Bitcoin Halving: Understanding Its Impact on Prices and Miners
Bitcoin halving is a pivotal event in the cryptocurrency world that occurs approximately every four years and has a profound effect on the Bitcoin economy. On April 20, 2024, the fifth halving cycle began, significantly reducing the block subsidy miners receive and impacting the Bitcoin inflation rate and miner returns. This deflationary mechanism not only generates a supply shock but may also influence Bitcoin price forecasts as the halving event historically leads to price increases. With a recent surge in Bitcoin’s hashrate, the anticipation of future price growth incentivizes miners, despite the decreased rewards per block mined. Understanding the impact of Bitcoin halving is crucial for anyone interested in the cryptocurrency market, as it shapes the landscape for both investors and miners alike.
The term ‘Bitcoin halving’ refers to a critical threshold in the Bitcoin ecosystem where the rewards for mining new blocks are cut in half, affecting both miners and market investors. It is also known as the halving event, a mechanism embedded in the Bitcoin protocol designed to control the cryptocurrency’s inflation and manage its supply over time. As mining rewards dwindle, the anticipated consequences on the Bitcoin price and miner economics come into focus, especially in light of the relationship between Bitcoin’s hashrate and future price movements. This unique event not only reshapes Bitcoin’s inflation rate but also serves as a barometer for the broader crypto market sentiment. As we delve into the effects of this phenomenon, we explore its implications on Bitcoin miner returns and the overall economic landscape surrounding this leading digital currency.
Understanding Bitcoin Halving: A Key Event in Cryptocurrency
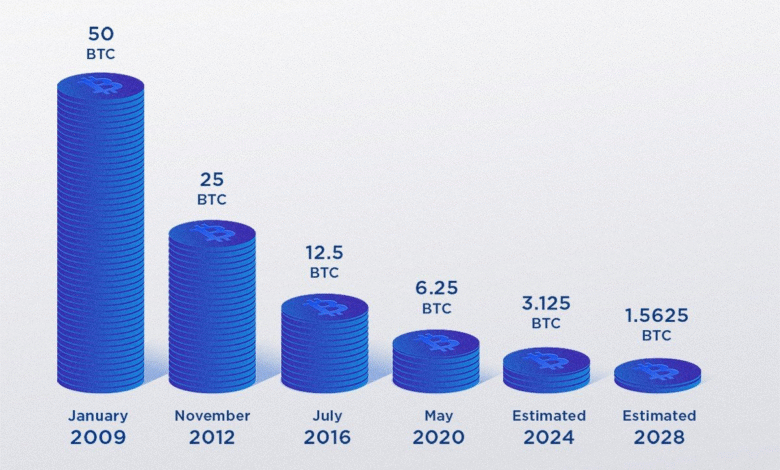
Bitcoin halving is a significant occurrence that plays a vital role in the dynamics of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. This event happens approximately every four years when the Bitcoin network reduces the block reward received by miners for confirming transactions. The last halving took place on April 20, 2024, diminishing the block subsidy from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC, effectively curtailing the influx of new coins into the market. This deliberate configuration, overseen by Bitcoin’s core protocol, results in a supply shock that historically drives up Bitcoin prices as demand surges amid dwindling supply.
Moreover, understanding the mechanics of Bitcoin halving is essential for investors and miners alike. It serves as a reminder of Bitcoin’s unique monetary policy compared to traditional fiat currencies, especially in the context of inflation. With the inflation rate of Bitcoin decreasing with each halving, the current estimate post-2024 halving stands at approximately 0.84%. As Bitcoin continues to position itself as a digital store of value superior to gold, recognizing these supply dynamics can aid investors in forming sound price forecasts.
The Impact of Bitcoin Halving on Miner Returns
The implications of Bitcoin halving extend deeply into the mining sector, which forms the backbone of the Bitcoin network. For miners, halving periods represent a challenging yet strategic time. With each halving reducing the rewards for successfully mined blocks, miners must increasingly rely on transaction fees and the prospect of rising Bitcoin prices to sustain their operations. While the immediate effect is a decrease in Bitcoin income, many miners invest in more efficient hardware anticipating future price surges. The expectation of increased Bitcoin miner returns in USD makes it imperative that they adapt to the changing landscape.
However, this model also carries risks. In previous cycles, significant falls in Bitcoin prices during market corrections have posed existential threats to miners, leading to ‘miner capitulation’. The delicate balance between rewards and operational costs has been a vital consideration. The most recent data indicates that while Bitcoin earnings decrease, the USD returns for miners have shown resilience, benefiting from the robust performance of Bitcoin post-halving. Understanding these trends can enhance strategies and preparedness in the mining landscape.
