Cryptocurrency Dating Scam: DOJ Seizes $868K in Assets
In recent years, the rise of cryptocurrency dating scams has alarmed many digital enthusiasts and casual users alike. These schemes typically lure individuals with promises of romantic connections, only to ensnare them in a complex web of investment fraud and deception. The recent seizure of $868,000 in crypto by U.S. federal agents underscores the magnitude of these scams, showcasing how victims are manipulated into transferring funds to fake asset platforms. Often, the initial allure of high returns masks a nefarious plot to defraud individuals seeking love in the digital age. As reports of romance scams continue to rise, it is crucial for potential victims to engage in online fraud prevention and to remain vigilant against such deceptive tactics that exploit both trust and technology.
Recently, there has been growing concern over fraudulent activities tied to online romantic pursuits, commonly referred to as romance scams. These schemes often involve swindlers posing as potential partners, gradually gaining their targets’ trust before guiding them towards phony investment opportunities. In a disturbing twist, they utilize fake cryptocurrency platforms that promise astronomical returns, misleading victims into believing they are making sound investments. The U.S. Department of Justice has taken significant steps to address this issue by cracking down on such operations, including substantial asset seizures and public awareness campaigns. As technology advances, so does the sophistication of these scams, making awareness and education paramount for anyone engaging in online dating.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Dating Scams
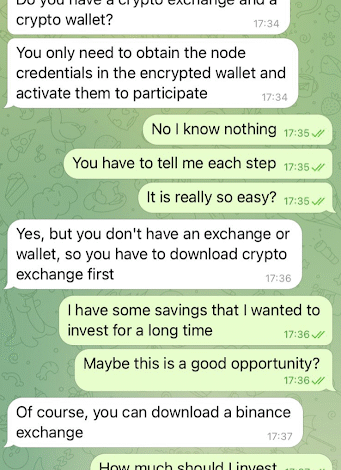
Cryptocurrency dating scams are a particularly insidious form of online fraud that exploit the emotional vulnerabilities of individuals seeking romance. Scammers typically pose as genuine romantic interests and engage in a gradual process of building trust. Once a connection is established, they introduce victims to elaborate fake investment opportunities, often centered around cryptocurrency. This manipulation leads victims to believe they are participating in a legitimate investment that promises high returns on their contributions, ultimately resulting in significant financial losses.
Moreover, these scams are not just about misleading victims; they are structured to ensure that victims remain hopeful. Scammers may allow initial withdrawals to reinforce the illusion that their platforms are credible and profitable. By showcasing fake success, they lure victims into depositing even more money, often draining their wallets without any possibility of recovery. As recent cases, including one involving an $868,000 seizure, demonstrate, the scope of these scams can be vast, with the potential for devastating financial consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cryptocurrency dating scam?
A cryptocurrency dating scam is a type of online fraud where scammers use dating platforms to establish a romantic relationship with victims and subsequently manipulate them into investing in fake cryptocurrency schemes. These scammers often create fake identities and use emotional tactics to build trust before promoting non-existent digital asset investments.
How do cryptocurrency dating scams work?
Cryptocurrency dating scams typically start with the scammer connecting with a victim on a dating app or social media. Once a rapport is established, the scammer presents fake investment opportunities on phony crypto platforms that promise high returns. Victims are encouraged to send money or cryptocurrency to these platforms, which are actually controlled by the scammers.
What signs indicate that I am involved in a cryptocurrency dating scam?
Signs of a cryptocurrency dating scam include a quick progression from online romance to investment advice, requests for money or cryptocurrency transfers, and the use of fake investment platforms that show unrealistic profits. Additionally, if the person you are communicating with avoids meeting in person or becomes secretive about their identity, these may be red flags of a scam.
What should I do if I fell victim to a cryptocurrency dating scam?
If you believe you have fallen victim to a cryptocurrency dating scam, it is crucial to report the incident to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) and your local authorities. Additionally, try to gather all your transaction details and communications with the scammer, as this information can be helpful in investigations.
How can I protect myself from cryptocurrency dating scams?
To protect yourself from cryptocurrency dating scams, be cautious when sharing personal information online, especially on dating platforms. Never invest in cryptocurrency that you haven’t thoroughly researched, and be skeptical of anyone who pressures you to send money or cryptocurrency. Look for legitimate investment opportunities and consult with financial experts before committing funds.
What role does the DOJ play in addressing cryptocurrency dating scams?
The Department of Justice (DOJ) plays a critical role in combating cryptocurrency dating scams by investigating fraudulent schemes, seizing assets generated from these scams, and prosecuting offenders. For example, recent seizures of over $868,000 in cryptocurrency linked to dating scams demonstrate the DOJ’s commitment to fighting online fraud and protecting victims.
How can I report a cryptocurrency dating scam?
You can report a cryptocurrency dating scam by filing a complaint with the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3). Provide as much detail as possible about the scam, including communication with the scammer and any financial transactions that occurred, to assist authorities in their investigation.
What is the relationship between romance scams and cryptocurrency scams?
Romance scams and cryptocurrency scams are interconnected forms of online fraud where scammers exploit emotional connections to manipulate victims into investing in fake financial opportunities. Scammers often use romantic narratives to gain trust before leading victims to cryptocurrency schemes, further complicating the recovery of funds for the victims.
What were the consequences for perpetrators of the recent cryptocurrency dating scam?
The DOJ recently announced the seizure of over $868,000 in cryptocurrency from perpetrators involved in a dating scam, highlighting the legal consequences for those engaged in such fraudulent activities. These actions are part of a broader effort to dismantle sophisticated online scams that defraud individuals of their investments.
Are there resources available to help prevent online fraud and cryptocurrency scams?
Yes, resources for preventing online fraud and cryptocurrency scams include the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), and various online fraud prevention organizations. These resources provide information on recognizing scams, reporting fraudulent activities, and protecting your personal information online.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Cryptocurrency Seizure | Federal agents seized $868,000 in crypto from a romance scam. |
| Nature of Scam | Victims were lured through dating apps and text messages into investing in fake crypto platforms. |
| Methodology | Scammers posed as romantic interests, gaining trust before urging investments in non-existent ventures. |
| Signs of Fraud | Fraudulent platforms showed inflated returns and provided early withdrawals to foster trust. |
| Legal Action | The DOJ is actively investigating and has encouraged reporting similar scams through the FBI. |
| Related Cases | On the same day, about $2.5 million was recovered from other similar schemes. |
Summary
Cryptocurrency dating scams are an alarming trend that has led to significant financial loss for countless victims. The recent seizure of $868,000 by federal authorities underscores the destructive nature of these scams, where fraudsters use romantic deception to lure individuals into investing in fake crypto platforms. With the rise of online dating, awareness of such scams is crucial, as they often involve complex tactics that manipulate trust and exploit emotions. The DOJ’s actions signal a strong response to these fraudulent activities, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and reporting any suspicious behavior to prevent future scams.




