Sen. Van Hollen El Salvador Trip and Its Constitutional Implications
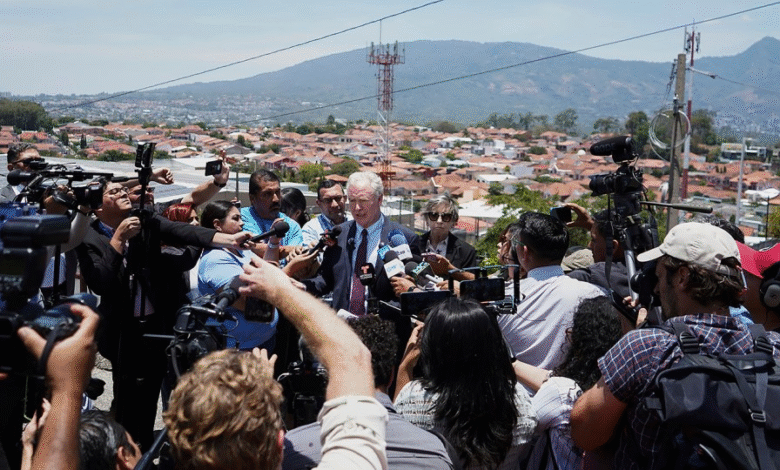

Sen. Van Hollen’s recent trip to El Salvador has sparked significant conversation about the importance of due process, particularly in the case of Kilmar Abrego Garcia, who was wrongfully deported under controversial circumstances. During his visit, Van Hollen emphasized that his mission was not to defend any individual but rather to uphold the fundamental rights that protect all citizens. With President Nayib Bukele resisting calls to return Garcia to the U.S., the Maryland senator raised alarms about the potential constitutional crisis facing the nation. He expressed concerns that denying Garcia’s due process could set a dangerous precedent that jeopardizes the rights of all Americans. By addressing these issues openly, Sen. Van Hollen seeks to amplify the critical debate surrounding the Trump administration’s handling of immigration and justice in America.
In the realm of international relations and human rights advocacy, Sen. Van Hollen’s journey to El Salvador represents a significant stance on legal protections and individual liberties. His advocacy for Kilmar Abrego Garcia, a man caught in a troubling legal predicament, highlights a broader concern regarding adherence to due process under various administrations, including that of former President Trump. Van Hollen’s dialogue around the constitutional rights at stake reinforces the notion that the safeguarding of due process is essential, not just for specific individuals, but for the integrity of American democracy as a whole. By focusing on these critical themes, the senator hopes to initiate a nationwide dialogue about the current political climate and the ramifications of a potential breakdown in the rule of law.
Sen. Van Hollen’s Mission to El Salvador: Upholding Due Process
Senator Chris Van Hollen made headlines this April with his visit to El Salvador, underscoring his commitment to protecting the fundamental rights of due process for individuals like Kilmar Abrego Garcia. During his trip, Senator Van Hollen emphasized that his purpose was not to defend any individual personally, but rather to advocate for the principles that safeguard everyone’s rights. This visit comes amidst growing concerns regarding constitutional crises in the United States and elsewhere, prompting a robust discourse around the importance of rule of law. By highlighting the injustices faced by Abrego Garcia, who was mistakenly deported, the senator seeks to bring attention to systemic issues affecting due process in immigration policy.
The visit also serves as a critical reminder of the delicate balance between governance and personal rights, as stated by Senator Van Hollen. He articulated the risk associated with denying due process to one person, which could endanger the rights of all individuals. This message resonates particularly in the context of previous actions taken during the Trump administration, where decisions about immigration and deportation were frequently criticized as lacking adherence to due process. Van Hollen’s stance challenges the narrative that political actions should overshadow foundational legal protections, amplifying his call for a robust legal framework that defends human rights universally.
