Databricks Revenue Growth Set to Hit $3.7 Billion by July
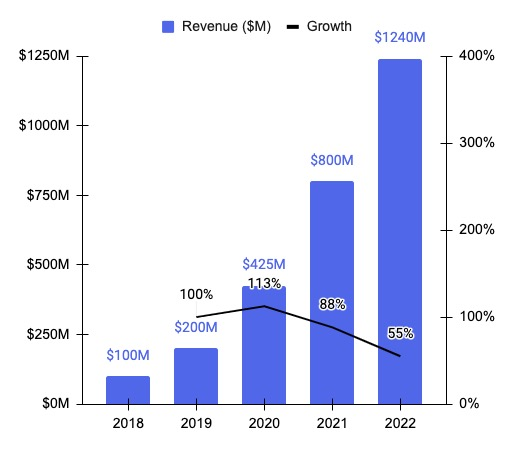
Databricks revenue growth continues to capture the attention of investors and analysts alike, as the company projects an impressive annualized revenue of $3.7 billion by July, representing a remarkable year-over-year growth of 50%. This announcement was made by CFO Dave Conte during the highly anticipated Data and AI Summit in San Francisco, where key industry players gathered to discuss advancements in data analytics software. With the financial landscape shifting rapidly, Databricks is looking to intertwine robust revenue growth with swift product innovation while achieving profitability. As part of its strategic vision, the company is poised to engage a broad base of Databricks customers, with many exceeding $10 million in annual spending. Amidst stiff competition from peers like Snowflake, all eyes are on Databricks as it gears up for potential milestones, including a future IPO that could redefine its market presence.
In recent times, the surge in Databricks’ financial performance has been notable, with projections indicating a significant uptrend in annual revenue reaching $3.7 billion by mid-year. This reflects a staggering growth rate of 50% year-over-year, a factor highlighted by CFO Dave Conte at the company’s annual gathering, the Data and AI Summit in San Francisco. Databricks, recognized for its advanced data analytics capabilities, aims to balance aggressive financial scaling with rapid technological advancements. Their commitment to customer satisfaction resonates through their strategies to cater to an expansive clientele, some of whom invest over $10 million annually. As the tech sector buzzes with discussions of Databricks, particularly regarding its upcoming IPO and innovations like the Lakebase database software, stakeholders remain keenly focused on the firm’s evolving market dynamics.
Databricks Revenue Growth: A Promising Future
Databricks has reported impressive revenue projections, with annualized earnings expected to reach $3.7 billion by July 2025. This reflects a remarkable year-over-year growth rate of 50%, indicating the company’s strong positioning in the data analytics space. This growth is attributed to its innovative approaches, including the recent enhancements announced at the Data and AI Summit in San Francisco, where CFO Dave Conte emphasized their focus on profitability alongside rapid product development.
This anticipated revenue growth places Databricks in a competitive position against industry giants. For instance, its closest competitor, Snowflake, currently boasts a market capitalization exceeding $70 billion with annualized revenue greater than $4 billion. However, Databricks’ net retention rate has remained above 140%, demonstrating its strong customer loyalty and satisfaction, which are key indicators of future growth.
Unearthing Databricks IPO Potential
Although currently not publicly traded, the anticipation surrounding a potential Databricks IPO is palpable among investors. The company has established itself as a frontrunner in data analytics software, ranking third on CNBC’s Disruptor 50 list, only behind innovative firms like Anduril and OpenAI. Given that it has raised an impressive $10 billion with a valuation of $62 billion, many see Databricks as a prime candidate for an IPO in the near future.
The CFO, Dave Conte, has refrained from providing a timeline for the IPO, but with their robust revenue and a growing customer base, the company is arguably in a prime position to consider this significant step. Analysts speculate that any move towards an IPO could further validate its strategic initiatives, especially as it continues to harness advancements in AI and data analytics.
Innovation at the AI Summit 2024
At the recent AI Summit 2024, Databricks showcased its forward-thinking approach to data analytics. By unveiling features related to its new Lakebase database software, which notably stems from their acquisition of Neon, Databricks aims to broaden its market scope. This suite of innovations demonstrates the company’s commitment to integrating advanced AI capabilities into its offerings, making data management easier for its enterprise customers.
The announcements made at the summit were met with enthusiasm from the investor community, as they are expected to drive further user engagement and acquisition. As businesses increasingly rely on data analytics for competitive advantage, Databricks is positioning itself as a critical player in this evolving landscape.
The Expanding Customer Base of Databricks
With over 15,000 customers, Databricks has built a diverse and extensive client base that drives its impressive growth trajectory. Remarkably, nearly 50 of these customers are spending over $10 million annually, underscoring the value Databricks provides to its users. This level of customer investment showcases a strong demand for their data analytics solutions, indicating that Databricks has established itself as a trusted partner in the enterprise data sector.
Moreover, the company maintains a net retention rate above 140%, suggesting that once customers are onboard, they tend to deepen their usage of Databricks products. This loyalty not only contributes to stable revenue but also highlights the effectiveness of Databricks’ customer success strategies.
Competitive Landscape: Databricks vs. Snowflake
As Databricks continues to solidify its market position, it faces stiff competition from Snowflake and other cloud providers that offer data warehousing software. While Snowflake currently leads in terms of market capitalization, Databricks’ rapid growth and significant funding present an exciting challenge. With continued innovation, such as the new features introduced at the AI Summit, Databricks is poised to capture a larger segment of the market.
