iPhone Tariffs: Hassett States No Intent to Harm Apple
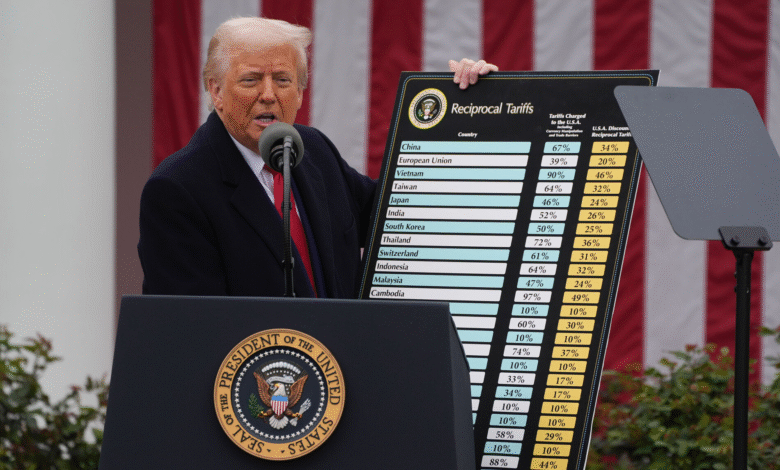
In discussions surrounding iPhone tariffs, the implications for Apple and its manufacturing practices have come to the forefront. The Trump administration, spearheaded by advisor Kevin Hassett, has made it clear that it aims not to harm Apple with the proposed tariffs, despite recent announcements of potentially sweeping tariffs on electronics produced overseas. With President Trump warning that iPhones manufactured outside the U.S. could incur a 25% tariff, many are considering how this could spike consumer prices significantly, possibly pushing U.S.-made iPhones to exorbitant prices. Hassett appeared on CNBC, arguing that the conversation about U.S. tariffs and their impact on iPhone production has been exaggerated. Ultimately, the ongoing debates hint at a pivotal moment for Apple’s manufacturing strategy, as they navigate these tariffs and their business impact with the U.S. economy in mind.
When examining the potential financial implications of tariffs on Apple products, particularly iPhones, it becomes evident that the narrative extends beyond mere taxation. Recent conversations have spotlighted how trade policies from the previous administration could affect pricing structures and production strategies in the tech industry. Many industry experts, including notable figures like Kevin Hassett, have been vocal about not wanting to impede Apple’s business, advocating for solutions that mitigate cost burdens. As discussions about imposing tariffs on imported electronics intensify, essential terms like pricing, domestic production, and economic strategies all play a crucial role in shaping the landscape for consumers. The outcome of these tariffs could redefine how technology is made and sold in the United States, stressing the importance of understanding the broader economic implications.
Understanding iPhone Tariffs Under the Trump Administration
The discussion around iPhone tariffs has become a significant issue during the Trump administration, receiving much attention from economic advisors and industry leaders alike. Kevin Hassett, the Director of the National Economic Council, highlighted that the administration’s intent is not to jeopardize Apple. By implying a tariff of 25% or higher on iPhones manufactured outside of the U.S., the government aims to incentivize Apple to localize production. This specific focus on tariffs is not merely a punitive measure; rather, it is part of a broader strategy to bolster domestic manufacturing and create jobs within the United States.
The ramifications of these tariffs could have far-reaching effects on the consumer price of iPhones. As estimates suggest, the cost of an iPhone made domestically could skyrocket to approximately $3,500, which raises concerns about affordability for the average consumer. This proposal also aligns with President Trump’s previous statements urging Apple to shift its manufacturing base from countries like India back to the U.S. Overall, the discussions surrounding iPhone tariffs reflect a complex interplay between trade policy and the realities of globalized production.
Apple Manufacturing: Balancing Costs and Compliance
Apple’s manufacturing strategies are constantly evolving, especially in light of changing political and economic landscapes. The firm is at a crossroads, needing to consider not just production costs but also the implications of U.S. tariffs on its international supply chain. As Hassett stressed, the aim of the tariffs is for companies like Apple to absorb these costs instead of passing them on to consumers. This statement simplifies a complex dilemma; while the goal is to protect American jobs and manufacturing, Apple must also ensure that its products remain competitive in a global market.
