Render Token Price Analysis: A Strong Rebound to Watch
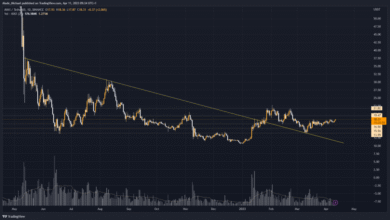
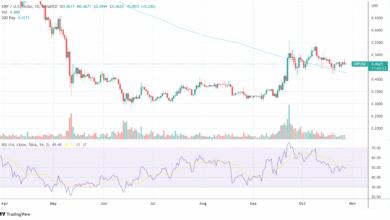
Render Token price analysis reveals a significant shift in momentum as RNDR has recently rebounded from a prolonged period of weakness. With a remarkable 28% surge over the past week, this AI-focused cryptocurrency has emerged as one of the top performers among the 100 largest digital assets. Starting its resurgence at a low of $2.51, RNDR’s price has accelerated to approximately $3.93, benefitting from a broader recovery linked to Nvidia’s stock, which has also seen a boost of around 30%. This analysis also highlights critical resistance levels, particularly the area between $4.03 and $4.43 that the bulls need to overcome to maintain upward momentum. As investors turn their attention to RNDR price prediction amidst notable cryptocurrency market trends, the potential for further gains could be unfolding, depending on how well buyers manage to hold the price above these pivotal points.
Examining the latest developments in Render Token (RNDR), we notice an encouraging trend as the cryptocurrency breaks free from its prior struggles, indicating a potential reversal in its market dynamics. With recent trading data reflecting a robust price increase, Render Token is gaining attention not only for its strong performance but also for the correlation with Nvidia’s market movements. As we delve into factors influencing RNDR, key elements such as resistance levels and the possibility of a rebound from recent lows become essential for traders and enthusiasts alike. Understanding the broader implications of RNDR’s price trajectory within the context of cryptocurrency market trends can provide valuable insights for investors looking to navigate this volatile space. Hence, keeping an eye on the RNDR price action and its interactions with pivotal price zones will be crucial going forward.
Render Token Price Analysis: A Reversal in the Market
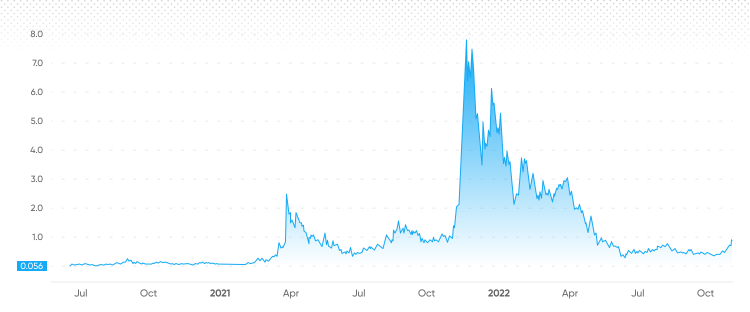
Render Token (RNDR) has showcased a remarkable ability to rebound, experiencing a significant price increase of 28% within just seven trading days. This bullish momentum has positioned RNDR as one of the leading performers among the top 100 cryptocurrencies, showcasing its resilience in a competitive market. Starting from a low point of $2.51 last Monday, the token surged to approximately $3.93, indicating a robust recovery that’s closely aligned with the resurgence of Nvidia’s stock prices, which similarly have appreciated by about 30%. This correlation highlights the potential influence of technological advancements and market sentiment on RNDR’s price trajectory.
For investors and traders looking at RNDR price predictions, the current price movements suggest a bullish trend if the token can consistently increase above critical resistance levels. The $4.03 to $4.43 resistance area is particularly crucial; a sustained breakout beyond this threshold could indicate further upward momentum toward the $5.37 mark. This potential advancement serves as an intermediate goal before reaching the pivotal level at $6.56, which has historically acted as a significant pivot point for RNDR. Establishing a foothold above this level could enhance bullish sentiments among traders, further driving RNDR’s price in a favorable direction.
Nvidia Stock Impact on RNDR Prices
The close relation between Nvidia’s stock performance and Render Token’s recovery is noteworthy, especially in the context of technological cryptocurrencies. Nvidia has been a dominant player in the graphics processing market, and its stock price directly impacts investor sentiments across tech-related tokens. As Nvidia’s shares have climbed, RNDR has mirrored this trend, underscoring the interconnectedness of technology stocks and their associated cryptocurrencies. This relationship implies that ongoing developments in Nvidia’s business or advancements in AI technology may foster increased demand for the Render Token as developers and creators seek efficient solutions for rendering graphics.
