitoring these developments, as they have significant implications for economic growth and interest rates. With a projected slow down in GDP growth and concerns regarding tariffs, the Fed’s approach to managing inflation will be crucial in stabilizing the economy.