With Apple’s potential move towards increased domestic production, it is crucial to analyze the cost-benefit relationship effectively. Manufacturing iPhones in the U.S. may entail higher operational costs due to labor and resource expenditures. However, compliance with U.S. tariffs could signal to consumers and investors that Apple is committed to upholding American job growth and economic health. The ultimate challenge for Apple will be finding a balance between maintaining profit margins and adhering to the pressures imposed by the tariff regime.
Kevin Hassett’s Role in Shaping Economic Policy Regarding Tariffs and Technology
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential impacts of iPhone tariffs on Apple manufacturing?
iPhone tariffs, particularly those proposed by the Trump administration, could significantly affect Apple manufacturing. If Apple is forced to pay tariffs on iPhones made outside the U.S., the company may consider shifting production to domestic facilities to avoid these extra costs. However, as Kevin Hassett indicated, the administration does not seek to harm Apple, suggesting that the deployment of such tariffs may be moderated to prevent excessive financial strain on the company.
How would U.S. tariffs on iPhones affect their pricing?
U.S. tariffs on iPhones could lead to higher prices for consumers. For instance, Trump mentioned a possible tariff of 25% or more on imported iPhones, which could push the price of American-made iPhones to as high as $3,500. However, Hassett notes that Apple could absorb these costs, meaning they may not always be passed on to consumers, depending on Apple’s pricing strategies and production decisions.
What stance has the Trump administration taken regarding tariffs and iPhone production?
The Trump administration has taken a firm stance on iPhone production, indicating that Apple should manufacture its iPhones in the U.S. to avoid high tariffs. According to Trump, failure to comply would result in substantial tariffs on imported devices. However, Hassett emphasizes that the goal is not to harm Apple but to encourage domestic manufacturing.
Will iPhone tariffs impact the availability of smartphones in the U.S.?
While iPhone tariffs may lead to increased prices, they are unlikely to significantly affect the overall availability of smartphones in the U.S. The Trump administration’s approach, as reiterated by Kevin Hassett, aims to balance the needs of American manufacturing with market accessibility, ensuring that companies like Apple remain competitive while adapting to tariff regulations.
How do tariffs affect consumers when it comes to buying iPhones?
Tariffs can indirectly affect consumers by increasing the retail prices of iPhones. If Apple is subject to high tariffs, they may either raise prices to maintain profit margins or absorb some costs to remain competitive. Hassett pointed out that the intent is to minimize the impact on consumers, although the implications of U.S. tariffs on imported iPhones could still lead to higher life-cycle costs for buyers.
What are Kevin Hassett’s views on the exaggeration of iPhone tariff discussions?
Kevin Hassett, during his appearance on CNBC, expressed that the discussions surrounding iPhone tariffs might be exaggerated. He clarified that the Trump administration’s goal is to avoid harming Apple through these tariffs. This indicates a more measured approach to the economic implications of tariffs on iPhone production and pricing.
Could iPhone production in the U.S. lead to reduced tariffs?
Yes, producing iPhones in the U.S. could potentially reduce or eliminate tariffs imposed by the Trump administration. As emphasized by Trump, domestic manufacturing aligns with the policy goal of minimizing reliance on foreign production. Kevin Hassett mentioned that by establishing U.S. factories, Apple could circumvent the steep tariffs associated with importing iPhones, thereby stabilizing prices for consumers.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Concerns Over Tariffs | The Trump administration, represented by Kevin Hassett, emphasizes that they do not want to harm Apple with proposed tariffs. |
| Potential Tariff Impact | President Trump suggested a possible tariff of 25% or more on iPhones produced outside the U.S., significantly raising costs. |
| Cost of U.S.-Made iPhones | Estimations indicate that an iPhone manufactured in the U.S. could cost up to $3,500. |
| Trump’s Expectations | Trump has urged Apple to manufacture its iPhones in the U.S. rather than in countries like India, warning of hefty tariffs for non-compliance. |
| Burden of Tariffs | Hassett clarified that the aim is for Apple to absorb the tariff costs rather than transferring them to consumers. |
Summary
iPhone tariffs are a significant issue as outlined by Kevin Hassett, who stated that the intention behind the tariffs is not to harm Apple. The Trump administration is considering imposing substantial tariffs on iPhones manufactured outside of the U.S., which could lead to dramatically increased prices for consumers. With calls for Apple to shift production back to the U.S., the economic implications for the tech giant remain critical, and ongoing discussions highlight the delicate balance between domestic manufacturing and pricing strategies.