Morgan Stanley Second-Quarter Results Exceed Expectations
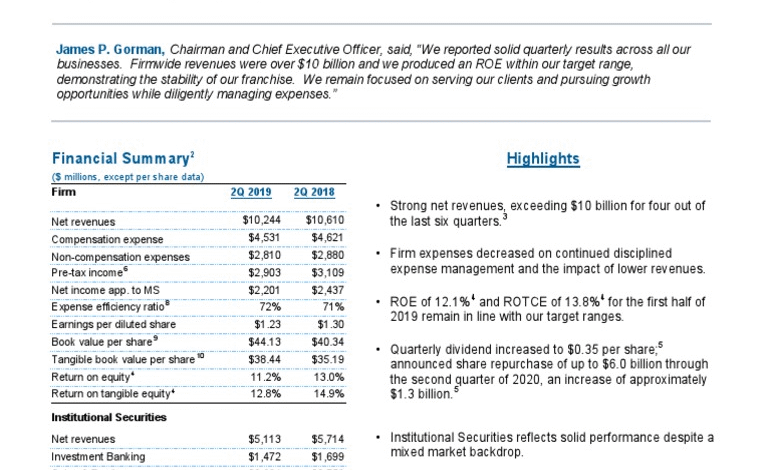
Morgan Stanley second-quarter results have showcased impressive financial performance, exceeding Wall Street expectations and highlighting the bank’s resilience in a fluctuating market. The recently released earnings report reveals a notable net income increase of 15%, reaching $3.54 billion, bolstered by strong trading revenues. With earnings per share hitting $2.13 against the anticipated $1.96, it’s clear that the firm has significantly outperformed analyst predictions. Additionally, wealth management growth played a vital role, contributing $7.76 billion in net revenue as more clients engaged with the firm’s asset management services. Overall, Morgan Stanley’s latest performance signals a robust standing amidst ongoing financial market challenges, making it an eye-catching report for investors and analysts alike.
The latest quarterly financial performance from Morgan Stanley has revealed substantial gains that surpass the projections set by market analysts. This earnings report highlights a considerable enhancement in several key areas, including a robust increase in net income as well as growth within the firm’s wealth management sector. Driven by heightened trading activities, the bank demonstrated a remarkable performance that indicates a thriving business model. Investors are particularly intrigued by the firm’s ability to maintain growth despite external challenges, reflecting the bank’s strategic resilience in financial management. Such promising financial results position Morgan Stanley as a formidable player in the competitive landscape of banking and investment services.
Morgan Stanley Second-Quarter Results
Morgan Stanley’s second-quarter results have officially surpassed Wall Street expectations, showcasing a remarkable performance with an earnings per share of $2.13, compared to the anticipated $1.96. This achievement signifies a robust increase in profitability, reflecting the bank’s effective strategies in managing its operations and capitalizing on market opportunities. Notably, the reported net income climbed by 15% to reach $3.54 billion, marking a substantial rise from the previous year. This stellar performance has not only reinforced investor confidence but also demonstrated Morgan Stanley’s resilience amid fluctuating market conditions.
Representatives from Morgan Stanley highlighted the factors contributing to this impressive financial outcome, particularly increased trading revenues that surged due to heightened client activity, specifically in equity trading. The institutional securities segment realized a net revenue of $7.64 billion, indicating a year-over-year improvement from approximately $6.98 billion. Such growth can be attributed to Morgan Stanley’s proactive approach in positioning itself favorably within the competitive landscape, primarily as market volatility often activates trading opportunities. This pattern of success underscores the bank’s adaptability and effectiveness in navigating various market scenarios.
Wealth Management Growth at Morgan Stanley
Another noteworthy aspect of Morgan Stanley’s financial success in the second quarter lies within its wealth management division, which reported a notable growth in net revenues amounting to $7.76 billion. This figure represents a significant increase from the previous year when the wealth management segment generated $6.79 billion. The growth in asset management revenues within this sector reflects the bank’s commitment to enhancing its service offerings and client engagements, ultimately driving client loyalty and business expansion. This highlights Morgan Stanley’s effective investment strategies that cater to diverse client needs.
The continuous enhancement in the wealth management division signals a strategic alignment with market demands, allowing the bank to harness potential revenue streams effectively. While many financial institutions have struggled to maintain substantial growth in this area, Morgan Stanley has effectively differentiated itself by providing personalized services and innovative investment solutions. This focus has resulted in a competitive edge over peers, further solidifying its position in the wealth management industry, which remains a vital component of the bank’s overall revenue portfolio.
Wall Street Expectations vs. Actual Performance of Morgan Stanley
In terms of performance metrics, Morgan Stanley’s second-quarter results were met with bullish sentiments from analysts and investors alike, particularly given the strong earnings compared to Wall Street expectations. The total revenue reached $16.79 billion, outpacing the forecast of $16.07 billion. The unexpected surge in earnings not only showcases the bank’s robust operational capabilities but also aligns with broader economic patterns that suggest a rebound in investment activity as market conditions improve. This stark discrepancy between expectations and outcomes serves as an essential case study for investment analysts.
Analysts have attributed this success to Morgan Stanley’s effective risk management and strategic trading decisions, which enabled the bank to capitalize on market volatility. Such superior performance during challenging market conditions exhibits the resilience of the bank’s business model, which has been crucial in positioning itself favorably for future growth. The consistent performance of Morgan Stanley as seen in this quarter serves as a benchmark for its colleagues and emphasizes the importance of strong leadership and a clear vision in achieving sustained profitability.
