July Jobs Report Confirms U.S. Economy is Slowing
The July jobs report has sparked significant debate, as it highlights the alarming trend of the U.S. economy slowing sharply. With nonfarm payrolls increasing by just 73,000 positions, the report confirmed fears of a declining job growth that could signal stronger recession concerns ahead. Economic experts are now grappling with the implications of this downturn, as Goldman Sachs forecasts a mere 1% growth for the last two quarters, primarily driven by a drop in consumer spending and a decline in real income growth. While White House officials assure that the economy remains resilient, the specter of recession looms large over investors and consumers alike. As these economic indicators shift, the July jobs report serves as a pivotal moment that could redefine the trajectory of America’s economic future.
In reviewing the unsettling findings of the latest employment statistics for July, it becomes evident that the labor market is facing heightened strain. This report, which outlines the grim state of job creation, reflects broader economic challenges that include a slowdown in the U.S. economic engine. Analysts are now concerned about the potential for a downturn, given the sharp decline in consumer spending and job growth. As economic forecasts suggest a slowdown may be imminent, discussions surrounding recession anxieties and diminished job opportunities have intensified. Thus, the conversation shifts from mere statistics to the real implications these trends may have on American families and businesses moving forward.
Understanding the Implications of the July Jobs Report
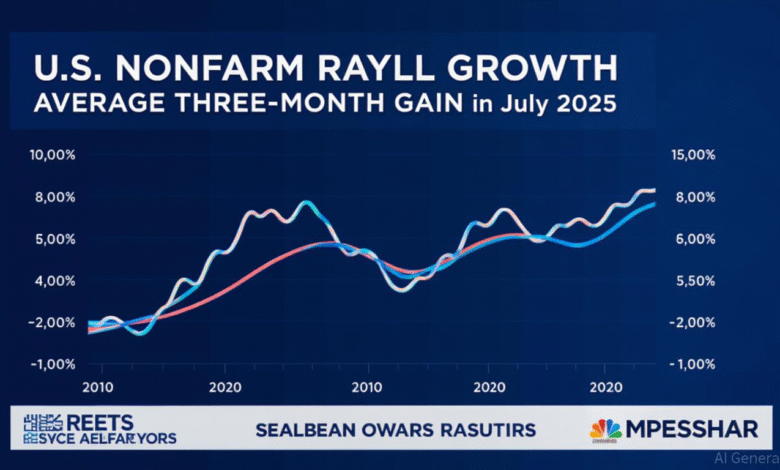
The July jobs report, which revealed a modest increase of just 73,000 nonfarm payrolls, has stirred intense discussions regarding its implications for the overall U.S. economy. This report is more than just a statistical update; it corroborates fears that the job market is stagnating amidst broader economic turmoil. With the revisions of previous months pushing the three-month average job gains down to an alarming 35,000, the labor market is demonstrating signs of wear that were previously unrecognized. Economists argue that this diminishing pace of job creation is a precursor to a potential recession, evoking concerns about the future stability of consumer spending, a critical driver of economic activity.
Moreover, as analysts dig into the numbers, they emphasize the connections between job growth decline and other economic indicators. The lesser job creation not only reflects a softening job market but signals a potential slowdown in consumer confidence, given that rising employment usually leads to increased spending. With Goldman Sachs projecting a mere 1% growth rate for the final two quarters of the year, it’s evident that apprehension about recession concerns is warranted. This interplay between employment figures and consumer behavior paints a troubling picture for the near-term economic outlook.
The Broader Economic Context and Recession Concerns
The contentious nature of the recent July jobs report aligns with increasing worries regarding the U.S. economy’s trajectory. As data points towards a deceleration in economic growth, discussions pivot to potential recession signals, suggesting that the economy may be more fragile than official rhetoric indicates. For instance, a significant drop in consumer spending, which constitutes approximately 68% of economic activity, hints at the underlying pressures prompted by a combination of steigifying net income and anxiety over tariff impacts. Economists from various institutions have echoed similar sentiments, positing that the combination of a sluggish job market and rising inflation could lead to a more pronounced decline.
Additionally, the growing tension between economic forecasts and actual performance underpins the volatility seen in financial markets. Falling factory orders and a decrease in the Conference Board’s employment trends index further reflect economic strains that policymakers must address. Evidence that consumer sentiment falters due to high mortgage rates, coupled with reduced business investment, places tremendous pressure on the Federal Reserve to evaluate monetary strategies as anxiety around recession mounts. How policymakers respond to these alarming trends will be crucial in either mitigating or exacerbating the forthcoming economic challenges.