Bitcoin Inflation Rate: Halving’s Effect on Value Preservation
The Bitcoin inflation rate is a critical factor in determining its long-term viability as a store of value. Following the latest halving, this rate has reportedly dropped to around 0.84%, significantly lower than that of gold, which stands at 1.6%. This reduction is a direct outcome of the programmed halving events that strategically manage Bitcoin’s supply. Consequently, as Bitcoin increasingly becomes recognized for its deflationary characteristics, investors are drawn to the idea of holding Bitcoin as a hedge against traditional inflation.
Furthermore, the decreasing inflation rate underscores Bitcoin’s potential to appreciate over time, aligning with the historical price trends observed post-halvings. As miners continue to extract Bitcoin at a lower rate, a sustained demand amidst reduced supply can bolster its price upwards. This phenomenon offers insights into the psychological and economic factors influencing investor behavior towards Bitcoin as an exceptionally global investment asset in the current economic climate.
Analyzing the Bitcoin Hashrate: Post-Halving Trends
The Bitcoin hashrate serves as a barometer for the health and security of the Bitcoin network, reflecting the total computational power utilized by miners. Following the 2024 halving, there has been a notable increase in the hashrate, reaching an all-time high of over one zettahash per second. This trend suggests not only that more miners are joining the network but also that technological advancements in mining hardware are resulting in greater efficiency and contribution to the network’s overall security. As halving events impact miner profitability, the rising hashrate indicates confidence in Bitcoin’s future performance.
Importantly, the rising hashrate also triggers adjustments in mining difficulty, which occurs approximately every two weeks. This automatic adjustment ensures that Bitcoin maintains its ten-minute block generation time. A higher hashrate generally leads to an increase in difficulty, which can further influence miner operations and profitability. Therefore, tracking the hashrate and the corresponding changes in difficulty is essential for understanding the implications of a halving event on the broader miner community and, consequently, Bitcoin’s overall market stability.
Future Price Forecasts: What to Expect After Halvings
Historical trends post-Bitcoin halving events give investors valuable insights into future price forecasts. Analyzing previous cycles reveals consistent upward movement in Bitcoin’s price following halvings—each event has set the stage for substantial appreciation over the ensuing months and years. For instance, post-second halving, Bitcoin surged from around $650 to over $2,500 within a year. Such patterns are encouraging for those considering Bitcoin as a long-term investment, suggesting that the ongoing impacts of supply constraints can lead to price surges.
That said, it’s essential to temper expectations with realism; while the nominal growth of Bitcoin’s price has been impressive, the percentage increase tends to decline with each halving. Currently, as Bitcoin’s market prices approach new highs of around $94,000, investors must remain vigilant regarding market dynamics, investor sentiment, and potential regulatory changes. Long-term projections should factor in these variables to better gauge Bitcoin’s trajectory in the coming years, especially in light of supply constraints exacerbated by future halvings.
The Role of Transaction Fees in Sustaining Bitcoin Mining
As Bitcoin miners navigate the challenges posed by halving events, transaction fees have emerged as a critical component of their revenue model. With the reduction in block rewards, miners are compelled to rely increasingly on transaction fees to cushion the impact of diminished Bitcoin earnings. The efficiency and volume of Bitcoin transactions during busy periods tend to enhance miners’ income, allowing them to maintain operations despite lower rewards. Understanding the correlation between transaction volume and miner returns is therefore fundamental for predicting the sustainability of mining operations.
In this context, the mining industry must adapt by leveraging innovative models that improve transaction efficiency and miner profitability. As the Bitcoin network matures, the increasing reliance on transaction fees could pave the way for a more robust and resilient mining ecosystem. This evolution will be essential in preparing miners for a future where block rewards diminish entirely, thereby forcing them to depend solely on transaction fee revenues post-2140, when the last Bitcoin is mined.
Market Reactions to Bitcoin Halving Events
Market reactions surrounding Bitcoin halving events are often filled with anticipation and speculation, driving volatility leading up to and following the event. This pattern is consistent across past halvings, where significant price movements were noted both pre and post-event. Traders and investors pay close attention to past performance and current market sentiment to capitalize on potential opportunities arising from supply shocks that result from such halvings.
Moreover, the psychology of the market participants plays a crucial role in amplifying these reactions. Speculative buying ahead of the halving can lead to price increases as traders aim to benefit from post-halving price surges. This behavior emphasizes the importance of historical data and trends when making informed investment decisions. Future traders must navigate this complex landscape, balancing hype and fundamentals to leverage the opportunities that bitcoin halving presents.
Understanding the Interplay Between Bitcoin Supply and Demand
The interplay between supply and demand lies at the core of Bitcoin’s valuation, particularly during periods marked by halving events. As the block subsidy decreases following a halving, miners produce fewer Bitcoins, fostering a tight supply in the marketplace. If demand remains steady or increases, this disconnect can lead to substantial price increases, a phenomenon observed consistently in prior cycles. An understanding of this relationship is vital for predicting future price trajectories and the overall health of the Bitcoin market.