The Impact of Nayib Bukele’s Policies on Human Rights
Nayib Bukele’s administration has garnered attention for its controversial policies that some critics argue may undermine human rights and due process in El Salvador. His recent statements regarding Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s deportation highlight a willingness to disregard international norms and obligations, raising alarms among human rights organizations and political figures alike. As he refuses to return Garcia to the U.S., the situation illustrates the complex interplay between domestic law enforcement and international human rights commitments, posing serious questions about the integrity of El Salvador’s judicial system under Bukele’s leadership.
Furthermore, the responses from U.S. officials, including Senator Van Hollen, to Bukele’s stance reflect an ongoing diplomatic tension. By addressing these human rights concerns publicly, Senator Van Hollen not only challenges Bukele’s policies but also aims to pressure the Trump administration to uphold its responsibility in international relations. The situation highlights the broader implications of governance shifts in Central America on the rights of individuals, as well as the critical role the United States must play in advocating for due process abroad. This advocacy is particularly necessary in contexts where leadership may lean towards authoritarianism, thereby jeopardizing democratic principles.
Challenges Ahead for Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s Return
The case of Kilmar Abrego Garcia encapsulates the myriad challenges faced by individuals caught in the crossfire of international politics and immigration policies. Despite the U.S. Supreme Court’s directives for the Trump administration to facilitate his return, the current administration’s inability to negotiate effectively raises concerns about the efficacy of legal remedies in cases of wrongful deportation. Senator Van Hollen’s interventions in El Salvador are pivotal, serving both as a plea for justice for Garcia and a critique of administrative failures that prevent due process from being realized.
Moreover, the ongoing diplomatic relationship between the U.S. and El Salvador under Bukele’s regime complicates the situation further. The refusal of Bukele to capitulate to U.S. demands indicates a potential shift in power dynamics, with El Salvador asserting more sovereignty over its immigration policies. This standoff poses significant questions about future U.S. foreign policy strategies in the region, particularly regarding how the United States will advocate for human rights when faced with intransigent leadership. As both nations navigate this complex landscape, the fate of Kilmar Abrego Garcia remains a litmus test for evaluating the commitment to due process amidst a constitutional crisis.
The Constitutional Crisis: A Broader Reflection on Democracy
Senator Van Hollen’s reflections on a potential constitutional crisis in the U.S. resonate deeply with discussions about democracy and governance. He articulates the danger of undermining individual rights as a broader threat to the constitutional framework that holds American democracy together. This concern is vividly illustrated in situations involving immigrants and due process, particularly when discussing individuals like Kilmar Abrego Garcia, who has become emblematic of the struggles many face under polarizing political climates. Van Hollen’s perspective sheds light on the importance of an active and engaged citizenry in defending democratic principles.
As public discourse channels through the ramifications of recent administrations, it prompts a reevaluation of the safeguards in place designed to protect civil liberties. The implications of a constitutional crisis extend far beyond legal interpretations and touch upon the very fabric of civic responsibility and ethical governance. By speaking out, Senate Van Hollen aligns his advocacy not only with immediate humanitarian concerns but also with long-term visions for a more just society. In grappling with the legacies of previous administrations and ongoing political tumult, the emphasis remains on the necessity for consistent advocacy for due process and accountability.
U.S. Responses to Human Rights Violations in Latin America
The ongoing issues surrounding human rights violations in Latin America, specifically in El Salvador, necessitate a reevaluation of the U.S. approach to foreign relations and policy-making. Historically, the United States has grappled with its role as a protector of human rights internationally, yet interpretations and implementations of this role have often fluctuated. Senator Van Hollen’s recent trip to El Salvador illustrates a recommitment to these values, focusing on the legal and ethical responsibilities of the U.S. in relation to allies that may diverge from democratic norms, notably under leaders like Nayib Bukele.
