Russia Interest Rate Cut Signifies Economic Easing
In a significant move to stimulate economic stability, the recent Russia interest rate cut marks the Bank of Russia’s first reduction since September 2022. By lowering the interest rate to 20%, down from an unprecedented 21%, the central bank signals easing inflation pressures that had been labeled “alarming” by President Vladimir Putin. This strategic adjustment comes as the inflation rate shows signs of decreasing, having dropped to 6.2% in April, compared to an average of 8.2% earlier this year. With a focus on the weakening ruble and its impacts on the Russian economy, officials have emphasized the importance of maintaining a tight monetary policy to achieve a target inflation rate of 4%. This rate cut not only reflects the latest economic indicators but also highlights the broader implications for future growth and the overall financial landscape in Russia.
The Bank of Russia’s recent decision to decrease interest rates indicates a pivotal shift in monetary practices as the nation grapples with inflation dynamics. This alteration in fiscal measures underscores the central bank’s ongoing efforts to stabilize the economy, considering the recent fluctuations in domestic demand and the performance of the ruble in global markets. The adjustments in monetary policy are crucial, especially in light of the geopolitical tensions affecting the broader economic environment. As the authorities navigate these complexities, the prospects for the Russian economy hinge on their ability to manage inflation effectively and foster sustainable growth. This latest chapter in Russia’s financial strategies reflects an evolving narrative shaped by both domestic and international challenges.
Impact of the Russia Interest Rate Cut on the Economy
The recent decision by the Bank of Russia to cut interest rates to 20% marks a significant shift in the country’s monetary policy. This move aims to alleviate some of the economic pressure stemming from high inflation rates, which President Vladimir Putin previously labeled as alarming. With inflation for April reported at 6.2%, down from an average of 8.2% in the preceding quarter of 2025, the central bank is signaling confidence in the gradual stabilization of the Russian economy. The rate cut is expected to stimulate domestic demand as consumers and businesses respond positively to lower borrowing costs.
However, this cut also comes with challenges, as the Russian economy has been navigating the effects of ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly due to the invasion of Ukraine. The depreciation of the ruble has contributed to rising import prices, complicating the central bank’s efforts to maintain effective monetary policy. Observers are keen to see how the ruble’s performance will be affected by these new measures and whether the central bank will need to adjust its strategy again if inflation begins to rise unexpectedly.
Understanding the Monetary Policy of the Bank of Russia
The Bank of Russia’s approach to monetary policy is an essential factor in maintaining economic stability amid high inflation and geopolitical unrest. Despite the recent interest rate cut, the bank has indicated that its monetary policy remains tight and will likely continue to be so for an extended period. The objective is clear: drive inflation back down to the target rate of 4%. This proactive stance by the central bank is aimed at ensuring long-term economic sustainability, even as it grapples with immediate challenges posed by the conflict with Ukraine and shifting global economic conditions.
Additionally, the Bank of Russia’s strategies are closely linked to the performance of the ruble in foreign exchange markets. As the central bank navigates these tumultuous waters, each policy decision has ripple effects not just domestically but also internationally. By maintaining rigorous control over monetary policy, the bank aims to reinforce investor confidence, which is essential for the ruble’s ongoing strength, especially as it has performed remarkably well this year against the backdrop of a volatile dollar.
Inflation Trends in the Russian Economy
Inflation has remained a critical concern for the Russian economy, particularly following the shocks related to geopolitical conflicts. After peaking earlier in the year, the inflation rate’s drop to 6.2% in April demonstrates some relief in price pressures, which the central bank attributes to a more balanced growth trajectory. However, the factors influencing inflation rates are multifaceted, and the interplay between domestic demand and supply remains crucial as the economy attempts to stabilize.
Monitoring inflation trends provides insight into the broader economic health of the nation. The Bank of Russia’s commitment to controlling inflation reflects the challenges of realigning the economy toward sustainable growth while managing external shocks. As the economic landscape continues to evolve, further adjustments in monetary policy are expected to ensure that inflation remains within acceptable limits, augmenting the central bank’s credibility and fostering trust with consumers and investors alike.
