Mortgage Demand Surges 20% Amid Rate Volatility
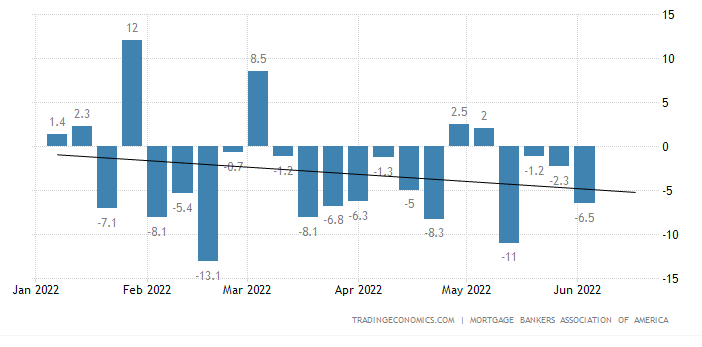
Mortgage demand has surged recently, witnessing an impressive 20% increase in just one week as fluctuations in tariffs led to a temporary dip in mortgage rates. This spike emphasizes the ongoing interest in refinancing loans, with a staggering 35% jump in mortgage refinance applications as homeowners rushed to take advantage of favorable conditions. Additionally, the homebuyer demand has reached its pinnacle, marking the highest levels observed in over a year, as consumers scramble to secure the best possible deals. Adjustable-rate mortgages have also gained traction, reflecting a growing trend among buyers seeking lower initial rates. With mortgage rates currently enjoying a momentary decline, many are keen to capitalize on this window of opportunity.
The recent surge in mortgage interest is underscored by the significant uptick in home financing activity, showcasing the heightened consumer interest in obtaining loans against residential properties. With a pronounced increase in refinancing opportunities, homeowners are motivated to reassess their existing loans in light of current favorable rate environments. Additionally, the appetite for purchasing homes has intensified, as prospective buyers engage more proactively in the housing market. Various types of loan products, including variable-rate options, are seeing a shift in preference, demonstrating an adaptive strategy amidst fluctuating market conditions. As financial dynamics evolve, so too does the landscape for securing optimal home financing solutions.
Understanding Mortgage Demand Trends
Mortgage demand has shown significant fluctuations, driven by various economic indicators and market conditions. Last week’s notable increase of 20% reflects the impact of lower interest rates, which have made mortgages more accessible for both homebuyers and those looking to refinance. This surge comes after a prolonged period of high rates, indicating a responsive market eager to capitalize on favorable conditions.
In particular, the recent volatility in tariffs has created a temporary dip in mortgage rates, leading to a rush in applications. As borrowers respond to these lower rates, the shift signifies a heightened consumer confidence, which is crucial in maintaining steady demand over time. Market analysts suggest that understanding these trends is essential for potential homebuyers and investors looking to navigate the mortgage landscape effectively.
The Surge in Mortgage Refinance Demand
Mortgage refinance demand experienced an impressive surge of 35% over the past week, illustrating the potential benefits of lower interest rates for existing homeowners. Many borrowers who either didn’t act earlier are now seizing this opportunity to refinance their loans, thus minimizing their monthly payments. This trend underscores the importance of timing in the financial decisions that homeowners make concerning their mortgages.
With refinancing loans often offering substantial savings, especially with larger loan amounts, the spike in applications also highlights a strategic move among homeowners looking to optimize financial resources. As rates decreased, homeowners rushed to lenders, attracted by the prospect of lower payments and the potential for financial breathing room amid rising living costs. Experts predict that this trend in refinancing may continue as market conditions evolve.
Homebuyer Demand Reaches New Heights
The demand from homebuyers has escalated to its highest level in over a year, with a 9% increase in mortgage applications reported last week. This upsurge signals a robust interest in home purchases, notably amidst various economic pressures. Many prospective buyers appear to be undeterred by higher home prices, indicating a determined search for suitable properties.
As homebuyer demand rises, the real estate market becomes more competitive, especially with more listings appearing. Despite the challenges posed by increased home prices, buyers are still entering the market, eager to take advantage of lower mortgage rates at present. This situation can create a favorable environment for adjustable-rate mortgages, which saw a corresponding increase in applications last week, indicating a strategic financial choice by many homebuyers.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages Gain Popularity
As mortgage rates fluctuate, the popularity of adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) has increased significantly. Recent data shows that ARMs constituted 8.6% of all mortgage applications, a jump from 5.4% the previous week. This shift suggests that consumers are increasingly interested in securing loans with lower initial rates, even if they come with the risk of rate adjustments down the road.
The decrease in the average contract interest rate for 5/1 ARMs highlights a potential opportunity for borrowers seeking lower monthly payments. Homebuyers may prefer ARMs as a means to enter the market at slightly lower costs, particularly in a competitive landscape where every point counts. This trend reflects a broader adaptation in consumer preferences toward more flexible mortgage options as they seek to maximize their purchasing power.
The Impact of Mortgage Rates on Demand
Mortgage rates play a pivotal role in shaping borrowers’ behavior and overall demand in the housing market. The recent decrease in rates has not only prompted a higher volume of mortgage applications but has also encouraged a surge in both refinancing and purchase applications. Understanding the correlation between mortgage rates and demand can provide buyers with vital insights into the best times to secure a mortgage.
However, the recent volatility in rates poses a challenge for both prospective homebuyers and existing homeowners who are contemplating refinancing. The influencer effect of inflation data and market sentiment can lead to rapid changes in rates, affecting overall purchasing power. As the market adjusts, remaining informed about these fluctuations will be crucial for making strategic decisions.
