German Fiscal Boost: Will It Counteract Tariff Impact?
The recent German fiscal boost, characterized by increased infrastructure spending, aims to support the euro zone economy amid ongoing challenges. Despite this strategic financial injection, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) warns that the anticipated benefits may not fully offset the negative drag caused by U.S. tariffs. With the IMF’s downgraded growth outlook for the region, including a reduction of 0.2 percentage points for the euro area, Germany’s efforts face a formidable test. As highlighted by IMF official Alfred Kammer, the tensions from tariff policies greatly overshadow the positive impacts of fiscal measures. The European Central Bank (ECB) remains cautious, suggesting that only one more interest rate cut may occur this year to navigate these complexities, emphasizing the delicate balance between growth initiatives and external pressures on the economy.
Germany’s financial revitalization initiatives signify a crucial attempt to uplift the broader euro area amidst external economic pressures. This fiscal enhancement focuses on substantial infrastructure investments aimed at fostering economic stability and growth; however, it stands at risk of being undermined by the detrimental effects of transnational tariff disputes, particularly from the United States. The IMF’s latest assessment paints a concerning picture for growth in European economies, nudging forecasts downwards while acknowledging Germany’s fiscal interventions. Additionally, the ongoing advisory stance from the European Central Bank reflects a growing apprehension regarding interest rate adjustments, which could further impact economic performance. Together, these factors underline the complex interplay between national fiscal strategies and global trade dynamics in shaping Europe’s economic landscape.
Impact of U.S. Tariffs on Euro Zone Growth
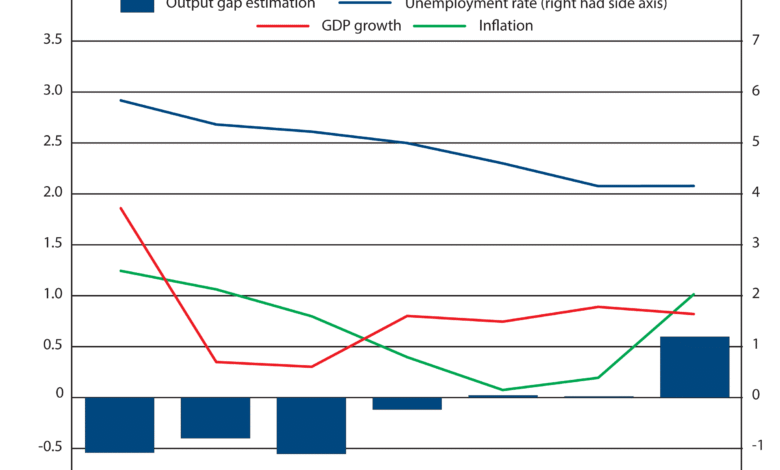
The escalating U.S. tariffs have cast a shadow over the euro zone economy, prompting the IMF to issue a stern downgrade of its growth outlook. According to recent data, the IMF has reduced its projections for the euro area by 0.2 percentage points, bringing anticipated growth down to 0.8% in 2025 and 1.2% in 2026. These adjustments reflect the widening repercussions of U.S. trade policies, which have inflicted financial strain on many countries within this economic block. Tariffs not only disrupt trade flows but also inflate costs for consumers, thus curtailing spending and further undermining economic expansion within the euro zone.
IMF officials, including Alfred Kammer, emphasize that the negative impact from the U.S. tariffs significantly overshadows any potential benefits that may arise from fiscal enhancements or infrastructure initiatives. The hesitation of businesses to invest amidst the uncertainty further complicates the economic landscape, influencing both consumer confidence and market dynamics. As a consequence, the IMF is closely monitoring these developments, suggesting that without a conducive global trade environment, the euro zone’s economic recovery remains fragile.
The Role of German Fiscal Boost in Economic Recovery
Germany’s commitment to ramping up infrastructure spending through a €500 billion climate fund could be pivotal for the euro zone’s overall growth. This fiscal boost aims to enhance investments in both physical infrastructure and sustainable projects, which have the dual potential to create jobs and stimulate economic activity. However, despite these positive intentions, experts highlight that such measures will only provide limited relief against the mounting pressure from U.S. tariffs.
Alfred Kammer pointed out that while German infrastructure initiatives might stimulate short-term economic benefits, they alone will not be sufficient to counterbalance the persistent declines caused by external trade tensions. The combination of fiscal measures and monetary policy adjustments from the European Central Bank is vital for a more robust recovery. Thus, even with increased spending, the overarching tariffs and trade disputes portray a complex challenge for Germany and the wider euro zone economy.
