Maryland Man Deportation Case Shocks Nation Amid Charges
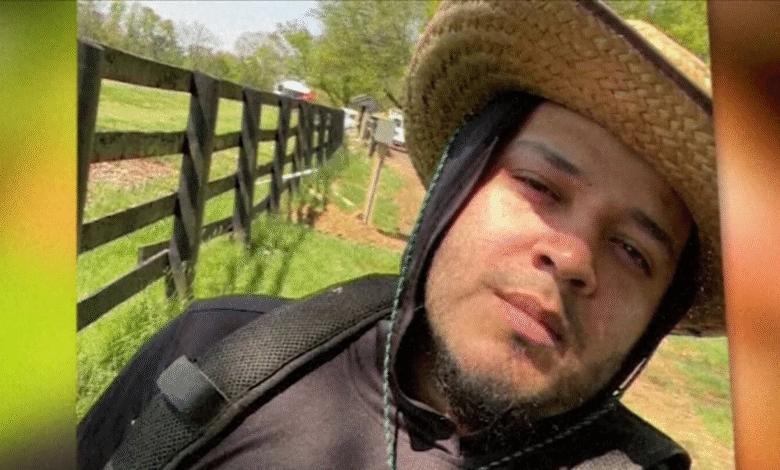

The Maryland man deportation case of Kilmar Abrego Garcia has become a contentious issue at the intersection of immigration and criminal law. After being mistakenly sent back to El Salvador, he has now returned to the U.S. to face serious federal court charges. Allegations against Abrego Garcia suggest he played a pivotal role in a smuggling ring that transported undocumented immigrants across borders, making multiple trips and impacting countless lives. The involvement of the notorious MS-13 gang in this case has further heightened concerns about human trafficking and violence associated with these smuggling operations. With demands for justice echoing from community leaders, the outcome of this case is poised to shine a spotlight on the broader challenges within the immigration system and the enforcement of laws against organized crime.
In the recent developments surrounding the deportation saga of a Maryland resident, Kilmar Abrego Garcia, the implications of his alleged involvement in a human smuggling operation come to the forefront. This case underscores the complex interplay between immigration enforcement and national security concerns, especially given the alleged connections to the MS-13 gang. Accusations highlight Garcia’s role in facilitating the entry of undocumented individuals into the United States, a process fraught with danger and exploitation. As authorities seek to unravel the full extent of his activities, questions arise about the efficacy of current legal frameworks in addressing human trafficking and the accountability of involved parties. This situation illustrates not only individual legal battles but also the larger narrative concerning immigration policy and the protection of vulnerable communities.
Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s Role in a Smuggling Ring
Kilmar Abrego Garcia has been accused of orchestrating a significant smuggling operation that transported undocumented immigrants through perilous routes from Central America to various states in the U.S. According to authorities, the smuggling ring allegedly operated from 2016 until 2025, highlighting a span of nearly a decade where Abrego Garcia utilized his network to facilitate illegal border crossings. His activities reportedly involved extensive logistics, including arranging transportation through Mexico and into Texas, where many of the immigrants would then be processed before disappearing into the U.S. immigration system.
The indictment reveals that Abrego Garcia’s network was not just a simple smuggling operation but a well-organized ring that profited off the desperation of undocumented individuals seeking safety and opportunity in the United States. Over 100 trips were documented, during which thousands of undocumented immigrants reportedly passed through his hands, confirming his significant impact on the illegal immigration crisis. His operation has raised concerns among law enforcement about the methods used, including the reported abuse of women and trafficking of firearms and drugs linked to his activities.
Legal Proceedings Against Kilmar Abrego Garcia
After being wrongfully deported, Kilmar Abrego Garcia has made his return to the U.S. to face serious federal court charges in Tennessee. The nature of these charges emphasizes the government’s commitment to holding individuals accountable for their involvement in human trafficking and illegal smuggling operations. The charges filed against him indicate that the legal system is gearing up for a rigorous battle, with prosecutors likely to present compelling evidence of his involvement in transporting undocumented immigrants, which not only violates immigration laws but endangers the lives of vulnerable populations.