Moreover, the implications of the previous Trump administration’s value-driven rhetoric often contrasted sharply with the realities on the ground, emphasizing a critical disconnect between policy initiatives aimed at fostering democracy and the actual promotion of civil liberties. This highlights the challenges faced by current lawmakers, like Senator Van Hollen, in their efforts to reconstruct an image of U.S. foreign policy that prioritizes human rights, particularly amidst complex relationships fraught with historical tensions. By addressing the issues faced by individuals such as Kilmar Abrego Garcia, U.S. legislators can serve as catalysts for change within an international context, advocating for accountability and lawfulness that transcend borders.
Kilmar Abrego Garcia: A Case Study in Immigration Policy
Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s ordeal serves as a poignant case study in the discussions surrounding U.S. immigration policy and the rights of detained individuals. His wrongful deportation underscores significant failures in the legal system and raises fundamental questions about due process in immigration enforcement. As Senator Van Hollen asserts the need to protect the constitutional rights of Abrego Garcia, this situation illustrates the broader failures in a system that should ideally safeguard every individual’s legal rights and humanity, regardless of their immigration status.
Additionally, Garcia’s case challenges the effectiveness of current immigration policies under both the Trump administration and subsequent administrations, drawing attention to the need for comprehensive reform that prioritizes fairness over political expedience. The U.S. commitment to human rights must extend beyond rhetoric; it necessitates actionable policies that rectify past injustices and allow for a more humane response to individuals in similar predicaments. By taking a firm stance on Garcia’s case, Senator Van Hollen not only advocates for his return but also urges a necessary reconsideration of a system that impacts countless lives.
The Importance of Advocacy in Immigration Cases
Advocacy plays a critical role in shaping the dialogue around immigration and human rights. Senator Van Hollen’s commitment to speaking out for Kilmar Abrego Garcia exemplifies how individual cases can galvanize broader movements for reform. His visit to El Salvador signifies a commitment to ensuring that voices of the marginalized are heard, especially in contexts where they may face systemic injustices. The senator’s efforts also serve as a blueprint for how policymakers can actively engage with communities to address rights violations and push for accountability.
Through effective advocacy, more attention can be brought to pressing issues such as wrongful deportation and the need for adherence to due process. This can lead to tangible changes in policies that often appear rigid and unyielding. Moreover, it emphasizes the importance of community involvement in advocating for human rights, as collective voices can influence political decisions that shape the future of immigration law. Ultimately, the advocacy exemplified by Senator Van Hollen is not merely about individual cases; it reflects a broader commitment to safeguarding democracy and the principles of justice that should be upheld for all.
U.S. Foreign Policy: Navigating Tensions with Latin American Leaders
U.S. foreign policy towards Latin America has become increasingly complex, particularly as leaders like Nayib Bukele challenge traditional diplomatic practices. The interactions between the United States and El Salvador highlight the tensions that arise when U.S. interests conflict with the governance styles of foreign leaders. As Senator Van Hollen navigates these waters during his visit, he reflects on the essential need for diplomacy that respects human rights and due process while also being effective in achieving strategic objectives.
The challenges posed by Bukele’s administration, characterized by a more confrontational style, require U.S. lawmakers to engage thoughtfully and strategically. Building cooperative relationships necessitates addressing human rights concerns openly, as exemplified by the conversations surrounding Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s situation. Upholding shared democratic ideals becomes not only a matter of principle but a necessary approach to maintaining stability and fostering mutual respect and understanding between nations. As tensions with Latin American leaders continue to evolve, the examination of U.S. responses will undoubtedly shape future diplomatic engagements.
Importance of Due Process in the Current Climate
Due process is a cornerstone of any just legal system and holds particular significance in the context of current debates about immigration and civil rights. Senator Van Hollen’s emphasis on defending the due process rights of individuals like Kilmar Abrego Garcia offers critical insights into the prevailing challenges faced in the U.S. legal system. In light of recent political climates and actions taken by various administrations, the call for steadfast adherence to due process becomes imperative in ensuring that justice prevails for all individuals, irrespective of their status.