European Central Bank’s Response to Economic Risks
In response to the deteriorating economic conditions, the European Central Bank (ECB) has maintained an accommodative stance, despite pressure for further rate cuts. The IMF suggests that, given the current landscape dominated by U.S. tariffs’ adverse effects, the ECB may only consider implementing one more quarter-point rate cut within this year. Since mid-2024, the ECB has already reduced rates seven times, reflecting its attempts to support the euro zone economy amidst global uncertainties.
This cautious approach raises debates among economists, as the ECB’s recent decisions appear to be predominantly reactive to external pressures rather than proactive in fostering robust growth. The bank’s policy, aimed at ensuring inflation remains under control, must also contemplate the volatility introduced by trade disputes. With potential economic shocks looming, the ECB’s ability to effectively calibrate its monetary policies is crucial for stabilizing growth and protecting the euro area’s economic integrity.
Challenges Facing Emerging Euro Zone Economies
Emerging economies within the euro zone face distinct challenges amplified by both U.S. tariffs and tepid growth projections from the IMF. Countries on the periphery often rely more heavily on exports, making them particularly vulnerable to shifts in global trade dynamics. The IMF has signaled a much bleaker outlook for these emerging nations, with expected economic contractions that raise concerns over longer-term stability within the euro zone.
The disparity of fiscal resources across euro zone countries further exacerbates these challenges, as emerging economies typically lack the robust fiscal defenses seen in larger, more stable nations like Germany. This fiscal imbalance could lead to increased economic instability if trade tensions persist, emphasizing the need for cohesive fiscal strategies that support all member nations equally. Strengthening economic ties within the euro zone will thus be vital for nurturing a resilient recovery amid ongoing external pressures.
Inflation Control and Trade Tensions in Europe
The tension between managing inflation and addressing the impacts of trade conflicts poses significant hurdles for European economies. The ECB has successfully implemented measures to maintain inflation within target ranges, yet there remains a sense of unease over how tariffs and broader geopolitical uncertainties could disrupt this balance. Persistent trade tensions have potential ripple effects, driving costs up and eroding consumer purchasing power, which could thereby hinder inflation control efforts.
As highlighted by IMF observations, ongoing inflation control initiatives should remain a priority, but they must also account for the unpredictable repercussions of U.S. tariffs. The delicate balancing act involves ensuring that monetary policy adaptations do not inadvertently stifle growth while simultaneously keeping the threat of inflation muted. This juggling act will define the ECB’s roadmap in navigating the complexities of the current European economic environment.
Long-Term Implications of Increased German Military Spending
Germany’s recent decision to increase military spending marks a significant shift in its fiscal policy, with implications that extend beyond national defense. Allocations for military expenditures can stimulate local economies through job creation in manufacturing and technology sectors. Additionally, this shift reflects Germany’s commitment to international obligations, which could strengthen its geopolitical stance within Europe and beyond. However, the long-term economic impacts remain to be seen, particularly in how these funds are balanced against critical infrastructure projects.
While the focus on military spending may address immediate security concerns, critics argue that neglecting investment in economic infrastructure could prove detrimental in the long run. Infrastructure enhancements have far-reaching benefits that promote sustainable economic growth and development. As Germany navigates this transition, policymakers must evaluate how to optimize resource allocation to meet both defense requirements and the pressing infrastructure needs of the euro zone.
The Intersection of Infrastructure and Economic Growth
Investing in infrastructure is widely recognized as a catalyst for economic growth, particularly in a union as interconnected as the euro zone. Germany’s ambitious infrastructure spending aims to alleviate some of the economic pressures stemming from U.S. tariffs, presenting an opportunity for revitalizing sectors that have experienced stagnation. Improved infrastructure can enhance connectivity, reduce operational costs for businesses, and ultimately foster a more favorable business environment for both local and international enterprises.
However, the potential benefits of such investments are tempered by the stress of international trade disputes. If tariffs continue to disrupt trade flows, the positive effects of infrastructure spending may not fully materialize. Thus, while these projects signal a commitment to bolster the economy, they must be strategically complemented by addressing the external trade pressures to unlock their full potential in fostering robust growth across the euro zone.
The Euro Zone’s Path to Economic Stability Amidst Trade Disputes
Navigating towards economic stability in the euro zone amidst the backdrop of U.S. tariffs presents a complex challenge. The IMF has urged for coordinated policy actions to mitigate the detrimental effects of trade tensions and to bolster resilience against future shocks. By aligning fiscal policies with robust monetary measures, the euro zone could enhance its capacity to withstand external pressures while promoting sustainable growth.
The cooperative efforts among euro zone nations will be particularly vital in establishing a collective response that fortifies economic stability. Strategies such as shared investment initiatives and aligned monetary policies could enable countries to address vulnerabilities more effectively. In the midst of trade disputes, fostering unity within the euro zone becomes essential for navigating towards a more stable and prosperous economic future.