The Role of the Ruble in Global Markets
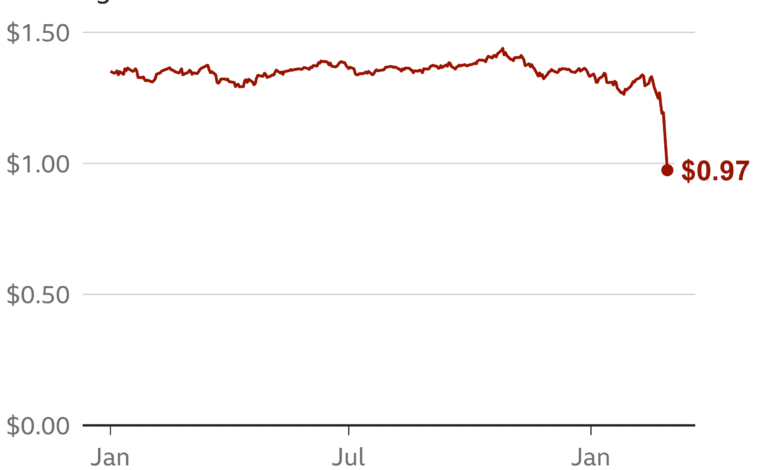
The ruble’s recent performance as one of the world’s strongest currencies has garnered significant attention, particularly in light of strict capital controls and monetary measures implemented by the Bank of Russia. Following the interest rate cut announcement, the ruble faced an uptick against the dollar, indicating a resilient response to ongoing economic pressures. The strengthening of the ruble may reflect investor confidence in Russia’s ability to navigate the current economic challenges despite the war-related sanctions and inflationary pressures.
This remarkable turnaround in ruble performance contrasts sharply with earlier predictions of its volatility following geopolitical tensions. Analysts suggest that the ruble’s resilience can be attributed to effective monetary policy and the structure of the Russian economy, which has managed to adapt during a time of crisis. How the ruble continues to perform will likely depend on global oil prices, foreign policy developments, and the central bank’s ongoing commitment to controlling inflation.
Challenges Faced by the Russian Economy Post-Invasion
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has created multifaceted challenges for the Russian economy, leading to significant adjustments in domestic policy and economic strategies. Economic sanctions have strained various sectors, making it critical for the government to find ways to manage inflation and stimulate growth despite external pressures. In response, the Bank of Russia’s recent interest rate cut aims to foster economic stability while navigating these complex issues, but the ongoing military engagement continues to overshadow recovery prospects.
Furthermore, the need to rebuild and realign the economy in the wake of geopolitical upheaval adds to the urgency of effective monetary policy implementation. As domestic demand begins to outpace supply capabilities, the central bank’s approach will be critical for fostering an environment conducive to stable growth. Future economic forecasts remain uncertain, heavily dependent on both the evolution of the conflict and the international response to Russia’s actions and policies.
The Future of Russian Monetary Policy
Looking ahead, the trajectory of monetary policy in Russia will be heavily influenced by both internal and external factors, particularly inflation and geopolitical dynamics. The Bank of Russia’s decision to cut interest rates is merely the beginning of a potentially transformative period for the country’s financial strategy. Continued inflation management will be key, as the central bank is committed to keeping the inflation target of 4% in sight, thereby ensuring economic stability in the long run.
Market reactions to these upcoming monetary policy changes will also play a critical role, as they can influence consumer confidence and spending. The Bank of Russia will need to maintain a delicate balance between fostering growth and controlling inflationary pressures amid uncertain global economic conditions. As these factors unfold, it will be essential for policymakers to remain vigilant and adaptable in their approach to ensuring Russia’s economic resilience.
Geopolitical Impacts on Economic Stability
Geopolitical tensions have not only shaped the backdrop of Russia’s economic policies but have also had direct implications on the central bank’s decisions. The ongoing issues stemming from the Ukraine conflict are forcing the Bank of Russia to implement a more conservative monetary approach while supporting the economy through challenging times. Increased military spending and trade embargoes have exacerbated inflation, complicating the already intricate monetary landscape.