Implications of Morgan Stanley’s Earnings Report
The implications of Morgan Stanley’s earnings report extend beyond just impressive numbers; they resonate throughout the financial sector, influencing market perceptions and peer performances. A significant rise in net income, reported at $3.54 billion, signals to the market that Morgan Stanley is solidifying its place within the finance industry during a period where many navigated headwinds. This increased profitability is likely to enhance investor sentiment, potentially leading to more investments and support for the bank’s future endeavors.
Furthermore, the strong earnings performance may set a precedent for other financial institutions observing Morgan Stanley’s tactics. As the bank has demonstrated an ability to outpace Wall Street’s predictions, competitors may need to reassess their strategies to realign with evolving market conditions. This could potentially create a ripple effect, prompting other banks to enhance their operational efficiency and focus on client engagement, particularly in wealth management and trading divisions, which have proven to be lucrative for Morgan Stanley.
Morgan Stanley’s Stock Performance Post-Earnings
Despite the impressive results from its second-quarter earnings report, Morgan Stanley witnessed a decline in its stock price, falling more than 2% following the announcement. This counterintuitive outcome highlights the complexities involved in market reactions to earnings reports. The increase in stock price throughout the year—approximately 10%—suggests that while investors maintain a long-term positive outlook, short-term movements can be influenced by various external factors beyond the fundamental performance metrics.
Investor behavior post-earnings can often reflect broader market sentiments, possibly leading to cautious trading patterns. As evidenced, a combination of market volatility, sector performance, and general economic outlook can sway stock prices independent of strong earnings reports. For Morgan Stanley, maintaining investor confidence will require continued emphasis on delivering strong results and transparently communicating strategies that address any concerns emerging from minor stock fluctuations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were the key highlights from Morgan Stanley’s second-quarter results?
Morgan Stanley’s second-quarter results notably exceeded Wall Street expectations, showcasing an earnings per share of $2.13 compared to the anticipated $1.96. The reported revenue was $16.79 billion, outpacing estimates of $16.07 billion. Additionally, net income rose by 15% to $3.54 billion from $3.08 billion a year earlier, reflecting strong performance in trading revenues and robust wealth management growth.
How did trading revenues contribute to Morgan Stanley’s earnings report in the second quarter?
In its second-quarter earnings report, Morgan Stanley highlighted a significant increase in trading revenues, with institutional securities net revenue reaching $7.64 billion, up from approximately $6.98 billion a year ago. This surge was attributed to heightened client activity in equity trading, which played a crucial role in surpassing Wall Street expectations.
What was the growth in wealth management for Morgan Stanley as reported in the second quarter?
Morgan Stanley reported robust growth in its wealth management segment during the second quarter, with net revenues increasing to $7.76 billion from $6.79 billion in the previous year. This 14% growth underscores the bank’s strong performance in asset management and reflects its continued focus on this key area of business.
Did Morgan Stanley meet Wall Street expectations in its second-quarter earnings report?
Yes, Morgan Stanley significantly exceeded Wall Street expectations in its second-quarter earnings report. Analysts had predicted earnings per share of $1.96 and revenue of $16.07 billion, whereas the actual results were $2.13 per share and $16.79 billion in revenue, indicating strong financial performance driven by increased trading revenues.
What impact did the second-quarter results have on Morgan Stanley’s stock performance?
Following the release of its second-quarter results, Morgan Stanley’s stock experienced a decline of more than 2%. Despite this immediate reaction, shares have shown a year-to-date increase of approximately 10%, reflecting overall positive investor sentiment amidst solid earnings performance.
What does Morgan Stanley’s net income increase signify in the second quarter?
Morgan Stanley’s net income increased by 15% in the second quarter, rising to $3.54 billion from $3.08 billion the previous year. This increase signifies strong operational efficiency and successful revenue generation strategies employed by the bank, particularly in the context of changing market conditions.
How has Morgan Stanley performed in terms of consistent earnings over recent quarters?
Morgan Stanley has demonstrated consistent earnings performance, achieving six consecutive quarters of robust results. This trend reflects the bank’s ability to navigate various market environments effectively, as highlighted by CEO Ted Pick in the recent second-quarter earnings report.
What factors contributed to Morgan Stanley’s strong second-quarter performance?
Key factors contributing to Morgan Stanley’s strong second-quarter performance included increased trading revenues driven by elevated client activity, significant growth in wealth management revenues, and overall improved market conditions. These elements combined enabled the bank to surpass analyst expectations in its earnings report.
| Description | Morgan Stanley Q2 Results | Wall Street Expectations |
|---|---|---|
| Earnings per Share | $2.13 | $1.96 expected (increase of 8.67%) |
| Revenue | $16.79 billion | $16.07 billion expected (increase of 4.48%) |
| Net Income | $3.54 billion (up 15%) | $3.08 billion last year |
| Institutional Securities Net Revenue | $7.64 billion (up from $6.98 billion) | N/A |
| Wealth Management Net Revenues | $7.76 billion (up from $6.79 billion) | N/A |
Summary
Morgan Stanley second-quarter results indicate a remarkably strong performance driven by increased trading revenues and a solid growth in both institutional and wealth management segments. The bank’s earnings exceeded expectations significantly, showcasing resilience in varying market conditions, and affirming management’s confidence in future profitability.