Additionally, Databricks’ focus on integrating advanced AI technologies into their software solutions enhances their competitive edge. While Snowflake has established itself successfully, Databricks aims to differentiate its offerings by providing cutting-edge analytics capabilities that yield better outcomes for its clients.
Databricks Workforce Expansion Plans
Databricks is set to expand its workforce substantially by hiring 3,000 new employees in 2025, which reflects the company’s ambition to scale operations in response to growing demand. This recruitment drive signals confidence in their revenue trajectory and indicates that the company is preparing for future growth in the competitive data analytics market. A strong workforce will be essential as they look to enhance their product offerings and customer engagement.
The current workforce of approximately 8,000 is crucial in driving innovation and customer success at Databricks. By expanding their team, Databricks aims to enhance their capabilities in product development and customer support, ensuring they remain competitive and continue to meet the needs of their expanding customer base.
Lakebase Database Software: A Game Changer
The unveiling of Lakebase database software at the recent Data and AI Summit marks a significant milestone for Databricks. This new software is a product of the company’s strategic acquisition of Neon, aimed at leveraging cutting-edge technologies to improve database solutions for users. This innovative offering is expected to not only enhance the functionalities of Databricks’ platform but also attract new customers looking for state-of-the-art data management solutions.
Lakebase represents Databricks’ commitment to remaining ahead of industry trends, particularly as demand for sophisticated data analytics continues to grow. The advancements in this software could provide businesses with powerful tools to streamline their data operations, making Databricks an even more appealing choice for enterprises navigating the complexities of data management.
Financial Indicators of Success for Databricks
Databricks’ financial indicators reveal a strong upward trajectory, critical for potential investors. With a reported $2.6 billion in revenue for its recently ended fiscal year and nearly achieving cash flow positivity for the first time, the company illustrates solid financial health moving forward. These indicators are vital in supporting Databricks’ position as it considers public offerings and future expansions in the data analytics landscape.
Furthermore, the company has maintained a substantial net retention rate, suggesting that its existing customers derive valuable use from its products. This level of revenue predictability allows Databricks to plan strategically for future growth, whether through hiring and product development or considering opportunities for initial public offerings.
Databricks Connection to the Future of AI and Data Analytics
As the digital landscape evolves, Databricks is firmly positioned at the forefront of AI and data analytics. Their innovative solutions and advancements showcased at the AI Summit demonstrate a clear vision for merging data and artificial intelligence across various industries. This connection to the future of analytics not only establishes Databricks as a leader but also sets a benchmark for competitors in the field.
The emphasis on integrating AI technologies into their products is vital as organizations increasingly seek to harness the power of data to drive decision-making processes. Databricks’ approach positions it uniquely within the AI ecosystem, allowing them to cater to a growing demand and effectively serve a diverse range of customer needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the projected revenue growth for Databricks in 2024?
Databricks is anticipating a substantial revenue growth, with projected annualized revenue reaching $3.7 billion by July 2024, reflecting a remarkable year-over-year growth rate of 50%.
How does Databricks revenue growth compare to competitors like Snowflake?
Databricks, valued at $62 billion, reported $2.6 billion in revenue for its fiscal year, while Snowflake, its closest competitor, has a market cap of approximately $70 billion and annualized revenue exceeding $4 billion. This demonstrates the competitive landscape in the data analytics software market.
What strategies is Databricks implementing to sustain its revenue growth?
Databricks aims to integrate strong revenue growth with rapid product development and profitability, as stated by CFO Dave Conte. Their commitment to enhancing customer experience and expanding their product offerings, such as the new Lakebase database software, supports their growth strategy.
What is the significance of the upcoming AI Summit 2024 for Databricks?
The AI Summit 2024 is crucial for Databricks as it showcases their latest innovations and provides opportunities to engage with investors and analysts, highlighting their strong revenue growth and future potential in the data analytics software sector.
How many customers contribute significantly to Databricks’ revenue growth?
Databricks has reported nearly 50 customers spending over $10 million annually, which reflects a strong net retention rate above 140% and underscores their capacity for sustained revenue growth.
What new developments in software is Databricks pursuing to increase revenue?
Databricks has introduced the Lakebase database software, leveraging recent acquisitions to expand its offerings. This type of innovation aims to capture a broader market share and enhance their revenue growth potential.
Is Databricks planning an IPO amid their revenue growth successes?
While no specific timeline has been provided for a Databricks IPO, the company’s strong revenue growth and recent valuation increases indicate that an IPO may be a future possibility as they continue to flourish in the data analytics software market.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Databricks projects $3.7 billion in annualized revenue by July, reflecting a 50% year-over-year growth. |
| CFO Dave Conte presented the revenue forecast at the Data and AI Summit in San Francisco. |
| Growth in the October quarter was reported at 60% year-over-year. |
| Databricks raised $10 billion in December, achieving a valuation of $62 billion. |
| Databricks employed roughly 8,000 people and plans to hire an additional 3,000 in 2025. |
| The company reported $2.6 billion in revenue for the fiscal year ending in January. |
| Databricks has a net retention rate above 140% and nearly 50 customers spending over $10 million annually. |
| Databricks revealed a preview of its Lakebase software, expanding market opportunities. |
Summary
Databricks revenue growth is poised to reach $3.7 billion by July, which marks a remarkable 50% increase year-over-year. The company’s strategic focus on integrating robust revenue growth with rapid product development positions it favorably in the competitive landscape of data analytics. With a strong year of financial performance and ambitious hiring plans, Databricks is clearly on a trajectory of exceptional growth, ranking as one of the most valuable tech startups in the industry.