Tesla Optimus Robotics: Milan Kovac Announces Departure
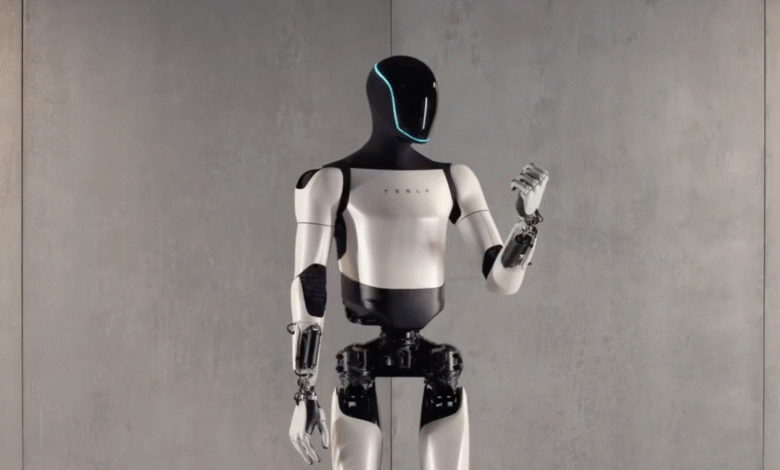

Tesla Optimus robotics is swiftly becoming a focal point in the world of humanoid technology, as the company pushes the boundaries of innovation under the leadership of influential figures like Milan Kovac. Recently, Kovac shocked the industry by announcing his departure from Tesla, where he was pivotal in advancing the development of the Optimus humanoid robot. This cutting-edge technology is designed to perform diverse tasks from manufacturing to caregiving, marking Tesla’s ambitious stride into robotics alongside CEO Elon Musk’s visionary aims. As Tesla prepares for builds on its Fremont pilot production line in 2025, the buzz surrounding Tesla robotics news indicates a future where humanoid robots could significantly impact industries. With a goal to catapult market capitalization to unprecedented heights, the unveiling of humanoid robots in 2025 is anticipated to revolutionize labor and productivity across various sectors.
The realm of automated solutions is abuzz with excitement as Tesla’s advancements in robotic technology, particularly through the development of their humanoid robots, come into sharper focus. Milan Kovac, a key player at Tesla, has been integral in steering the initiative towards creating a versatile bipedal robot that can handle numerous everyday tasks. As we look ahead, the landscape of automation, especially in humanoid machines, is gearing up for a significant transformation in the coming years. Tesla’s efforts in the field of robotics, led by the visionary Elon Musk, promise to redefine what we understand about intelligent machines and their capabilities. The anticipation surrounding these innovations positions Tesla as a frontrunner in the humanoid robotics race, showcasing the potential for these devices to integrate seamlessly into both industrial applications and personal assistance roles.
Tesla Optimus Robotics: A New Era of Humanoid Innovation
Tesla Optimus robotics is at the forefront of innovation, with its ambitious plans to harness advanced technology in humanoid forms. As explained by Milan Kovac, departing vice president for Optimus, the company aims to develop an intelligent robotics solution that can seamlessly integrate into everyday tasks – from manufacturing in their plants to home assistance. This vision embraces technological advancements with the goal of significantly enhancing operational efficiency and improving quality of life. Tesla has scheduled the production line for Optimus robots in Fremont for 2025, signifying its commitment to entering the humanoid robotics market effectively.
The field of humanoid robotics has recently gained significant attention, with innovators like Elon Musk driving forward the ambitions of companies like Tesla. The potential of the Optimus humanoid robot extends beyond simple mechanized tasks; it is designed for adaptability and intelligence. Tesla’s strategy includes deploying these robots to perform myriad tasks, which could disrupt traditional job markets while also creating new opportunities. As the company prepares for broader deployment, all eyes are on how well Optimus can deliver on these promises and reshape industries by 2025.
Milan Kovac’s Legacy: Paving the Path for Future Robotics
Milan Kovac played a pivotal role in Tesla’s journey into humanoid robotics, contributing to concepts that have the potential to revolutionize the sector. His insights, cultivated through years of experience and direct mentorship from Elon Musk, underscore the importance of having a forward-thinking approach in robotics development. Kovac’s departure from Tesla marks the end of an era, but his influence can be seen as planting seeds for a new generation of robotic innovation. His focus on resilience and engineering fundamentals will undoubtedly inspire future robotics engineers.
With Tesla’s robotics news echoing across the industry, the legacy of figures like Kovac becomes more significant. His public expression of gratitude towards Musk highlights a culture of innovation cultivated at Tesla, which sets it apart from competitors like Boston Dynamics and Agility Robotics. As the industry looks ahead to 2025, the impact of leaders like Kovac will resonate through their commitment to enhancing humanoid technology and adjusting to the increasing demand for intelligent automation solutions.
