China US Treasury Investments Surge Amid Trade War Tensions
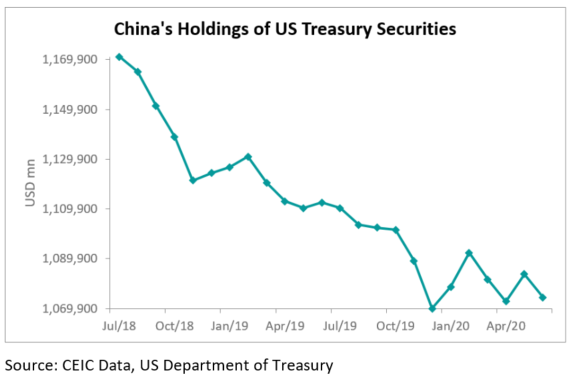
China US Treasury Investments have become a focal point in discussions surrounding the nation’s economic strategy, especially amid the shifting dynamics of global trade. In February, as tensions escalated with the introduction of tariffs by the Trump Administration, China significantly increased its treasury holdings, reaching $784.3 billion. This decision underscores the vital role that US Treasury investments play for China, particularly in light of the ongoing trade war effects impacting the financial landscape. The increase in Chinese investments in US debt highlights concerns over economic stability, as both China and its regional counterpart, Japan, opted to bolster their positions in US Treasury bond purchases. As such, these movements reflect both a self-preservation strategy and a complex interplay of global financial relations.
The landscape of Chinese investments in American debt assets has gained critical attention, particularly in the wake of mounting trade tensions. As China navigates the intricacies of its treasury holdings, the notable rise in US Treasury investments signals a strategic response to external pressures. The interplay between these economic maneuvers is intricately linked to broader themes, such as the repercussions of the ongoing tariff disputes and the consequential effects on global markets. Furthermore, this increase in Treasury bond purchases by China dovetails with Japan’s own similar actions, emphasizing a collective approach in safeguarding economic interests. Understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping the full impact of international finance amid the shifting tides of trade relations.
China’s Increased Treasury Investments Amidst Trade Tensions
In recent times, China has significantly increased its investments in U.S. Treasuries, boosted by geopolitical tensions arising from the trade war. As tariffs were imposed by the Trump Administration, particularly a 10% levy on imports from China, the Asian giant responded by raising its U.S. debt holdings. This elevation reflects a strategic move to stabilize its economic footprint in light of unstable trade relations. By the end of February, China’s Treasury holdings surged to $784.3 billion, underscoring its commitment to maintaining influence in the U.S. financial system despite the escalating trade conflict.
This tactical decision by China can be seen as a defensive mechanism against economic uncertainty fueled by tariff protections. With U.S. Treasury investments regarded as a safe haven, the Chinese government seeks not only to protect its large portfolio but also to sustain its market stability. The increase in Treasury bond purchases by China underscores an inherent understanding of the risks associated with selling off significant portions of their holdings, which could exacerbate market volatility and adversely impact both economies. Consequently, this dynamic poses a fascinating interplay between investment strategies and global economic policies.
The Role of U.S. Treasury Bonds in International Finance
U.S. Treasury bonds hold a prominent position in international finance, serving as a benchmark for other financial instruments globally. Countries like China utilize these bonds to diversify their foreign reserves while simultaneously backing the U.S. dollar’s value. The stability associated with U.S. Treasury investments is reinforced by the fact that these bonds are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government, making them a favored asset among foreign investors. China’s focus on increasing its Treasury holdings despite trade tensions showcases the global reliance on U.S. debt instruments to weather financial storms.
Moreover, U.S. Treasury investments play a critical role in the capital structure of nations, particularly for those whose economies are closely tied to trade with the United States. As seen with China’s increased investments, such actions can paradoxically be both a sign of economic support for the U.S. and a hedge against potential fallout from deteriorating trade relations. By securing significant Treasury holdings, countries can mitigate short-term financial risks while reinforcing their bargaining positions in ongoing trade discussions. Thus, the intricate balance between investment and diplomacy underscores the vital role of U.S. Treasury bonds in shaping international economic policies.
Impact of Trade War on Chinese Investments in the U.S.
