Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts: Officials Reject Stability
Federal Reserve interest rate cuts have entered the spotlight as officials voice dissent regarding the central bank’s current monetary policy. With concerns swirling around the economy and labor market, two governors have advocated for a reduction in the interest rate, highlighting the risks of postponing policy easing. Their arguments emphasize that tariffs are only temporarily influencing inflation, suggesting that a proactive approach is necessary to stimulate growth. As the Federal Open Market Committee maintains its stance, these differing opinions reflect deep divisions on interest rate decisions within the Fed. The ongoing debate not only underscores the complexities involved in interest rate policy but also signals the potential for economic shifts ahead.
Recent discussions surrounding the reduction of benchmark interest rates have sparked a noteworthy debate among Federal Reserve officials. As certain members disagree with the current stance of maintaining rates steady, there emerges an urgent call for adjustments in response to economic signals. Observations regarding the transient nature of tariff impacts on inflation add a layer of complexity to the interest rate strategy. With discussions of labor market stability and overall economic health being at the forefront, the pressure mounts for the central bank to navigate its decisions wisely. This dialogue encapsulates the broader debate on how effectively the Fed can manage its monetary policy amid fluctuating economic conditions.
Understanding Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts
The Federal Reserve plays a pivotal role in shaping the economy through its interest rate policies. Interest rate cuts are crucial tools used by the Fed to stimulate economic growth, especially in times of uncertainty. By lowering rates, the Fed aims to make borrowing cheaper, thereby encouraging spending and investment amongst consumers and businesses. This approach is vital, particularly in light of rising concerns about the labor market and overall economic stability.
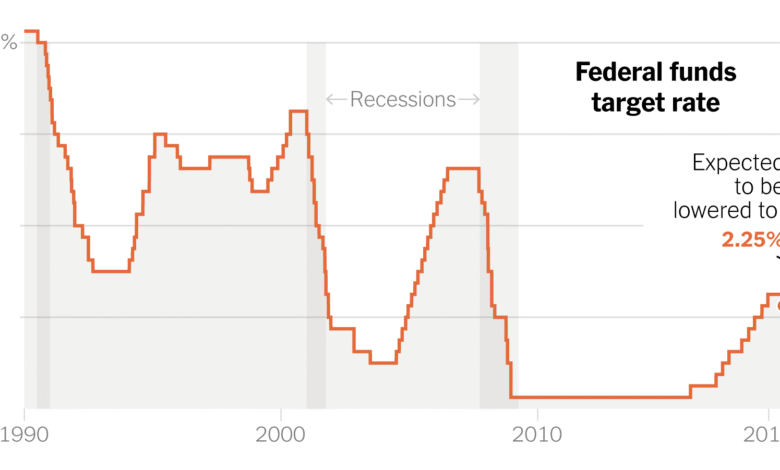
In recent discussions, Federal Reserve governors Christopher Waller and Michelle Bowman have indicated that the need for interest rate cuts has become more pressing. Their dissenting votes against maintaining current rates highlight a growing recognition that delaying policy easing could pose significant risks to economic recovery. As tariffs continue to impact inflation, the potential for rate cuts moves closer to the forefront of monetary policy discussions.
The Role of Federal Reserve Dissent in Monetary Policy
Federal Reserve dissent is not uncommon, but it can signal important shifts in monetary policy philosophy. When members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) voice differing opinions, it underscores the complexity of navigating the economy’s multifaceted landscape. Waller and Bowman’s articulated dissent represents a robust conversation regarding the impact of inflation, tariffs, and the labor market. Their insights reveal the delicate balance the Fed must maintain between inflation control and fostering economic growth.
This dynamic is crucial, especially as the Fed faces pressure from outside sources, including political figures criticizing its decisions. The debate around interest rate policy becomes central to understanding the underlying economic theories that inform these decisions. By observing dissenting voices within the Fed, economists and analysts can better grasp the intricacies of U.S. monetary policy, which plays a significant role in shaping overall economic health.
Inflation and the Tariff Impact on the Economy
Tariffs and their effects on inflation rates have become a hot topic in recent economic discussions. Both Waller and Bowman assert that the inflationary impacts stemming from tariffs are likely temporary. These tariffs, enacted as a part of broader trade policies, may have prompted short-term price increases but could present minimal lasting effects on overall inflation. The debate surrounding tariff implications emphasizes the need for the Federal Reserve to carefully analyze these variables when making interest rate decisions.