The Future of Humanoid Robots: Tesla’s Bold Vision for 2025
The market for humanoid robots is set to explode by 2025, aided by Tesla’s ambitious goals articulated by Elon Musk. Tesla’s development of the Optimus robot aims to create a practical and advanced solution for a variety of tasks, from simple activities to more complex roles. The company’s directed approach, focusing on ‘primitive tasks’ like object manipulation, serves as the foundation for achieving a versatile humanoid robot. As industries gear up for a more automated future, the significance of achieving autonomy and efficiency through robotics cannot be overstated.
In examining Tesla’s preparations, it becomes clear that the company is not merely trying to keep pace with competitors but is instead aiming to lead a paradigm shift in the robotics space. By integrating artificial intelligence with humanoid functionality, Tesla’s Optimus can shape the landscape of labor in sectors traditionally reliant on human workforce. The company’s commitment to innovation will foster an environment where robots serve as productive partners rather than replacements, emphasizing collaboration in future workplaces.
Elon Musk’s Ambitious Robotics Goals and Market Implications
Elon Musk’s vision for Tesla extends beyond automobiles into the realm of robotics, specifically with the introduction of the Optimus humanoid robot. During discussions about future market capitalizations, Musk’s optimistic perspective foresees an impact of $25 trillion for Tesla if their robotic ambitions succeed. This ambitious outlook reflects Musk’s longstanding belief in transforming industries through technology while addressing imminent societal shifts in labor dynamics. The intersection of technology and economics brought forth by Tesla highlights the significant implications robotic automation will have in the coming years.
Musk’s insights also underscore the growing competition within the humanoid sector, especially against established players. With rivals like Apptronik and Figure also developing humanoid solutions, it is clear that the race for advancing robotics capabilities is more competitive than ever. As companies push the envelope in engineering and design, the implications for the labor market are immense, hinting at potential job transformations and new roles that may arise in the face of automation. The future of the workforce will likely require an adaptive approach, where humans and humanoid robots coalesce harmoniously.
Key Competitors in the Humanoid Robotics Sector
The humanoid robotics market is becoming increasingly competitive, with several key players striving for technological superiority and market share. Companies like Boston Dynamics and Agility Robotics are notable competitors that have been making waves with their own advancements, from agile movement to nuanced precision in task execution. Tesla’s commitment to developing Optimus is not only a challenge to these companies but also a push for innovation that could redefine the standards of robotic capabilities and integration.
With leaders like Milan Kovac and Elon Musk at the helm of Tesla’s strategies, there’s a clear ambition to set new benchmarks in humanoid robotics. As new entrants and established companies alike continue to innovate, the emphasis on collaboration, safety, and versatility will be pivotal in shaping the future landscape. This competitive spirit in the sector will likely accelerate advancements, allowing for more sophisticated and capable robots that can perform an ever-expanding range of tasks.
The Potential Market Impact of Tesla’s Humanoid Robots
The introduction of Optimus humanoid robots could lead to major shifts in market dynamics, particularly for sectors heavily reliant on manual labor. As Tesla gears up for its production timetable, there’s a palpable sense of anticipation regarding how these robots will redefine efficiency across industries. Whether at Tesla’s own facilities or in the broader market, the capacity for humanoid robots to perform various tasks could lead to increased productivity and cost efficiency, significantly benefiting businesses that adopt this technology.
However, this transformation does bring challenges, particularly in labor displacement and the need for reskilling workers. The deployment of humanoid robots raises questions about the future of jobs traditionally held by humans. The balance between robots enhancing productivity while ensuring job security is critical as society navigates this technological transition. As stakeholders in various industries monitor Tesla’s progress, the implications of these advancements will undoubtedly shape discussions around workforce integration and the evolving role of automation.
Elon Musk and the Vision of Intelligent Robotics
Elon Musk has long been a visionary in the tech realm, and his latest pursuits in robotics underscore his commitment to pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Tesla’s Optimus project aims to create a highly intelligent humanoid that can adapt to various environments and tasks, reflecting Musk’s philosophy of using technology to enhance human capabilities. This alignment of AI and robotic design seeks to create solutions that not only automate but also complement human efforts in the workplace and beyond.
Musk’s optimism regarding robotics is contagious, fueling excitement within the tech community as well as skepticism about the feasibility of such ambitious goals. Nevertheless, his directives have proven successful in past projects, instilling faith in stakeholders that Tesla’s vision for the future of robotics could yield significant breakthroughs. The narrative surrounding intelligent robotics is shifting, emphasizing that collaboration between humans and machines will be the focal point of upcoming innovations.
Future Predictions: Humanoid Robots in Everyday Life by 2025
As we approach 2025, the mantra of ‘humanoid robots in everyday life’ is becoming more than just a futurist’s dream; it’s shaping into a plausible reality. Tesla’s Optimus robots are being designed with practical applications in mind, promising to assist in various daily tasks that could range from mundane to complex. As early prototypes emerge from production, the societal embrace of such technology is crucial in determining how seamlessly these robots integrate into households and businesses.