The trade war between the United States and China has led to a complex re-evaluation of Chinese investments in the U.S. As tariffs were introduced, many speculated that these high-stakes negotiations would dissuade China from increasing its holdings of U.S. Treasuries. However, the opposite occurred; China opted to strengthen its position by amplifying its Treasury investments during this period. This counterintuitive trend illustrates how geopolitical factors can often redirect investor behavior in unexpected ways, reinforcing commitment to U.S. securities as both an investment and a strategic financial move.
Furthermore, the repercussions of the trade war extend beyond mere tariffs, impacting investor sentiment and the underlying stability of U.S. Treasury offerings. As China continues to enhance its treasury holdings amidst these escalations, it highlights a strategic choice centered around securing financial safety in a turbulent economic landscape. The trade war not only influences the volume of Chinese investments in U.S. Treasuries but also reshapes the broader narrative of trust and reliability associated with American financial instruments. This highlights a unique dynamic where economic competition and cooperation coexist, ultimately driving the global financial markets.
Understanding China’s Treasury Holdings in a Global Context
China’s U.S. Treasury holdings must be understood within a broader global economic context. As one of the largest holders of U.S. debt, China’s approach to managing its Treasury investments is significantly influenced by international economic conditions and trade relations. Particularly during periods of economic uncertainty, such as during the trade war, the amplification of these holdings signifies China’s attempt to hedge against potential economic fallout. The juxtaposition of increasing Treasury purchases while engaging in tariff disputes symbolizes a nuanced strategy whereby China seeks to protect its economic interests.
Additionally, China’s Treasury holdings hold implications not just for bilateral relations, but for the entire international financial architecture. The strategic growth in these investments amid trade tensions showcases a dual role: on one side, it reinforces China’s economic ties with the U.S., while on the other, it is a measure of self-preservation in the face of trade hostilities. This complicated interaction emphasizes the need for comprehensive strategies that consider the multi-layered influences of trade, investment, and foreign policy on global economic stability. By maintaining robust Treasury investments, China can ensure it remains integral to the global economic system, even if faced with adverse trade conditions.
The Economics Behind Treasury Bond Purchases
Treasury bond purchases are a cornerstone of economic strategy for many nations, especially those like China, which are heavily invested in maintaining a strong dollar. These bonds are seen as a secure investment due to their low default risk and the liquidity they offer. For China, increasing Treasury holdings serves not only as a means to preserve foreign exchange reserves but also as a tactical approach to managing its currency’s strength against the dollar. The decision to invest in U.S. debt is often driven by a broader economic strategy that encompasses trade balances and currency stabilization.
In the context of the ongoing trade war, where economic policies fluctuate rapidly, the act of purchasing Treasury bonds also signifies a political message of confidence in the U.S. economy. By bolstering their investments, China communicates its commitment to maintaining a stable economic relationship with the U.S., despite the discord expressed through tariffs and trade negotiations. Thus, U.S. Treasury bonds become more than just financial instruments; they encapsulate the intricate ballet of trust, strategy, and resilience between powerful economies navigating periods of uncertainty.
The Consequences of Selling Treasuries During Trade Wars
The possibility of countries like China selling off substantial amounts of U.S. Treasuries during trade conflicts raises critical questions about market stability and economic repercussions. Such an action could lead to plummeting bond prices and rising yields, causing a tumultuous ripple effect across global financial markets. The potential for disruption poses risks not just for the U.S. economy but also for the economies of countries dependent on Treasury securities. Hence, China’s strategic decision to increase its Treasury holdings underscores an awareness of the far-reaching consequences that come with active selling during volatile times.
Furthermore, Lou Brien’s insights indicate that both China and Japan are cognizant of the self-preservation instinct that governs their Treasury strategies. The hesitance to divest from Treasuries amid trade turbulence reflects a consensus on the necessity of preserving economic ties and minimizing loss. By choosing to bolster their Treasury investments rather than sell, these nations signal their enduring belief in the stability and reliability of U.S. debt as a safe asset amidst uncertainty. This mutual understanding between investor actions and market responses encapsulates the delicate balance of international finance during times of geopolitical strife.
Future Outlook for China and U.S. Treasury Relations
Looking toward the future, the relationship between China and U.S. Treasury investments will remain critical as both nations navigate through periods of potential economic volatility. The extent to which China continues to increase or adjust its Treasury holdings will greatly depend on the evolving landscape of trade relations and economic policy decisions made by both the U.S. and China. As market dynamics shift, these investments will continue to serve as a touchstone for assessing the broader economic sentiment and trust that exists between the two formidable economies.
