Bitcoin Price Analysis: Can Bulls Regain Control Above $112K?
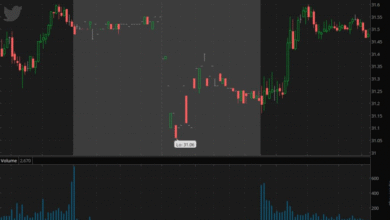
In the realm of Bitcoin price analysis, understanding the fluctuations of BTC is crucial for traders navigating the ever-changing cryptocurrency market. Recently, Bitcoin has been tethered between $110,936 and $111,110, showcasing a tightening trading range indicative of potential volatility. With its market capitalization resting at a staggering $2.20 trillion and a daily trading volume of $39.70 billion, Bitcoin is reaffirming its stature as a dominant player in Bitcoin trading. Price predictions for BTC reveal a current consolidation phase following a prior rally, creating an interesting backdrop for those interested in Bitcoin bullish trends. As traders assess levels of resistances and supports, this analysis provides insight into the possible direction of Bitcoin’s journey ahead.
Exploring the intricacies of Bitcoin valuation requires a keen eye on the current market dynamics that influence its price shifts. As we delve into the recent trading patterns and behavioral trends of this leading cryptocurrency, it becomes apparent that Bitcoin’s latest movements reflect typical characteristics of speculative trading within the cryptocurrency space. Identifying price levels that act as significant barriers—both above and below—can offer critical information for traders looking to capitalize on upcoming trends. The ongoing bullish sentiment juxtaposed against potential price corrections invites a thorough examination of the key indicators that could dictate future market behavior. Engaging with Bitcoin’s price story not only highlights the prevailing bullish tendencies but also emphasizes the critical resistances and supports shaping its trajectory.
Understanding Bitcoin’s Current Price Dynamics
As of now, Bitcoin is showing signs of price stabilization after fluctuating between $110,936 and $111,110. This comparative calm in the Bitcoin trading environment suggests that the cryptocurrency is entering a phase of consolidation. With a market cap now sitting at $2.20 trillion and a daily trading volume of approximately $39.70 billion, traders are carefully observing Bitcoin’s price maneuvering within an intraday range of $108,644 to $111,742. Such action typically indicates a market in transition, where bullish sentiment may give way to a cautious approach as investors assess the broader implications of current price movements.
Recent Bitcoin price analysis reveals a developing trend that poses both opportunities and risks. The bullish momentum seen in the BTC price predictions has resulted in a peak price at $112,040, which analysts consider an important resistance level. With price action exhibiting indecision in the form of smaller-bodied candles, there is a clear indication of potential market hesitation. This indecisiveness calls for alertness among traders, as the aspect of uncertainty can lead to either a bullish breakout or a bearish reversal, depending on how the price interacts with key support and resistance levels.
Bitcoin Price Prediction: The Road Ahead
Looking forward, Bitcoin’s price prediction remains contingent on its ability to maintain stability above crucial support levels. The daily charts suggest that while the immediate indicators may lean bullish, recent deceleration in momentum raises questions about the sustainability of this trend. The price has notably oscillated between $110,500 and $111,500, and while a breakthrough above $112,000 could reignite bullish enthusiasm, the current market conditions embody a wait-and-see approach.
Additionally, it is essential to monitor the prevailing support level at $110,800. If Bitcoin fails to maintain this support, it may lead to a retracement into the $109,000 region, where previous breakout zones await. Thus, traders are urged to exercise caution and keep abreast of BTC price predictions as movements below critical support could embolden bearish traders to step in. Ultimately, Bitcoin’s ability to regain control above $112,000 is pivotal not only for its price trajectory but for investor sentiments within the broader cryptocurrency market.
The Bullish Trend: Can Bitcoin Maintain Momentum?
In recent trading sessions, Bitcoin has showcased a bullish trend characterized by high-volume breakouts. The initial surge from approximately $109,000 to $112,040 indicates strong bullish momentum, suggesting that traders are still finding opportunities in Bitcoin despite the volatility. As momentum indicators such as MACD signal potential buying interest, the market reflects ongoing confidence. If Bitcoin can successfully reclaim and hold the $112,000 mark, it could signal the resumption of a bullish trend, allowing traders to set their sights on new price levels.