As the Fed monitors inflation readings, understanding how tariffs influence consumer prices is crucial for shaping effective policies. Governors like Bowman argue that without the current tariffs, inflation would likely fall below critical thresholds, reaffirming the idea that judicious cuts in interest rates could help stabilize the economy. Thus, reevaluating tariff impacts plays a central role in forecasting future monetary policy and interest rate adjustments.
The Relationship Between Interest Rate Decisions and Economic Growth
Interest rate decisions serve as a barometer for economic health, influencing everything from housing markets to business investments. The Federal Reserve’s approach to cutting rates is guided by the broader economic signals it receives, particularly concerning labor market trends. Waller and Bowman’s push for a moderate reduction in interest rates reflects their concern for maintaining robust growth in the face of potential downturns in the labor market, affirming the interrelatedness of these economic factors.
By implementing strategic interest rate cuts, the Fed can support not just immediate economic recovery but also longer-term growth objectives. The dynamics at play necessitate that policymakers strike a balance between responding to current economic indicators while anticipating future challenges. Decisions regarding interest rates are thus not merely reactions to prevailing conditions but are integral to setting the stage for sustainable economic vitality.
Gradual Cuts: A Considered Approach to Economic Stability
Advocating for gradual cuts in interest rates, as both Waller and Bowman suggest, exemplifies a measured approach to monetary policy. This strategy allows the Federal Reserve time to assess the implications of each reduction thoroughly, mitigating risks associated with sudden changes in the interest rate landscape. A slow pace in rate cuts translates to a more considered reflection of economic shifts, making it essential to align policy adjustments with ongoing assessments of inflation and labor market conditions.
Moreover, gradual rate reductions can help ensure that any easing measures do not inadvertently trigger destabilizing effects on the economy. The careful calibration of these cuts demonstrates the Fed’s commitment to a balanced monetary policy that seeks to promote growth while countering inflationary pressures effectively. This strategic prudence is especially important given the unpredictability of external economic factors such as tariffs and global market fluctuations.
The Impact of Political Pressure on Federal Reserve Decisions
Political pressures surrounding the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies often shape public perception and the decision-making process. High-profile criticisms, such as those from former President Donald Trump, emphasize the tensions between governmental expectations and independent monetary policy formulation. Trump’s vocal discontent with the Fed’s approach to interest rate cuts highlights the intertwining relationship between political narratives and economic decision-making.
As politicians push for rates to be lowered, the Fed must navigate these pressures while remaining committed to its dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices. The potential for political influence necessitates transparency in the Fed’s decision-making processes which can help alleviate concerns about external pressures compromising the integrity of monetary policy. This ongoing negotiation between independence and political scrutiny is key to understanding the landscape of U.S. monetary policy.
Economic Forecasting and the Role of the Federal Reserve
Economic forecasting is an essential component of the Federal Reserve’s decision-making framework, particularly when considering policies regarding interest rates. Nearby forecasts not only provide insights into inflation trends but also reveal potential shifts in the labor market, supply chain disruptions, and other relevant economic indicators. By employing a range of forecasting models, the Fed is better equipped to make informed choices regarding rate adjustments.
Furthermore, the varied perspectives among Fed officials enhance the forecasting process. Diverse opinions, as exhibited by dissenting votes, contribute to a more holistic understanding of potential economic outcomes. This multiplicity of views fosters critical discussions that ultimately lead to more adaptive and resilient monetary policies tailored to the evolving economic landscape.
The Importance of Balancing Risks in Monetary Policy
Balancing risks in monetary policy is a fundamental priority for the Federal Reserve, particularly when navigating the complexities of economic recovery. As demonstrated in Waller and Bowman’s discussions, interest rate decisions carry inherent risks that must be carefully weighed to avoid steering the economy into undue contraction. Their call for rate cuts underscores the belief that maintaining the status quo poses its own set of dangers, potentially stalling growth and exacerbating labor market challenges.
Effective monetary policy demands not only an evaluation of current data but also foresight into potential future scenarios. The Fed’s responsibility is to remain vigilant and proactive in its responses to emerging threats while leaning on data-driven analyses. Hence, finding the right balance between stimulating the economy and managing inflation remains a pivotal challenge for the Federal Reserve.