Moreover, developments surrounding future trade agreements, tariff adjustments, or economic reforms will invariably influence China’s investment strategies in the U.S. Treasury market. The balancing act of securing investments while engaging in diplomatic negotiations will be paramount, as any disruptions could prompt adjustments in Treasury holdings. Ultimately, the outlook for China-U.S. Treasury relations will be dictated by ongoing interactions and the strategic maneuvering that defines not just economic exchanges, but also foreign policy at large. As we observe these changes, it will be vital for investors and policymakers to stay attuned to the underlying geopolitical currents shaping this pivotal financial landscape.
Trade Negotiations and Their Impact on Treasury Investments
As trade negotiations between China and the U.S. evolve, their impact on Treasury investments remains a significant concern for global financial markets. The relationship between trade policy and treasury bond purchases reflects the intricate interplay between economic cooperation and competition. When tariffs are heightened, as seen during recent trade disputes, it often leads to considerable shifts in investor behavior, prompting nations like China to reassess their strategy concerning U.S. Treasury holdings in order to navigate the ensuing economic turbulence.
Furthermore, the momentum of trade talks can influence the sentiment surrounding Treasury investments among foreign buyers. A resolution to trade disputes might alleviate investor concerns, potentially restoring greater confidence in U.S. economy. Conversely, if negotiations falter, countries may opt to either increase or decrease their Treasury holdings in reaction to perceived risks. This unpredictability emphasizes the role of diplomacy in shaping economic strategies, particularly for nations deeply embedded in the U.S. debt market, such as China, highlighting the effective use of Treasury investments as both economic leverage and a barometer of international relations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of China’s increased US Treasury investments during the trade war?
China’s increased US Treasury investments during the trade war, rising to $784.3 billion in February, demonstrate an effort to maintain economic stability amid escalating tariffs. This strategic move reflects a reaction to the Trump Administration’s tariffs, with potential impacts on trade relations and financial markets. As China and Japan enhance their Treasury bond purchases, their economic security becomes intertwined with US financial systems.
How do China treasury holdings affect US financial markets?
China treasury holdings significantly influence US financial markets due to their substantial dollar value, currently at $784.3 billion. These investments impact interest rates and overall market confidence. Increased holdings can stabilize the US dollar, while any shift away from these investments could lead to market volatility, directly affecting US Treasury investments.
What role does the trade war play in Chinese investments in US Treasuries?
The trade war has played a crucial role in shaping Chinese investments in US Treasuries. The increase in holdings to $784.3 billion amid tariff tensions indicates that China views US debt as a relatively safe asset, prioritizing financial security over immediate economic retaliation. This strategy helps mitigate potential losses from trade-related disruptions.
Are there risks associated with Chinese investments in US Treasury bonds?
Yes, there are risks associated with Chinese investments in US Treasury bonds. Although these investments are considered safe, a significant shift in China’s Treasury bond purchases could affect US interest rates and market stability. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and trade disputes could influence China’s willingness to continue investing heavily in US Treasuries.
What strategies do China and Japan employ regarding US Treasury investments?
China and Japan employ strategies focused on balancing their economic interests while navigating trade tensions. Their increased US Treasury investments reflect a dual strategy of safeguarding foreign reserves and maintaining influence in the global financial system, particularly during the uncertainties of the trade war. This collective approach helps stabilize their economies and minimizes potential losses.
How do fluctuations in Chinese treasury holdings impact US economic policy?
Fluctuations in Chinese treasury holdings can significantly impact US economic policy by influencing interest rates and the overall economic environment. As China adjusts its US Treasury investments, policymakers in the US may need to consider these changes when shaping monetary policy, particularly in response to trade tensions and international market conditions.
| Country | US Treasury Holdings (in billions) | Key Event | Market Strategist Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | $784.3 | 10% tariff on imports | Selling Treasuries could harm them significantly. |
| Japan | Increased (exact figure not specified) | Affected by similar tariff measures | Holding Treasuries is crucial for them. |
Summary
China US Treasury Investments saw a significant increase as the trade war escalated, coinciding with a 10% tariff imposed on imports from China by the Trump Administration. This strategic move by China, which raised its U.S. debt holdings to $784.3 billion, indicates a strong commitment to maintaining its fiscal position amidst turbulent trade relations. The rise in Treasury investments not only underscores China’s economic strategy but also highlights the inherent risks involved for countries like Japan and China when considering divestment from U.S. Treasuries.