Consumer Spending Trends and Their Economic Impact
As indicated by the July jobs report, a notable decline in consumer spending has surfaced as a critical factor affecting economic performance. With consumer expenditures barely rising by 1%, the relationship between income levels and spending habits is under scrutiny. When people are uncertain about job security or face stagnant wage growth, they tend to pull back on spending, which, in turn, exacerbates economic slowdowns. The ripple effects from lowered consumer spending can shift the balance of economic growth, leading to reduced business revenues and, ultimately, cutting jobs further — creating a detrimental cycle that threatens to engulf the economy.
This trend also juxtaposes sharply with the recent surge in GDP growth reported by policymakers, which raises questions about the sustainability of such levels in the face of rapidly declining consumer activity. While a rebound in GDP growth at a 3% annualized rate may seem promising, the underlying issues reveal a slower and more precarious real economic backdrop. Expectations that the economic landscape will strengthen once the effects of certain fiscal policies take hold are countered by looming concerns over how effective such measures will be amidst decreasing consumer confidence and increased inflation driven by tariffs.
Economic Forecasts Amid Uncertain Job Growth
In light of the recent July jobs report, economic forecasts appear murky, raising concerns about the sustainability of growth in upcoming quarters. As Goldman Sachs predicts that the U.S. economy’s expansion might dwindle to a mere 1%, the apprehension over falling job growth looms large on economic policymakers. Analysts suggest that without a robust rebound in job creation, the expected consumer spending surge may not materialize, potentially holding the economy back from traversing the path of recovery. This stagnation highlights the threats posed by persistent tariff impacts that not only inflate costs but also dampen consumer sentiment.
Compounding these issues, economists are increasingly vocal about the looming specter of a recession, with Wilmington Trust’s analysis assigning a 50% chance of such an outcome. This duality between economic forecasts and the reality reflected in key indicators raises critical questions on policy effectiveness. The challenge for government officials is to bolster confidence without losing sight of the genuine economic threats that surface from declining job growth and reduced consumer expenditure. Navigating this complex landscape of economic indicators will require foresight and adaptive strategies in policymaking.
Tariff Impact on Job Growth and Economic Performance
The imposition of tariffs has brought significant repercussions for job growth and economic performance, as underlined by the contentious nature of the July jobs report. Economists like Luke Tilley have warned that tariffs not only undermine the labor market but also limit consumer spending and investment. Tariffs may drive up costs for consumers and businesses alike, leading to diminished purchasing power that trickles through the economy, reflecting in reduced job creation and slower economic expansion. When businesses anticipate higher costs due to tariffs, they often choose to scale back hiring initiatives, resulting in a ripple effect that stymies job growth.
Furthermore, as consumer spending drops in response to inflated prices caused by tariffs, businesses may struggle to maintain growth, leading to additional layoffs or hiring freezes. The vicious cycle stemming from tariff-induced costs creates an environment of uncertainty that stifles businesses’ willingness to invest or expand. This has become increasingly apparent in sectors reliant on consumer demand, where businesses report apprehension over potential negative impacts on performance stemming from elevated operational costs engendered by tariffs. Thus, the interplay between tariffs and job growth remains a pivotal concern for the sustainability of the U.S. economy.
Market Reactions and Stock Performance in a Slowing Economy
The mounting economic concerns reflected in the July jobs report have begun to affect market sentiment, showcasing a tangible reaction within stock performance. Recent declines in major indices, including a 1.7% drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average, signal that investors are becoming increasingly cautious as recession concerns rise. The initial optimism surrounding temporary economic rebounds becomes overshadowed by the reality of continuous economic signals indicating a slowdown. Investors are now more prone to monitor employment data closely, adding another layer of complexity to trading strategies. This volatility necessitates precise calibrations by market participants who recognize that sustained economic prosperity hinges on the health of the job market.
Moreover, the response of market players is also influenced by broader economic indicators, such as factory orders and employment trends, which reveal the underlying fragility of economic growth. As the market reacts to these shifts, analysts stress the importance of a long-term perspective in navigating the financial landscape. Effectively, while short-term fluctuations can create trading opportunities, they must be balanced against the rigorous scrutiny of economic fundamentals. Understanding the economic relationship between job growth and stock performance may help investors brace for potential changes in market dynamics and align their strategies accordingly.
Policy Considerations in Response to Job Market Weakness
In response to the subdued job growth highlighted in the July jobs report, policymakers are faced with the pressing need to implement strategies that stabilize and, ideally, rejuvenate the labor market. The calls for reducing interest rates have grown louder, as financial leaders aim to lower borrowing costs and encourage both consumer spending and business investment. The intricate landscape of economic indicators emphasizes the necessity for decisive action that addresses not only job growth decline but also broader recessive pressures stemming from decelerating consumer confidence and sluggish demand.