As the Bank of Russia continues to navigate these tumultuous waters, strategic policy adjustments will be crucial to mitigating the impacts of external factors on the Russian economy. Ensuring stability while addressing the economic fallout from international sanctions and military engagement helps to underline the importance of effective monetary policy as a tool for resilience and recovery in an increasingly unpredictable global market.
Assessing the Current Economic Outlook for Russia
In conclusion, the economic outlook for Russia remains a topic of intense scrutiny and debate. The recent interest rate cut, alongside the declining inflation rate, suggests a possibility for cautious optimism. However, the realities of the ongoing conflict and the need for sustained economic adaptability make long-term predictions difficult. Analysts are examining both the Bank of Russia’s commitment to maintaining a stable ruble and the overarching impacts of geopolitical events on the economy.
The central bank’s decisions will undoubtedly have lasting repercussions on the Russian economy as it attempts to position itself for future growth. As the landscape evolves, close monitoring of these developments will be crucial for understanding how effectively the Russian economy can weather the storms it currently faces while striving for a return to stability and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the Russia interest rate cut indicate about the current monetary policy?
The recent Russia interest rate cut by the Bank of Russia signals a shift in monetary policy aimed at easing inflationary pressures. With rates lowered from 21% to 20%, it indicates that inflation, which was previously described as ‘alarming’ by President Putin, is beginning to stabilize. This move reflects the central bank’s attempt to balance the Russian economy while maintaining a tight monetary policy to eventually reduce inflation to the target of 4%.
How does the interest rate cut by the Bank of Russia affect the inflation rate?
The interest rate cut by the Bank of Russia is expected to influence the inflation rate positively. With the inflation rate reducing to 6.2% in April, the central bank aims to sustain this trend by adjusting its monetary policy. Lower interest rates may stimulate domestic demand, which, although currently outpacing supply, can help prepare the economy for balanced growth, further driving down inflation.
What impact does the Bank of Russia’s interest rate cut have on ruble performance?
The Bank of Russia’s interest rate cut could have mixed effects on ruble performance. While the ruble has been one of the best-performing currencies this year, the reduced interest rates may attract less foreign capital in the short term. However, the central bank’s tighter monetary policy supports the ruble in the face of ongoing geopolitical challenges, helping to stabilize its value against currencies like the U.S. dollar.
Why did the Bank of Russia decide to cut interest rates now?
The Bank of Russia decided to cut interest rates now due to signs that inflationary pressures are easing. After maintaining an exceptionally high rate of 21% since October, the central bank recognized the economic conditions were improving—indicated by the April inflation rate of 6.2%. This rate cut aligns with their objectives to promote balanced growth in the Russian economy while remaining vigilant about inflation control.
What are the implications of lowered interest rates for the Russian economy?
Lowered interest rates can stimulate investment and consumer spending in the Russian economy. With the Bank of Russia reducing rates to 20%, it aims to encourage economic growth while managing inflation. This careful adjustment reflects the central bank’s strategy to navigate the impacts of external pressures, including the ongoing conflict arising from the invasion of Ukraine, while fostering a more sustainable economic environment.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate Cut | Russia’s central bank cut interest rates by 100 basis points to 20%, the first reduction since September 2022. |
| Inflation Trends | As of April, the inflation rate is 6.2%, down from an average of 8.2% in Q1 2023. |
| Economic Recovery | The Russian economy is slowly returning to a balanced growth path despite ongoing tensions. |
| Impact of the Ukraine Conflict | The conflict has pressured prices, with a depreciating ruble increasing import costs. |
| Ruble Performance | The ruble is the best-performing currency this year, aided by capital controls and tighter policies. |
| Future Outlook | The Bank of Russia maintains a tight monetary policy to achieve a target inflation rate of 4%. |
Summary
The recent Russia interest rate cut by the central bank marks a significant shift in monetary policy amid easing inflation pressures. This decision signals a potential stabilization in the Russian economy as inflation rates decline and growth begins to rebalance. While external factors, particularly the ongoing Ukraine conflict, continue to impact economic dynamics and the ruble’s performance, the rate cut offers a glimmer of hope for long-term economic recovery. Monitoring Russia’s monetary policy will be essential in understanding its impact on both domestic and international economic conditions moving forward.