The stakes surrounding due process are especially elevated during periods characterized by constitutional uncertainty, as highlighted by Senator Van Hollen’s observations about a possible constitutional crisis in the U.S. His advocacy for individuals facing the brunt of erroneous policies reflects a broader urgency for lawmakers to prioritize fundamental rights amidst shifting political landscapes. By spotlighting these issues, Senator Van Hollen encourages an ongoing discourse about the necessity of restoring credibility to the legal system while advocating fiercely for the rights of those who are often voiceless in the face of bureaucratic challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the purpose of Sen. Van Hollen’s trip to El Salvador in relation to Kilmar Abrego Garcia?
Sen. Van Hollen’s trip to El Salvador was focused on advocating for the right to due process for Kilmar Abrego Garcia. He emphasized that his mission was to uphold the rule of law and not to defend the individual personally.
How did Sen. Van Hollen describe the constitutional crisis in relation to his trip to El Salvador?
During his various media appearances, Sen. Van Hollen confirmed that the U.S. is facing a constitutional crisis, particularly highlighting concerns about the treatment of individuals like Kilmar Abrego Garcia and the implications it has for civil rights overall.
What did Sen. Van Hollen say about the Trump administration’s role in Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s case?
Sen. Van Hollen criticized the Trump administration for its handling of Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s deportation, noting that the administration has previously admitted in court that Garcia was wrongfully detained and deported, which raises serious concerns about due process.
Why is Kilmar Abrego Garcia significant in discussions about due process and constitutional rights during Sen. Van Hollen’s El Salvador trip?
Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s case is significant because it illustrates the broader implications of due process rights in the U.S. Sen. Van Hollen pointed out that undermining Garcia’s rights threatens the constitutional rights of all Americans, making this case a focal point for discussions during his El Salvador trip.
What were the conditions Kilmar Abrego Garcia faced that prompted Sen. Van Hollen’s intervention?
During his visit, Sen. Van Hollen described the trauma Kilmar Abrego Garcia experienced during his imprisonment in El Salvador, including being held in a notorious prison. These conditions were a critical part of why the senator advocated for Garcia’s right to due process.
What stance did President Nayib Bukele of El Salvador take regarding Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s return to the U.S.?
President Nayib Bukele stated that he would not allow Kilmar Abrego Garcia to return to the U.S., which complicates legal and diplomatic discussions and frames the context for Sen. Van Hollen’s trip.
How did Sen. Van Hollen’s visit to El Salvador reflect U.S. foreign policy concerns?
Sen. Van Hollen’s visit illustrated U.S. concerns about human rights and due process in foreign policy, especially under the Trump administration’s approach that many viewed as flouting judicial rulings regarding individual rights.
What impact did Sen. Van Hollen hope to achieve through his trip to El Salvador?
Sen. Van Hollen hoped to raise awareness about due process rights for individuals like Kilmar Abrego Garcia and to pressure the U.S. government to adhere to judicial directives, thereby reinforcing the rule of law and constitutional rights.
| Key Point | Detail |
|---|---|
| Purpose of the Trip | Sen. Van Hollen’s visit aimed to advocate for Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s due process rights. |
| Meeting with President Bukele | Bukele stated he would not return Kilmar Abrego Garcia to the U.S. |
| Constitutional Crisis | Van Hollen affirmed the U.S. is in a constitutional crisis regarding wrongful detentions. |
| Defense of Due Process | The senator emphasized that upholding due process is crucial as it affects everyone’s rights. |
| Trauma of Abrego Garcia | Van Hollen described Garcia’s experience of trauma from both abduction and imprisonment. |
| Trump Administration’s Approach | The administration has admitted to wrongfully detaining and deporting Garcia. |
| Future Legal Complications | Van Hollen warned that denying rights to one could jeopardize rights for all. |
Summary
Sen. Van Hollen’s trip to El Salvador was focused on the critical issue of due process for Kilmar Abrego Garcia. During his visit, he highlighted the alarming situation regarding constitutional rights being at risk in the U.S. Van Hollen’s advocacy underscores the importance of protecting individual rights, which if ignored, could lead to broader implications for civil liberties nationwide.