Assessing the IMF’s Growth Outlook for Europe
The IMF’s recent revision of growth forecasts for Europe sheds light on the economic challenges that lie ahead. With the euro area’s growth projection reduced to 0.8% by 2025, concerns over prolonged stagnation dominate the conversation. As international tensions escalate, the need for well-informed and agile policy responses is increasingly urgent. This cautionary outlook not only reflects hesitations over internal economic conditions but also highlights exogenous factors like U.S. tariffs that threaten to undermine any potential recovery trajectories.
Key stakeholders in the region must take these assessments seriously, as they serve as a wake-up call for re-evaluating economic strategies. Adapting to evolving market conditions while remaining resilient to external shocks should be a priority for policymakers aiming to revitalize the euro zone economy. Without significant shifts in approach, many countries may struggle to achieve sustainable growth in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is the German fiscal boost affecting the euro zone economy in light of U.S. tariffs?
The German fiscal boost, particularly through increased infrastructure spending, is expected to support economic growth across the euro zone. However, the impact of U.S. tariffs remains a significant concern. According to the IMF, while Germany’s initiatives could enhance growth, they may not fully counteract the adverse effects of tariffs on the euro area.
What are the IMF’s growth outlook adjustments for the euro zone due to the German fiscal boost and U.S. tariffs?
The IMF recently downgraded its growth outlook for the euro zone, now projecting growth of 0.8% in 2025 and 1.2% in 2026. This revision accounts for the limited positive impact of the German fiscal boost amidst ongoing trade tensions and U.S. tariffs that negatively affect overall economic conditions in the region.
What role does the European Central Bank play in relation to the German fiscal boost and current economic challenges?
The European Central Bank (ECB) is advised to be cautious despite the German fiscal boost, considering only one more interest rate cut this year. The ECB’s decisions are influenced by the overarching economic challenges posed by U.S. tariffs and the muted growth outlook for the euro zone.
Will the increase in infrastructure spending in Germany be enough to offset the drag from U.S. tariffs?
While the increase in infrastructure spending in Germany is pivotal for bolstering economic growth, experts, including IMF officials, indicate that it may not be sufficient to fully offset the negative impacts of U.S. tariffs. The complexities of global trade tensions weigh heavily on the euro zone’s economic recovery.
What impact do U.S. tariffs have on the IMF’s predictions regarding the euro area and the German fiscal boost?
U.S. tariffs have led the IMF to adjust its growth predictions for the euro area negatively. Despite the anticipated benefits from Germany’s fiscal boost, the report suggests that the detrimental effects of tariffs overshadow potential growth, highlighting ongoing challenges for the euro zone economy.
How does the current economic climate affect Germany’s infrastructure initiatives?
Germany’s infrastructure initiatives, supported by increased fiscal spending, are seen as crucial for stimulating economic activity. However, the current economic climate, shaped by U.S. tariffs and global trade uncertainties, puts pressure on the effectiveness of these initiatives in achieving robust growth.
What recommendations did the IMF provide to the European Central Bank regarding the German fiscal boost and euro zone growth?
The IMF recommends that the European Central Bank maintain a cautious approach to monetary policy in light of the German fiscal boost and the economic risks posed by U.S. tariffs. They suggest that the ECB consider only one additional interest rate cut this year to navigate the uncertain economic landscape.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The IMF lowered its growth outlook for the euro area, reflecting the impact of U.S. tariff policies. |
| Germany’s infrastructure spending will provide some growth support, but its effect is limited in countering tariff impacts, according to IMF’s Alfred Kammer. |
| An advisory for the European Central Bank to consider only one more interest rate cut this year amidst growth risks. |
| The IMF downgraded the growth forecast for the euro area to 0.8% in 2025 and 1.2% in 2026 due to ongoing uncertainties. |
| Kammer remarked that tariff effects overshadow the benefits of Germany’s fiscal measures, indicating a grim outlook for advanced and emerging economies in Europe. |
| Germany’s budgetary reforms allow for increased military spending and the establishment of a €500 billion infrastructure fund, which could alter the economic landscape. |
| Despite ECB’s assurances about inflation, risks remain from U.S. tariffs that could affect global economic health. |
| Kammer’s recommendation for the ECB is to maintain a 2% policy rate unless significant shocks to the economy arise. |
| Overall, while Germany’s initiatives may help, the negative impact of tariffs will likely prevent a robust euro zone recovery. |
Summary
The discussion surrounding the German fiscal boost highlights that while Germany’s efforts to enhance infrastructure spending are commendable, they may not be sufficient to negate the adverse effects of U.S. tariffs on the euro zone economy. The IMF’s insights underscore the delicate balance between fiscal initiatives and external economic pressures, indicating that the German fiscal boost will face challenges amidst a broader economic downturn. It’s essential for policymakers to navigate these complexities as they aim to foster sustainable growth.