Furthermore, as adoption increases and institutional interest grows, we may witness heightened demand dynamics, further exacerbating the effects of supply constraint. With Bitcoin increasingly recognized as a digital gold alternative, investors are carefully observing how halving events influence market behavior. Balancing real-world demand against diminishing supply can provide insights not only into immediate price fluctuations but also long-term investment strategies as Bitcoin solidifies its position as a premier asset in the global financial landscape.
The Future of Bitcoin: Beyond Just Price Predictions
Looking beyond mere price predictions, the future of Bitcoin encompasses a complex array of factors including regulatory environments, technological advancements, and its role in global finance. As Bitcoin matures, it faces challenges and opportunities that will shape its trajectory far beyond the immediate implications of halving events. Adaptation to changing market conditions, along with continuous innovation within the protocol and its ecosystem, will also play critical roles in determining Bitcoin’s future significance.
Moreover, public sentiment, institutional adoption, and geopolitical factors will significantly influence Bitcoin’s development. As it continues to appeal to a broader audience seeking alternatives to traditional financial systems, Bitcoin’s emphasis on decentralization may drive further interest. Consequently, Bitcoin’s evolution will not only drive changes in price forecasts but fundamentally redefine how assets are perceived and valued in the coming years, making it crucial for investors and stakeholders to stay informed and engaged.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Bitcoin halving and how does it impact Bitcoin miner returns?
Bitcoin halving is a predetermined event that occurs approximately every four years, reducing the block subsidy given to miners for each block mined. This halving decreases the total supply of bitcoins, affecting the Bitcoin inflation rate. As the reward decreases, it can initially decrease Bitcoin miner returns in the short-term, but historically, the price of Bitcoin tends to increase over time post-halving, ultimately benefiting miners as the market adjusts.
How does Bitcoin halving affect the Bitcoin price forecast?
Bitcoin halving has historically led to significant price increases due to the reduced supply of new bitcoins entering the market. After each halving event, Bitcoin’s price has seen substantial surges within the months following. For example, after the previous halving in 2020, Bitcoin’s price rose from around $8,821 at the time of the halving to $55,986 a year later. This pattern suggests that Bitcoin halving creates bullish momentum in the market.
What is the impact of Bitcoin halving on the Bitcoin inflation rate?
Bitcoin halving directly impacts the Bitcoin inflation rate by reducing the number of new BTC generated. After the April 2024 halving, Bitcoin’s inflation rate dropped to about 0.84%, making it less inflationary compared to gold’s 1.6%. Each halving further decreases the rate, enhancing Bitcoin’s status as a deflationary asset, albeit it remains disinflationary as its inflation rate is still above zero.
How does Bitcoin hashrate change after a halving event?
Following a Bitcoin halving, the hashrate often increases as miners become more confident about future prices and invest in more efficient mining hardware. The 2024 halving saw the hashrate reaching new all-time highs, indicating increased participation in the network and improved security. This rise in hashrate also affects the mining difficulty, which adjusts roughly every two weeks to maintain an average block generation time.
What challenges do Bitcoin miners face after the halving?
Post-halving, Bitcoin miners face the challenge of reduced earnings per mined block, which can impact their profitability. For instance, while the nominal USD earnings may rise due to increased Bitcoin prices, miner returns in BTC diminish. In bear markets, significant BTC price drops can further threaten miner operations, leading to potential capitulation if revenues from transaction fees do not suffice.
Is Bitcoin a better store of value compared to gold after the last halving?
Yes, following the last Bitcoin halving, the cryptocurrency’s inflation rate of 0.84% is lower than gold’s inflation rate of 1.6%, making Bitcoin a superior store of value. The halving process reinforces Bitcoin’s deflationary characteristics, making it an attractive asset compared to traditional forms of value storage like gold.
When is the next Bitcoin halving scheduled and its expected impact?
The next Bitcoin halving is scheduled for 2028, at which point the block subsidy will be reduced to 1.5625 BTC per mined block. Historical trends suggest that this event will likely have a substantial positive impact on Bitcoin’s price, similar to previous halvings, as it will further decrease the supply of new bitcoins and potentially create upward price pressure in the market.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Date of Fifth Halving | April 20, 2024 |
| Block Subsidy Reduction | Halved from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC |
| Inflation Rate | Post-halving inflation is about 0.84% |
| Hashrate Impact | Increased significantly, reaching over 1 zettahash/second |
| Mining Economic Incentives | Miners invest in new equipment anticipating future price increases |
| Historical Price Trends | Post-halving, Bitcoin’s price rose to about $94,000 from $64,000 |
Summary
Bitcoin halving is a pivotal event in the cryptocurrency world, significantly shaping its economic landscape by reducing inflation and impacting miner rewards. The fifth halving cycle initiated on April 20, 2024, has led to an increase in price, with Bitcoin reaching approximately $94,000 currently. As the hashrate continues to rise and miners invest more into their operations, the long-term effects of the halving could further confirm Bitcoin as a superior store of value compared to traditional assets like gold.