However, it is crucial to note the warnings rendered by market oscillators, which indicate a potential cooling off in the bullish trend. The flat price action that has followed the high volume breakout exemplifies the market’s uncertainty. If Bitcoin continues to uphold its price above critical moving averages and sustains itself through a concerted effort to break through resistance points, this could reinforce the bullish case for Bitcoin. Traders will be keen to observe closely how Bitcoin navigates through resistance levels while weighing the impact of balances between bullish sentiment and bearish market corrections.
Identifying Key Bitcoin Resistance and Support Levels
Understanding Bitcoin’s pivotal resistance and support levels is essential for traders aiming to strategize around price movements effectively. Currently, essential resistance is noted around the $112,000 level, which Bitcoin must break decisively to forge ahead with its bullish narrative. Meanwhile, support around $110,800 has proven to be a critical barrier that any downward price actions will intensely test. Breaking below this support could trigger a re-evaluation of market dynamics, potentially sending Bitcoin back to previous support indicators around the $108,500 zone.
Moreover, as Bitcoin interacts with these identified resistances and supports, traders are advised to watch volume closely. A significant increase in trading volume upon testing these levels could provide clear directional cues to support ongoing bullish or bearish narratives. Maintaining awareness of these dynamics is crucial, as the cryptocurrency market can be highly volatile, and understanding where Bitcoin’s price stands in relation to these key thresholds can enhance trading strategies.
Short-Term BTC Trends: What Traders Should Watch
In the short term, Bitcoin’s trading patterns exhibit phases of consolidation interspersed with bullish attempts to advance. With price consistently testing the $110,800 support level, traders must closely monitor this zone for signs of strength or weakness. Market sentiment appears cautious as new entrants might hesitate due to the uncertainty reflected in the volume dynamics. As the short-term price actions indicate oscillations within tight corridors, it becomes vital for traders to identify breakouts above resistance levels or confirmations of support to guide trading decisions.
The 4-hour and 1-hour charts present critical insights for intraday traders monitoring Bitcoin’s movements. Recent lower-volume red candles following an initial breakout suggest a probable pause or consolidation phase. For traders looking for actionable insights, confirming a breakout or breakdown from established trading ranges could signal their next moves. The overarching principle remains to remain alert to changing momentum patterns that can directly impact Bitcoin’s price trajectory in the near future.
The Role of Volume in Bitcoin’s Price Movements
Volume plays a critical role in assessing Bitcoin’s price movements, as it reveals the strength or weakness behind price changes. Recent trading has shown a decline in volume accompanying the price fluctuations, which raises questions about the strength of the prevailing trend. A significant drop in volume often precedes central turning points in the market, and Bitcoin’s current condition warrants vigilant observation by traders for any signs of reversal or continuation in the bullish trend.
Furthermore, if volume spikes occur alongside upward price movements, this could serve as validation for current bullish predictions. Alternatively, prolonged low volume amidst rising prices could suggest waning momentum and potential corrections. For those engaged in Bitcoin trading, understanding the implications of volume in conjunction with price levels will be pivotal in navigating this volatile market.
Indicators to Watch: Moving Averages and Momentum Signals
The utility of moving averages, such as the 10-period EMA and the 200-period SMA, is paramount in forming a comprehensive analysis of Bitcoin’s price action. Presently, these indicators have continued to signal a bullish outlook, underscoring the structural strength of Bitcoin’s overall price trajectory. Traders should pay close attention to how price interacts with these averages, as movement above or below key moving averages could significantly sway market sentiment and trading strategies.
In conjunction with moving averages, momentum indicators like the RSI and MACD provide valuable insights into the prevailing market condition. While current momentum readings point towards residual bullish pressure, fluctuations in these indicators can serve as early warning signals for potential shift patterns. Therefore, integrating moving averages and momentum analysis into trading strategies will be essential for identifying both short-term opportunities and longer-term investment considerations.
Global Market Influences on Bitcoin Prices
As a key player within the cryptocurrency market, Bitcoin is significantly influenced by global economic events and trends. Factors such as regulatory developments, economic data releases, and macroeconomic conditions can sway market participants’ sentiments, thereby impacting Bitcoin’s price movements. For instance, recent discussions around cryptocurrency regulations may evoke feelings of caution among traders, resulting in diminished volume and price consolidation.