Market participants should pay attention to how Nvidia’s stock continues to perform as it may serve as a leading indicator for RNDR’s subsequent price movements. If Nvidia’s growth trajectory persists, it could enhance Render Token’s visibility among institutional and retail investors alike, potentially triggering a stronger rally. Awareness of Nvidia’s financial health and market responses will be pivotal for forecasting RNDR price movements under varying market conditions.
Resistance Level Analysis for Render Token
Analyzing RNDR’s resistance levels is crucial for predicting future price movements. Currently, the significant resistance identified between $4.03 and $4.43 is paramount. For the bulls to validate the ongoing recovery and confirm a double bottom formation, overcoming this resistance is essential. A decisive break above this zone could pave the way for RNDR to test the next critical level at approximately $5.37, enhancing bullish sentiments and attracting new investors into the market. Furthermore, if the token can reclaim the key level of $6.56, historical data suggests that we may see a subsequent price escalation towards $8.17.
Conversely, if RNDR fails to breach this resistance zone, traders should prepare for potential downward corrections. The technical zone around $3.40 has previously served as critical support; should this level be broken, we might witness a pullback towards earlier lows. Therefore, vigilant monitoring of these resistance and support zones is essential for traders to make informed decisions regarding RNDR to mitigate risks associated with volatility in the cryptocurrency market.
Cryptocurrency Market Trends Affecting Render Token
The broader cryptocurrency market dynamics play a crucial role in influencing the price trends of individual tokens such as Render Token (RNDR). As we look towards upcoming market trends, a general recovery within the cryptocurrency sector could significantly bolster bullish sentiment for RNDR. Market analysts are currently observing various indicators that suggest an uptrend could be on the horizon, especially as more investors return to bullish strategies post any significant market dips. Recent trends reflect a gradual rebuilding of confidence among traders, which could further intensify demand for key cryptocurrencies, including RNDR.
In the context of cryptocurrency market trends, factors such as regulatory developments, technological advancements, and macroeconomic indicators will heavily influence RNDR’s price action moving forward. For instance, if the institutional investment increases in cryptocurrencies, it could lead to a surge in demand and subsequently a price rise for RNDR. Investors must remain attuned to these market changes, as understanding broader cryptocurrency trends will be vital for making informed predictions about Render Token’s future price behavior.
The Future of RNDR: Price Predictions and Market Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of Render Token (RNDR) appears promising, contingent on key resistance levels being breached successfully. Based on recent price movements, analysts speculate that if RNDR can maintain its momentum and break past the resistance level around $6.56, the path towards reaching the target price of $8.17 becomes more realistic. This potential growth is supported by the ongoing technological innovations in the rendering space, driven partly by companies like Nvidia, which bolster market confidence in this niche cryptocurrency.
However, traders should also consider downside risks associated with RNDR. If the price fails to hold above critical support levels, particularly the $3.40 mark, we might witness renewed selling pressure that could push RNDR back toward its previous lows. Nevertheless, as long as the technological fundamentals and market interest in AI-related applications remain strong, the long-term outlook for RNDR continues to tilt towards favorable price predictions.
Understanding Render Token and Its Functionality
Render Token (RNDR) serves a unique function within the blockchain ecosystem, specifically targeting decentralized rendering solutions. By leveraging the power of distributed GPU systems, RNDR enables creators and developers to access high-quality rendering services at reduced costs and increased efficiency. This functionality opens the door for innovative applications in sectors such as gaming, VR, and content creation, making RNDR a pivotal player in the cryptocurrency landscape.
The technological aspects of Render Token not only enhance digital rendering capabilities but also create an essential marketplace where users can exchange GPU power and rendering services. As demand for high-performance graphic solutions continues to rise, RNDR’s utility could translate into increased demand for the token. Investors should keep an eye on developments related to Render Token’s technology and community engagement, as advancements may significantly influence the token’s value in the evolving cryptocurrency market.
Market Sentiment and Render Token Dynamics
Market sentiment plays a substantial role in the price dynamics of cryptocurrencies, including Render Token. The perception and behavioral trends among investors can lead to significant fluctuations in price, making understanding these dynamics crucial. Following the recent upward movement of RNDR, bullish sentiment appears to be gaining traction among market participants. This renewed investor confidence is reflected in higher trading volumes and increased interest from both institutional and retail investors.
Measuring market sentiment involves analyzing various indicators, including social media discussions, news relevance, and overall bullish or bearish trends in the cryptocurrency market. As render token dynamics are closely linked to these variables, sustained positive sentiment could further enhance RNDR’s resurgence. For traders, remaining attuned to market sentiment shifts can provide essential insights and prompt timely actions in their trading strategies.
