Tariffs Impact on Companies: Costs Surging for Major Firms
The impact of tariffs on companies is becoming increasingly evident, with major corporations like Stanley Black & Decker and Conagra revealing that the financial burden will significantly affect their bottom lines. These tariffs are poised to raise costs, with estimates suggesting that Stanley Black & Decker alone could face an annual hit of $800 million, while Conagra anticipates a $200 million increase in costs due to heightened import prices. Furthermore, Tesla has disclosed that tariffs are responsible for an added $300 million in expenses, affecting both its automotive and energy sectors. Such price hikes could lead to inflation from tariffs if companies eventually pass these increased costs onto consumers. As manufacturers navigate the complexities of tariffs, it’s clear that their impact extends beyond corporate earnings to the broader economy, raising concerns about future consumer pricing and economic stability.
The repercussions of import tariffs on businesses are a critical consideration for companies across various sectors. Leading manufacturers, including Stanley Black & Decker and Conagra, have cautioned stakeholders about the potential for increased operational costs as a direct result of trade policies. The financial strain is not limited to these firms; Tesla has also noted substantial tariff-related expenditures that could influence pricing strategies. With analysts predicting a broader impact on consumer prices, it becomes essential to examine how these trade barriers can create inflationary pressures within the market. Overall, the ongoing discourse surrounding tariffs and their effects exposes intricate dynamics between corporate financial health and consumer economics.
Understanding the Financial Impact of Tariffs on Major Companies
The financial landscape for companies like Stanley Black & Decker and Conagra has been significantly affected by the imposition of tariffs. Stanley Black & Decker, for instance, has announced an expected loss of around $800 million annually due to these tariffs. This staggering figure illustrates the direct financial burden that tariffs impose on manufacturing entities, forcing them to reevaluate their pricing strategies and cost management practices. Not only does this impact profit margins, but it also compels such companies to consider costly mitigation strategies to absorb some of these expenses.
Similarly, Conagra has projected an increase in its cost of goods sold, tallying an excess of $200 million attributed to tariff-related expenses. Such implications reverberate throughout the economy as these corporations represent significant sectors within American manufacturing and retail. The collective financial data from these firms signal a broader concern regarding the sustainability of maintaining competitive pricing amidst rising costs attributable to tariffs, prompting many to evaluate the longevity of their current business models.
Policy Changes and Their Ramifications on Prices
In the arena of corporate finance, rising tariffs inevitably lead to cost increases which trickle down to consumers. Conagra’s anticipated increase of 3% in cost of goods sold is a case in point; this uptick translates directly into higher prices for consumers on products ranging from frozen meals to snacks. As outlined by CEO Sean Connolly, such price adjustments are necessary for offsetting losses incurred from tariffs. Not only does this affect individual consumers, but it also signals a paradigm shift where consumers might need to adapt to a new norm of pricing influenced heavily by global trade policies.
The ripple effect extends beyond groceries, influencing consumer electronics and automotive industries too. For instance, Tesla has reported an increase of approximately $300 million due to tariffs, predominantly affecting its auto sector. Such cost fluctuations raise questions about the viability of consumer purchasing power in an economy where inflation driven by tariffs becomes more prevalent. As consumers feel the pinch of rising prices, the urgency for manufacturers to address these costs becomes increasingly critical.
Projecting Inflation Trends Amidst Tariff Debates
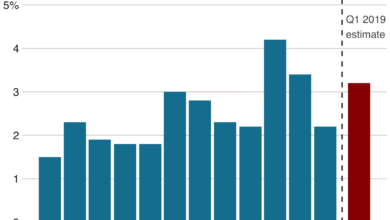
The potential inflationary impacts of tariffs have come under scrutiny as economists forecast significant shifts in consumer price indices. As indicated by Nancy Lazar, the anticipated rise from a core consumer price index rate of 2.1% to 3.2% highlights the real possibility that tariffs will contribute to an inflationary cycle. While current consumer prices have not yet reflected drastic increases, ongoing tariff negotiations carry the potential to push prices higher, bringing about an economic shift that could affect consumer behavior across multiple markets.