Market Volatility and Its Effects on Mortgage Applications
Recent market volatility has left a mark on mortgage applications, with significant shifts occurring in response to economic news. Borrowers are frequently adjusting their strategies based on the immediate changes in mortgage rates, which can happen seemingly overnight. The 20% rise in mortgage demand is a direct reflection of this dynamic environment where opportunities are keenly seized.
Moreover, the implications of tariff changes and inflation reports can trigger rapid responses from lenders and borrowers alike. As evidenced last week, applications increased while rates dipped—a reminder of the cyclical nature of the mortgage market. Staying alert to market news can give potential homebuyers and refinancers a competitive advantage, allowing them to make informed decisions in a fluctuating landscape.
Economic Indicators Influencing Mortgage Demand
Economic indicators such as inflation rates, employment figures, and consumer confidence levels significantly influence mortgage demand. When the economic outlook appears stable or improving, borrowers are more likely to apply for mortgages. This week, for instance, the anticipation of inflation data informed mortgage behaviors, illustrating how interconnected these elements are.
Investors and homebuyers alike should remain vigilant about changes in economic indicators, as they can herald shifts in mortgage rates and overall demand. The feedback loop between these factors demonstrates a complex but essential understanding for navigating the homebuying process or refinancing. An informed buyer will consider not just current rates but also how overall economic conditions may influence future borrowing costs.
Strategies for Homebuyers Amid Rising Prices
With home prices on the rise, potential homebuyers must adopt effective strategies to navigate this challenging market. As demand continues to surge, the competition for homes intensifies, necessitating a well-planned approach to securing financing. Understanding mortgage types, such as fixed-rate versus adjustable-rate options, can aid buyers in making the best financial decisions given their circumstances.
Additionally, being pre-approved for a mortgage can give buyers a competitive edge in the current market. Such preparation signals to sellers that buyers are serious and capable of completing their purchase, which can be particularly critical in hot markets where time is of the essence. Buyers should also consider consulting with mortgage professionals to tailor their options based on personal financial situations.
Preparing for Future Mortgage Rate Fluctuations
Understanding that mortgage rates can fluctuate significantly, preparing for future changes is vital for anyone considering a home purchase or refinancing. Monitoring economic trends and market news will aid borrowers in timing their applications effectively, potentially maximizing savings. The recent increase in applications indicates a proactive response to current rates; however, the potential for rates to rise again demands caution.
For homeowners looking to refinance or buyers contemplating a purchase, being strategically positioned can ensure that they take advantage of the best possible rates. However, remaining adaptable is equally crucial, as circumstances around economic factors may change rapidly, influencing future borrowing scenarios. Buyers should prepare by staying informed and possibly locking in rates when they find favorable conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are currently influencing mortgage demand?
Mortgage demand is significantly influenced by mortgage rates and market volatility. Recently, a drop in rates due to tariff fluctuations resulted in a 20% increase in total mortgage applications. Both homebuyer demand and refinancing loans surged as consumers sought to capitalize on lower rates.
How has mortgage refinance demand changed in recent weeks?
Mortgage refinance demand saw a dramatic 35% increase last week, largely driven by lower mortgage rates. Borrowers with larger loans are especially motivated to refinance, as the average refinance loan size reached $399,600, highlighting a strong interest in refinancing loans amid favorable conditions.
What impact do adjustable-rate mortgages have on mortgage demand?
Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) have become increasingly popular, with their applications rising to 8.6% of total mortgage applications last week. This surge in demand indicates that homebuyers are actively seeking the lowest rates possible, especially when fixed mortgage rates are higher.
How do current mortgage rates affect homebuyer demand?
Current mortgage rates play a crucial role in homebuyer demand. Recently, the average interest rate for 30-year fixed mortgages fell to 6.61%, stimulating a 9% increase in purchase applications, the highest level since January 2024. Homebuyers are leveraging these lower rates to navigate higher home prices.
Are mortgage rates expected to fluctuate in the near future?
Yes, mortgage rates can be quite volatile, as seen with a recent 25 basis point increase that reversed the previous week’s decline. Analysts suggest monitoring upcoming inflation data, as it often influences mortgage rate momentum, indicating that fluctuations are likely in the near term.
What should potential homebuyers consider regarding mortgage demand trends?
Potential homebuyers should stay informed about mortgage demand trends, particularly how shifts in mortgage rates can affect their purchasing power. With rates recently dropping and homebuyer demand rising, now may be an advantageous time to enter the market, but they should remain vigilant about potential rate increases.
What does an increase in mortgage demand indicate about the housing market?
An increase in mortgage demand typically signals positive momentum in the housing market. Recently, both refinancing and purchase demand rose sharply, suggesting that buyers are eager to take advantage of lower mortgage rates, despite ongoing challenges like higher home prices.
How do tariffs and market volatility influence mortgage demand?
Tariffs and market volatility can lead to fluctuations in mortgage rates, directly impacting mortgage demand. Recent volatility caused a temporary drop in rates, which subsequently spurred a significant rise in mortgage applications, illustrating the interconnectedness of these economic factors.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Mortgage Refinance Demand | Surged 35% in one week due to lower rates, attracting borrowers to lenders. |
| Homebuyer Demand | Reached highest level in over a year with a 9% increase in mortgage applications. |
| Adjustable-Rate Loans | Gained popularity; applications increased to 8.6% of total applications as consumers sought lower rates. |
| Rate Changes | Average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages fell to 6.61% from 6.70%. |
| Future Prospects | Potential for a decrease in mortgage demand as rates have started to rise again. |
Summary
Mortgage demand has experienced a significant surge, with an overall increase of 20% last week primarily driven by lower interest rates amid tariff volatility. This uptick in demand, particularly for refinancing and homebuying, highlights the sensitivity of consumers to interest rate changes. However, with recent increases in mortgage rates, the longevity of this surge remains uncertain.