However, effective policy measures must navigate the fine line between providing immediate relief and fostering long-term structural changes within the economy. The Trump administration’s focus on fiscal measures to stimulate jobs must be evaluated critically against tangible outcomes. As growing concerns over tariff implications complicate the policy environment, government officials must strike a balance between protecting domestic industries and preserving the consumer base. The complex interplay between various policy tools will ultimately determine the effectiveness of efforts to reverse the recent trends of job growth decline and safeguard against recession.
The Role of Economic Indicators in Assessing Growth
Amidst the unsettling implications of the July jobs report, understanding economic indicators has become paramount for gauging the trajectory of growth. Traditional measures such as GDP, unemployment rates, and consumer spending figures provide valuable insights into the overall health of the economy. Yet, as the labor market shows signs of weakening, it brings into question whether these indicators truly reflect the ongoing economic reality. Analysts highlight the importance of examining these numbers in context, considering factors such as inflation rates and global economic conditions that may skew conventional readings.
In light of this, economists advocate for a more nuanced approach to interpreting economic data, taking into account how metrics interact with each other. As job growth declines, it casts a shadow on consumer confidence and spending, essential components for fueling economic activity. Moreover, potential shifts in monetary policy should also factor into how these indicators are perceived moving forward. With a clearer understanding of the interconnected nature of economic indicators, stakeholders can better anticipate trends and prepare for potential outcomes in a fluctuating economic environment.
Navigating Future Challenges in the Job Market
Looking ahead, the challenges posed by the declining job market highlighted in the recent July jobs report require careful navigation from economic policymakers. As recession concerns become more pronounced, there is an urgent need to re-evaluate strategies that stimulate growth and employment. Analysts suggest that targeted interventions that prioritize skill development and labor market adaptability may provide pathways to bolster employment, catering to sectors adversely affected by shifting economic dynamics. The future of job growth will largely depend on collaborative efforts between the government, businesses, and educational institutions to align workforce skills with projected labor market demands.
Furthermore, employers must also play a constructive role in ensuring that the workforce remains resilient in the face of ongoing economic uncertainties. Beyond immediate hiring practices, long-term investment strategies in employee training and development are paramount to sustaining an adaptable labor force. Businesses should also engage with policymakers to advocate for sensible economic reforms that foster a conducive environment for growth. Ultimately, meeting the challenges head-on through coordinated efforts will be vital in navigating the complexities of the evolving job market in uncertain economic times.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the July jobs report indicate about the U.S. economy?
The July jobs report highlights a significant slowdown in the U.S. economy, with nonfarm payrolls rising by only 73,000 jobs. This figure is below expectations and reflects a declining job growth trend, raising concerns about potential recession.
How does the July jobs report relate to recession concerns?
The July jobs report reveals a decline in job growth, which contributes to recession concerns as economists are worried that the diminishing pace of employment may signal a broader economic slowdown.
What impact does the July jobs report have on economic forecasts?
The July jobs report impacts economic forecasts by suggesting lower growth expectations, with projections predicting only 1% growth in the final two quarters, largely due to weaker job growth and reduced consumer spending.
What are the implications of the July jobs report for consumer spending?
The July jobs report indicates a decline in job growth that may negatively affect consumer spending, which has already shown signs of a slowdown, accounting for a significant portion of economic activity.
How do revisions in earlier job reports relate to the July jobs report?
Revisions to the May and June job reports contributed to the understanding of the July jobs report. With the three-month average job growth dropping to 35,000, it highlights a concerning trend of declining employment in recent months.
What concerns does the July jobs report raise for future job growth?
The July jobs report raises concerns about future job growth, as economists note that declining trends may precipitate a recession, especially if job growth continues to weaken and consumer spending declines further.
In what way does the July jobs report reflect on the economic engine of the U.S.?
The July jobs report reflects a sputtering economic engine for the U.S., suggesting that despite previous growth in GDP, the underlying health of the economy may be deteriorating due to faltering job growth and consumer confidence.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The July jobs report confirms a slowing U.S. economy, with nonfarm payrolls rising just 73,000, below expectations. |
| Average job gains over the past three months totaled only 35,000, marking a significant decline compared to the previous year. |
| Economists express concern over consumer spending, business investment, and potential recession risks due to various economic factors. |
| Despite a recent GDP increase, growth remains weak with projections of just 1% in the next two quarters, largely influenced by tariffs and low consumer expenditure. |
| Housing market indicators are also weak, with high mortgage rates amidst overall economic uncertainty contributing to potential recession fears. |
Summary
The July jobs report highlights significant concerns regarding the U.S. economy’s health, indicating that growth may be much slower than expected. With only 73,000 new jobs created and a notable revision of past job gains, the report suggests that economic conditions could worsen in the near future. As unemployment figures and consumer spending face downward pressures, analysts warn that the economy is precariously close to a recession, reinforcing the need for careful monitoring of future employment trends.