Additionally, the legal proceedings against Abrego Garcia will address a multitude of other serious allegations, including his association with dangerous practices that involved violating the rights of women and involvement in violent crimes related to gang activities. His attorney’s claim regarding the abuse of power reflects the complex interplay between immigration law and criminal justice as this case unfolds. With the defense intending to challenge the government’s actions during the deportation process, it raises significant questions about due process in immigration cases and how they intersect with criminal charges related to organized crime.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Maryland man deportation case involving Kilmar Abrego Garcia?
The Maryland man deportation case revolves around Kilmar Abrego Garcia, who was erroneously deported to El Salvador and is now being brought back to the U.S. to face federal court charges related to his alleged involvement in a smuggling ring that transported undocumented immigrants across the United States.
What charges does Kilmar Abrego Garcia face in connection with the Maryland man deportation case?
Kilmar Abrego Garcia faces multiple federal court charges stemming from his involvement in a smuggling operation that transported undocumented immigrants from various countries, including Guatemala and Honduras, from 2016 to 2025. His activities allegedly resulted in human trafficking and were connected to significant incidents of danger and criminal behavior involving undocumented migrants.
How did the mistaken deportation of Kilmar Abrego Garcia occur in the Maryland man deportation case?
The mistaken deportation of Kilmar Abrego Garcia happened when he was wrongfully deported to El Salvador by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) prior to facing legal proceedings in the United States. This action was later recognized by the administration as an error, which led to complications in arranging his return.
What legal repercussions follow Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s return to the U.S. in the Maryland man deportation case?
Upon his return, Kilmar Abrego Garcia is set to face federal court charges for his role in a smuggling ring. His attorney argues that he should have the opportunity to defend himself before the same immigration judge who issued his non-removal order in 2019, emphasizing the importance of due process in this Maryland man deportation case.
What connection does Kilmar Abrego Garcia have with the MS-13 gang in the Maryland man deportation case?
Kilmar Abrego Garcia has been identified by the Trump administration as a member of the MS-13 gang, a designation that classifies the gang as a foreign terrorist organization. However, he denies these allegations, which add complexity to his legal battles following the Maryland man deportation case.
What impact did Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s deportation have on undocumented immigrants in the Maryland man deportation case?
Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s deportation has brought attention to the larger issues of undocumented immigration and human trafficking in the U.S. His alleged actions as part of a smuggling ring significantly affected thousands of undocumented immigrants, illustrating the risks and dangers associated with such operations as highlighted in the Maryland man deportation case.
What is the current status of the Maryland man deportation case involving Kilmar Abrego Garcia?
The current status of the Maryland man deportation case is that Kilmar Abrego Garcia has returned to the U.S. to face criminal charges in federal court. This case continues to develop as authorities, legal representatives, and the courts address the complexities arising from his mistaken deportation and alleged criminal activities.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Maryland man Kilmar Abrego Garcia was mistakenly deported to El Salvador despite a court order against his removal. |
| He returned to the U.S. to face charges related to his alleged role in a smuggling ring from 2016 to 2025. |
| Abrego Garcia is accused of transporting thousands of undocumented immigrants across the U.S. border, with links to the deaths of over 50 migrants. |
| Allegations also include the abuse of undocumented women, trafficking firearms and drugs, and soliciting inappropriate materials from minors. |
| His attorney criticized the deportation as an ‘abuse of power’ and argued for due process in his defense. |
| Abrego Garcia has been labeled a member of the MS-13 gang, but he has denied these allegations. |
Summary
The Maryland man deportation case involves Kilmar Abrego Garcia, who has returned to the U.S. to face serious criminal charges after being mistakenly sent to El Salvador. His situation highlights critical issues regarding immigration enforcement and due process, especially in cases where error leads to wrongful deportation. As the case unfolds, it raises concerns about both the legality of the actions taken by authorities and the broader implications for undocumented immigrants in the U.S. legal system.