Long-term Economic Prospects Amidst Rate Adjustments
Long-term economic prospects hinge significantly on the Federal Reserve’s approach to interest rate adjustments. The decisions made today will influence economic dynamics for years, affecting everything from consumer behavior to business investment decisions. As Waller and Bowman articulate their rationale for rate cuts, they underscore the need to foster conditions that will promote sustained economic growth while carefully monitoring inflationary impacts.
In this context, the Fed’s decisions must align with broader economic objectives aiming for stability and growth. The understanding that immediate actions can have long-lasting effects underscores the importance of responsible monetary policy. Balancing the need for timely rate adjustments with a long-term vision for economic health is critical in navigating the uncertainties of both domestic and global economies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of Federal Reserve interest rate cuts on the economy?
Federal Reserve interest rate cuts can stimulate economic growth by making borrowing cheaper. When rates are lowered, businesses and consumers are more likely to take loans for investments and spending, which can drive demand and potentially boost job creation in the economy and labor market.
How could Federal Reserve interest rate cuts affect inflation?
Federal Reserve interest rate cuts typically aim to combat low inflation by encouraging spending. However, if inflation rises significantly due to external factors like tariffs, the Fed may face challenges in balancing inflation control and interest rate decisions. It’s essential to assess the lasting impacts of tariffs on prices, as temporary spikes shouldn’t dictate long-term policy.
What does it mean when Fed governors dissent on interest rate policy?
Dissent among Federal Reserve governors, such as the recent votes against keeping interest rates steady, highlights differing views on the economic landscape. It indicates a healthy debate within the Fed about interest rate policy and the need to react to changing economic conditions, especially concerning labor market threats and perceptions on inflation.
How do tariffs impact the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions?
Tariffs can influence the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions by affecting inflation and economic growth. For instance, officials argue that while tariffs increase costs, their impact on persistent inflation is temporary. Consequently, the Fed must decide whether to prioritize immediate inflation responses or consider broader economic stability when addressing interest rate cuts.
Why are some Federal Reserve officials calling for interest rate cuts now?
Some Federal Reserve officials, like Waller and Bowman, are advocating for interest rate cuts now due to concerns about the economy and labor market stability. They argue that delaying these cuts could exacerbate risks and lead to slower economic growth, viewing the current tariffs as only a temporary inflation concern.
What has President Trump said regarding Federal Reserve interest rate cuts?
President Trump has been vocal in his criticism of the Federal Reserve’s approach to interest rate cuts, urging for substantial reductions. He believes that the Fed, under Jerome Powell’s leadership, should aggressively cut rates to support economic growth and counteract the potential negative impacts of tariffs.
How do Federal Reserve interest rate cuts affect labor market conditions?
Federal Reserve interest rate cuts can have a positive impact on labor market conditions by encouraging businesses to expand and hire more employees. Lower borrowing costs can lead to increased investments, which, in turn, may improve job opportunities and wage growth within the economy.
What is the significance of the Federal Open Market Committee’s recent interest rate decision?
The recent decision by the Federal Open Market Committee to maintain interest rates is significant as it reflects the committee’s cautious approach amidst differing opinions. The dissent can signal underlying concerns regarding the impacts of tariffs on inflation and the potential risks to economic growth and the labor market.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Two Federal Reserve officials, Christopher Waller and Michelle Bowman, voted against maintaining the current key interest rate. |
| Both officials expressed concerns over delaying policy easing, citing rising threats to the labor market. |
| Waller and Bowman advocated for a quarter percentage point reduction rather than maintaining the steady rate since December. |
| They believe that tariffs only have a temporary effect on inflation and thus should not dictate long-term monetary policy decision making. |
| The Federal Open Market Committee voted 9-2 to maintain the rate amidst their dissent, the first time since 1993 this has occurred. |
| Bowman emphasized that the delay in action could harm the labor market and economic growth. |
| Trump criticized the Fed, demanding significant rate cuts, showing political pressure on the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. |
Summary
The Federal Reserve interest rate cuts are a crucial topic as dissent within the Fed emerges from key officials, Waller and Bowman, who argue that maintaining the current interest rate could jeopardize the labor market and economic growth. Their advocacy for gradual rate reductions highlights a growing concern over the effects of sustained tariffs on inflation. As the central bank navigates these challenges, the implications of interest rate policy will be vital to watch, especially amidst external pressures from political figures like Trump urging more aggressive cuts.