The transformation envisioned by Tesla is multifaceted; from providing invaluable support in home environments to revolutionizing factory operations, the implications of having humanoid robots in everyday life are profound. The community’s readiness to adopt these innovations will dictate their success and acceptance. Given this trajectory, by 2025, society may not just witness robots performing specific tasks but rather ecosystems where humans and humanoid robots interact fluidly, changing the fabric of daily routines.
Milan Kovac’s Influence on Robotics Engineering at Tesla
Milan Kovac’s departure marks a significant point in Tesla’s Optimus journey, leaving behind a legacy defined by innovation and resilience in the field of robotics engineering. His influence on the development of Optimus is seen in the thoughtful approach to integrating engineering principles with advanced robotics capabilities. Kovac’s focus on fundamental engineering principles has shaped a robust framework for the ongoing development of Tesla’s humanoid robots, ensuring that they are not only functional but also reliable.
His perspective on engineering challenges and problem-solving has inspired a culture within Tesla that values creativity and persistence. As Tesla continues to pursue its vision in humanoid robotics, Kovac’s contributions will resonate in future designs and strategies. The legacy of leadership and ingenuity he leaves behind will undoubtedly influence the next generation of robotics engineers at Tesla and beyond, paving the way for exciting developments in the field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key features of the Tesla Optimus humanoid robot?
The Tesla Optimus humanoid robot is designed to be a bipedal, intelligent machine capable of performing a variety of tasks. Key features include advanced robotics technology for mobility, AI systems for task execution, and the ability to adapt to different environments such as factories or homes.
Who is Milan Kovac and what was his role in Tesla Optimus robotics?
Milan Kovac was the vice president in charge of Tesla Optimus robotics, overseeing the development of the humanoid robot project. He joined Tesla in 2016 and played a crucial role in advancing the Optimus initiative, contributing to its vision of deploying robots for real-world applications by 2025.
What is the expected timeline for Tesla Optimus robotics deployment?
Tesla anticipates that builds of the Optimus humanoid robot will begin in 2025, with plans for broader deployment across factories to perform useful tasks, following successful pilot productions at their Fremont facility.
How does Elon Musk envision the future of Tesla robotics?
Elon Musk envisions Tesla robotics, particularly with the Optimus humanoid robot, as transformative for the company, potentially elevating its market capitalization to $25 trillion. He believes these robots will revolutionize how tasks are performed in various sectors.
What primitive tasks is Tesla training the Optimus robots to perform?
Tesla is currently training its Optimus systems to handle primitive tasks such as picking up objects and throwing balls, focusing on basic functionalities that will lay the groundwork for more complex operations in the future.
Who are Tesla’s competitors in humanoid robotics?
Tesla faces competition in the humanoid robotics sector from companies like Boston Dynamics, Agility Robotics, Apptronik, 1X, and Figure, all of which are developing advanced humanoid solutions for various applications.
What was Milan Kovac’s previous position before leading Tesla Optimus robotics?
Before becoming vice president of Tesla Optimus robotics in 2022, Milan Kovac served as the director of Autopilot software engineering, where he contributed to advancements in Tesla’s self-driving technology.
How has Tesla communicated updates on its Optimus humanoid robot developments?
Tesla has communicated its Optimus developments through investor presentations and posts on social media, including updates on milestones and the expected timeline for production and deployment.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Milan Kovac’s Departure | Tesla’s vice president in charge of Optimus robotics, Milan Kovac, announced his departure from the company. He had been with Tesla since 2016 and worked directly under CEO Elon Musk. |
| CEO’s Gratitude | Elon Musk expressed his gratitude for Kovac’s contributions on social media, highlighting the skills and lessons learned during their decade of collaboration. |
| Optimus Production Timeline | Tesla aims to build the Optimus humanoid robots on a pilot production line in Fremont, scheduled for 2025, with plans for wider deployment of the bots for various tasks in factories. |
| Capabilities of Optimus | The Optimus robots are intended to be intelligent bipedal robots, capable of performing tasks ranging from factory work to babysitting. |
| Market Impact | Musk has stated that the introduction of humanoid robots could potentially elevate Tesla’s market capitalization to $25 trillion. |
| Competitors in Robotics | Tesla faces competition in the humanoid robotics sector from companies like Boston Dynamics, Agility Robotics, Apptronik, 1X, and Figure. |
| Kovac’s Previous Role | Before leading the Optimus project, Kovac was the director of Autopilot software engineering. |
Summary
Tesla Optimus robotics is rapidly becoming a significant topic of discussion in the tech world, particularly following the announcement of Milan Kovac’s departure from Tesla. The abilities and projected impact of the Optimus humanoid robots are anticipated to revolutionize various tasks, from manufacturing to possibly domestic duties. With significant backing from Elon Musk and a clear timeline for production, Tesla remains poised to become a leader in the humanoid robotics field. As developments unfold, the potential for Optimus to reshape market dynamics and increase Tesla’s valuation continues to generate excitement and speculation in the robotics industry.