Technical Analysis of RNDR: Key Indicators to Watch
When conducting a technical analysis of Render Token (RNDR), particular focus should be given to key indicators such as moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and trading volumes. These tools help traders identify potential entry and exit points based on RNDR’s price action. For instance, a bullish crossover in moving averages might indicate a potential buying opportunity, especially if aligned with heightened trading volumes, suggesting strong market backing.
Additionally, monitoring the RSI can provide insights into whether RNDR is nearing overbought or oversold conditions. As the price approaches resistance zones, traders can utilize such indicators to gauge market momentum and make strategic decisions. Technical analysis not only aids in predicting RNDR price trends but also assists in managing risk and optimizing trade performance in the evolving cryptocurrency space.
Risks and Challenges Facing Render Token
Despite the optimistic outlook for Render Token, potential risks and challenges loom over its future. The cryptocurrency market is notorious for its inherent volatility, which can strongly impact the prices of individual tokens, including RNDR. Factors such as regulatory changes, market manipulation, and macroeconomic events can trigger drastic price swings, posing risks for investors. For example, should regulatory bodies impose stringent guidelines on the cryptocurrency sector, it could adversely affect investor sentiments and lead to declines in token values.
Another potential challenge lies in the competitive landscape of cryptocurrencies focused on rendering and graphic services. As more projects enter this space, RNDR may face increased competition, possibly affecting its market share and utility appeal. Thus, investors must continuously monitor industry trends and be prepared for potential market shifts that could impact RNDR’s performance. Considering these risks allows traders to hedge their positions effectively and make informed decisions concerning their investments in Render Token.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current price analysis for Render Token (RNDR)?
The current price analysis for Render Token (RNDR) shows a significant recovery, with a price increase of approximately 28% over the past week, rising from a low of $2.51 to $3.93. This momentum is part of a broader trend influenced by the recovery of Nvidia stock.
How does Nvidia’s stock impact Render Token price analysis?
Nvidia’s stock recovery, with a 30% gain, positively influences Render Token price analysis. As RNDR is linked to the AI and GPU sector, Nvidia’s performance can enhance investor confidence in RNDR, leading to a potential price rebound.
What is the RNDR price prediction considering current market trends?
The RNDR price prediction suggests that if bulls succeed in breaking through resistance levels between $4.03 and $4.43, there is an increased chance of further gains towards $5.37 and eventually $6.56, contingent on broader cryptocurrency market recovery.
What are the critical resistance levels for Render Token price analysis?
In the Render Token price analysis, the critical resistance levels are identified between $4.03 and $4.43. A sustainable breakthrough in this area could signal potential advancements toward higher price targets around $5.37 and $6.56.
What support levels should investors monitor in Render Token price analysis?
Investors should monitor support levels between $2.79 and $2.51 in the Render Token price analysis. If the price falls below these levels, there could be an increased risk of further decline towards the previous lows or even down to $2.00.
What could indicate a rebound for Render Token based on price analysis?
A rebound for Render Token, based on price analysis, would be indicated by a successful breakout above the resistance zone of $4.03 to $4.43. Moreover, continued bullish momentum could lead to a retest of higher levels, specifically the pivotal mark of $6.56.
How does recent price activity affect RNDR price prediction?
Recent price activity, showing an uptrend with a rise to $3.93, positively affects RNDR price prediction, suggesting that with continued buying pressure, the token could target levels of $5.37 and $6.56 in the near future.
What should investors know about RNDR’s potential downside risks?
Investors should be aware that downside risks in Render Token price analysis include a potential decline back to the $3.40 support zone if bullish momentum falters, with further risks of dropping to $2.00 if the bears maintain control.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Recent Performance | Render Token (RNDR) has experienced a 28% increase over the last week. |
| Current Price | After starting at $2.51, the price has risen to $3.93. |
| Resistance Levels | Key resistance is between $4.03 – $4.43; breaking this zone is critical for further gains. |
| Next Price Targets | If the upper resistance is overcome, a move towards $5.37 and $6.56 is likely. |
| Support Levels | Key support lies at $3.40 and possibly lower to $2.79 – $2.51 if sellers take control. |
| Bearish Scenario | If downward momentum increases, prices might drop to $2.00. |
Summary
Render Token price analysis indicates a significant recovery from recent lows, with the price climbing to $3.93 following a broader bullish trend in the crypto market. To ensure continued upward momentum, RNDR must overcome resistance in the $4.03 to $4.43 range. Success here could pave the way for further advances towards $5.37 and ultimately toward the crucial $6.56 mark. Traders should watch for support at $3.40, with the potential for further declines if the price fails to hold key levels.