Moreover, companies such as Mohawk Industries are already responding to these pressures by instituting price increases as a preemptive measure. This proactive strategy demonstrates the interconnectedness of tariff policies and inflation worries, affecting everything from household goods to industrial products. The implications of such trends illuminate the critical intersection of trade policies and consumer economics, suggesting that the overarching narrative is one where tariffs may not only influence immediate manufacturing costs but also burden consumers with persistent inflation.
Challenges Faced by Manufacturers in Adapting to Tariff Changes
Manufacturers like General Motors and Carrier Global are grappling with the direct fallout from escalating tariffs, represented by a staggering $1.1 billion and $200 million hit respectively. The challenge lies not only in the financial dent caused by tariffs but also in the strategizing required to remain competitive while navigating these costs. These firms must weigh options like cutting operating expenses or absorbing costs to avoid immediate price hikes, but such measures can lead to long-term damage to their profitability if tariffs remain unchanged.
Additionally, manufacturers are compelled to adapt quickly to a rapidly changing policy environment. As tariffs are subject to renegotiation, the uncertainty requires firms to pivot their strategies, allocating resources toward monitoring tariff developments while planning for future cost structures. The ability to adapt is crucial, as evidenced by industry leaders adjusting their operational frameworks in anticipation of more tariff-related legislative changes. Without swift and strategic adaptation, many manufacturers risk long-term repercussions that could threaten survival.
Analysis of Consumer Reaction to Rising Prices from Tariffs
Consumer behavior is a critical component in understanding the full impact of tariffs on businesses. As manufacturers begin passing on tariff-related costs, consumers may reach a tipping point where they either alter their spending habits or seek alternative products. This shifting landscape poses a significant challenge for companies striving to maintain market share while facing a potential backlash from cost-sensitive consumers.
Furthermore, the hesitation in consumer spending can have a domino effect on revenue streams for various industries. For companies like Proctor & Gamble, which is facing potential pretax increases of $1 billion due to tariffs, the challenge intensifies. They must balance the need to adjust prices with the risk of alienating loyal customers, making consumer perception and reaction an essential aspect of pricing strategies in the realm of tariff impacts.
Strategies to Mitigate Tariff Impacts on Business Costs
In light of the financial pressures from tariffs, companies are exploring various strategies to mitigate these impacts on their cost structures. Many firms are investing in supply chain diversification, seeking alternative sources for raw materials that are less affected by tariffs. By reducing reliance on imports from countries subject to high tariffs, manufacturers can potentially lower costs and navigate the complexities of international trade more effectively.
Additionally, some businesses are optimistic about negotiating with suppliers for better rates or exploring domestic production options to reduce tariff exposure. These strategic adjustments highlight a proactive approach to managing the adverse effects of rising tariffs. It becomes increasingly evident that firms that can quickly adapt and innovate in their operational strategies will have a significant competitive advantage in this evolving economic climate.
Long-term Economic Projections Due to Tariff Policies
Long-term forecasts about the economic landscape suggest that the continuation of tariffs on imported goods could lead to lasting changes within industries. Reports indicate that sustained tariffs will keep costs elevated, affecting business investment decisions and potentially leading to a slowdown in economic growth. Firms that rely heavily on imports must continuously reassess their strategies in light of these evolving tariff policies, as maintaining profitability amidst increasing costs becomes a formidable challenge.
Moreover, economists warn that prolonged tariff policies may lead to uncertainty in international trade, hampering growth prospects for major sectors. For instance, the automotive industry, heavily impacted by tariff negotiations, could face a prolonged downturn if manufacturers are unable to adapt successfully. As companies brace for this uncertain future, it underscores the importance of understanding the broader implications of tariff policies on not just individual companies, but on the economy as a whole.