Moreover, Bitcoin’s correlation with traditional markets can also illustrate its price behavior amidst broader economic shifts. A downturn in stock indices often leads to increased movement in the cryptocurrency market, as investors may seek alternative assets for diversification. Thus, it becomes vital for Bitcoin traders to remain aware of global economic trends, as these often dictate the flow of capital into or away from Bitcoin, consequently affecting its volatility and pricing trends.
Preparing for Bitcoin Market Volatility
In anticipation of potential market volatility, Bitcoin traders should hone their strategies to accommodate the fickle nature of cryptocurrency price movements. Recognizing the characteristic volatility of Bitcoin, characterized by rapid price changes, traders must prepare for scenarios where swift price movements can occur. Setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit orders can serve as mechanisms to protect investments while allowing traders to capitalize on favorable conditions.
Moreover, conducting a thorough analysis of price patterns and market sentiment indicators can empower traders to make informed decisions amid volatility. Employing risk management techniques and remaining adaptable to rapid changes will ultimately enhance traders’ ability to navigate through Bitcoin’s volatile trading landscape effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Bitcoin price analysis guide traders in the cryptocurrency market?
Bitcoin price analysis provides traders with insights into market trends and potential price movements based on historical data and technical indicators. By understanding BTC price prediction models, traders can make informed decisions regarding entry and exit points for trades in the cryptocurrency market.
What are the key resistances and supports to watch for in Bitcoin price analysis?
In Bitcoin price analysis, key resistances are levels where the price struggles to move higher, while supports are levels where the price may bounce back up. For example, support around $110,800 and resistance near $111,800 have been identified as critical levels in recent Bitcoin trading activities.
What does a bullish trend indicate in Bitcoin price analysis?
A bullish trend in Bitcoin price analysis indicates that the price is expected to rise, often supported by patterns such as bullish engulfing formations and strong trading volume. Identifying these trends helps traders capitalize on upward price movements effectively.
Why is volume important in Bitcoin price analysis?
Volume is crucial in Bitcoin price analysis as it reflects the strength of price movements. A high volume during price breakouts indicates strong buying interest, while declining volume can suggest potential reversals or consolidations, impacting BTC price predictions.
What role do moving averages play in Bitcoin price analysis?
Moving averages play a significant role in Bitcoin price analysis by smoothing out price data to identify trends over specific periods. They help confirm bullish or bearish signals, guiding traders in making timely decisions in the cryptocurrency market.
How can traders interpret indecision in Bitcoin price analysis?
Indecision in Bitcoin price analysis is often indicated by smaller candle bodies on price charts, suggesting a pause in market momentum. Traders should remain cautious and await confirmation signals before making moves in Bitcoin trading, especially if prices are near critical resistance levels.
What are the implications of Bitcoin’s price fluctuations in short-term trading strategies?
Bitcoin’s price fluctuations create opportunities for short-term trading strategies. Traders can capitalize on price oscillations between support and resistance levels, as illustrated by recent movements around $110,500 to $111,500, which are essential for determining entry and exit points.
How do oscillators influence Bitcoin price analysis?
Oscillators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Stochastic, provide insights into market momentum and potential overbought or oversold conditions in Bitcoin price analysis. These tools help traders assess whether to enter or exit positions based on current price trends.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Price Range | Bitcoin fluctuated between $110,936 and $111,110, with a broader intraday range of $108,644 to $111,742. |
| Market Capitalization | $2.20 trillion, with a 24-hour trading volume of $39.70 billion. |
| Short-Term Trend | Bitcoin shows a continuation of a short-term uptrend from the $98,240 support level. |
| Resistance and Support Levels | Resistance at $112,000 with support around $110,800. |
| Momentum Indicators | Mixed indicators show caution with potential bullish continuation if key levels are sustained. |
| Bull Verdict | Bitcoin is structurally sound as long as it stays above $110,000 and reclaims $112,000 with volume. |
| Bear Verdict | Inability to sustain momentum may trigger a deeper retracement towards $108,500–$109,000 if support fails. |
Summary
Bitcoin price analysis indicates that the cryptocurrency is currently at a pivotal point. As traders closely observe the support and resistance levels, the mixed signals from momentum indicators reflect market indecision. Maintaining a price above $110,000 and overcoming $112,000 with increased volume could lead to new highs, reinforcing the bullish outlook. However, any failure in support could signal a deeper pullback, demanding caution among investors. Therefore, it remains critical for market participants to stay vigilant regarding these key price levels.