The Role of Government in Tariff Negotiations
The government’s facilitation in tariff negotiations plays a critical role in shaping the business environment for manufacturers. Trade policy discussions led by the U.S. government can directly influence how companies like Tesla, Conagra, and Stanley Black & Decker strategize their financial outlooks. Businesses are closely monitoring these discussions, as they have the potential to either alleviate some of the tariff burdens or exacerbate existing financial challenges.
With recent dialogues suggesting that tariffs may be negotiated down, companies are hopeful for a favorable outcome. However, even minor shifts in policy can set off waves of change, emphasizing the importance of government actions in navigating trade relationships. The delicate balance between protecting domestic industries and encouraging international competition remains a focal point in political discourse, as companies advocate for more adaptive policies that can benefit broader economic growth.
Assessing Corporate Resilience in the Face of Tariff Challenges
Amid the challenges posed by tariffs, corporate resilience has emerged as a vital quality for manufacturers looking to thrive. Firms like Whirlpool and Carrier Global have demonstrated an ability to navigate these turbulent waters through strategic planning and robust risk management. By anticipating potential challenges and diversifying their product offerings or sourcing channels, these companies are showing a commitment to long-term growth despite external pressures.
Moreover, corporate resilience isn’t just about weathering the storm; it’s also about taking calculated risks to invest in innovation and operational efficiency. Businesses that embrace technological advancements and lean manufacturing techniques may find pathways to ease some of the cost burdens imposed by tariffs. As the economic landscape continues to evolve, fostering resilience within corporate structures will be key to sustaining success in a competitive environment driven heavily by tariff impacts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of Stanley Black & Decker tariffs on their financial performance?
Stanley Black & Decker has projected an annual cost increase of $800 million due to tariffs, significantly impacting their financial performance. This figure does not include potential additional costs from mitigation strategies.
How are Conagra tariffs affecting consumer prices?
Conagra has warned that tariffs will increase their cost of goods sold by approximately 3%, translating to over $200 million in annual costs. These additional costs could likely be passed on to consumers, resulting in higher prices for products like Marie Callender’s and Slim Jim.
What are Tesla tariffs costs, and how do they affect the automotive sector?
Tesla has reported that tariffs have led to increased costs of around $300 million, particularly impacting the automotive sector. These costs may force the company to raise vehicle prices to maintain profitability.
How are manufacturers coping with inflation from tariffs?
Manufacturers like Proctor & Gamble have anticipated $1 billion in higher pretax costs due to tariffs. Although some companies have absorbed these costs, the inflation from tariffs may eventually lead to price increases for consumers.
What financial impacts have manufacturers and tariffs had on General Motors?
General Motors disclosed a substantial financial hit of $1.1 billion on its earnings before interest and taxes, primarily due to tariffs. This reflects the broader impact of tariff policies on major manufacturers.
| Company | Estimated Cost Impact | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Stanley Black & Decker | $800 million | Policy changes related to tariffs will significantly impact costs. |
| Conagra Brands | Over $200 million | Cost of goods sold expected to increase by 3%. |
| Tesla | $300 million | Costs mainly from auto sector increases. |
| General Motors | $1.1 billion | Heavy impact on earnings before interest and taxes. |
| Carrier Global | $200 million | Forecasting expenses to mitigate tariff effects. |
| Proctor & Gamble | $1 billion | Higher pretax costs could hurt earnings growth. |
| Whirlpool | Not specified | Profitability affected due to increased imports. |
| Mohawk Industries | Not specified | Already implementing price increases due to tariffs. |
Summary
The impact of tariffs on companies has been profound, with various organizations predicting substantial financial repercussions. Tariffs impact on companies is evident as businesses from Stanley Black & Decker to Conagra have reported anticipated costs amounting to hundreds of millions. These increased costs are likely to affect consumers in the long run, particularly if corporations begin passing on costs to maintain their profit margins. As companies brace for upcoming tariff changes, it remains critical to monitor the inflationary effects and subsequent price adjustments that may occur as a reaction to these tariffs.