Traditional Inflation Targeting by Powell’s Fed Signals Change
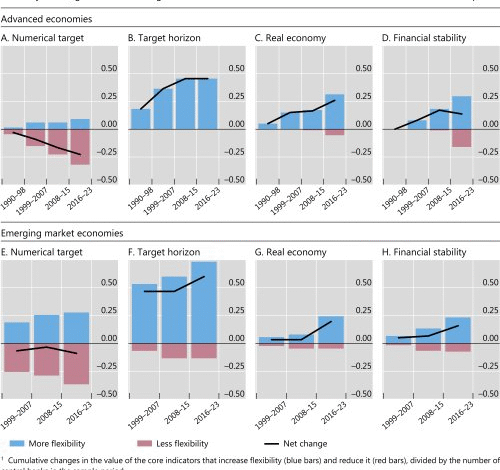
Traditional inflation targeting has emerged as a focal point in recent discussions surrounding Federal Reserve inflation policy, particularly following Chair Jerome Powell’s announcement during the Jackson Hole Economic Symposium. In a strategic shift from the previous framework, the Fed is laying a clear path towards maintaining stable prices through a firm 2% inflation rate target. This approach aligns with broader trends guiding Fed monetary policy changes, aiming for maximum employment while ensuring inflation remains in check. By moving away from the previously adopted averaging strategy, the central bank seeks to enhance transparency and effectiveness in its inflation strategy, addressing the new economic realities in today’s landscape. As the inflation landscape evolves, understanding these developments in traditional inflation targeting is crucial for market participants and policymakers alike.
In recent years, central banking has seen a resurgence of systems aimed at stabilizing price levels, commonly referred to as inflation control measures. These methodologies prioritize maintaining a consistent inflation rate, aiming to mitigate economic volatility and ensure sustainable growth, especially in light of post-pandemic changes. With Jerome Powell’s recent insights shared at key economic forums like the Jackson Hole Economic Symposium, there is a growing emphasis on revising previous strategies to adhere to specific inflation benchmarks. Such frameworks highlight a commitment to balancing employment levels with price stability in the backdrop of shifting regulatory landscapes. Adopting these systematic approaches is essential for navigating the intricate dynamics between employment and inflation in today’s economic climate.
Fed’s Renewed Commitment to Inflation Rate Targets
In a decisive move, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell announced a renewed commitment to maintaining a strict 2% inflation target during his recent address at the Jackson Hole Economic Symposium. This shift underscores the Federal Reserve’s intention to move away from previous strategies that had accepted higher inflation levels in exchange for economic recovery post-COVID-19. By anchoring its goals on a stable inflation rate, the Fed aims to restore confidence among investors and consumers, promoting long-term economic stability.
The updated inflation strategy marks a significant transition from the prior framework which had allowed for averaging inflation rates. This change not only simplifies the communication of the Fed’s objectives but also aligns with the current economic context characterized by turbulence and unpredictability. The focus on a precise inflation target enables the Fed to utilize its monetary policy more effectively, ensuring that the economy remains balanced without allowing inflation to spiral out of control.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is traditional inflation targeting and how does it relate to the Federal Reserve’s inflation policy?
Traditional inflation targeting is a monetary policy approach where a central bank explicitly sets and communicates a specific inflation rate target, typically around 2%. This strategy aims to stabilize prices and manage economic expectations. In relation to the Federal Reserve’s inflation policy, it signals a return to a more structured framework under Chair Jerome Powell, emphasizing a clear 2% inflation rate as a key indicator of economic health.
How did Jerome Powell’s address at the Jackson Hole Economic Symposium affect the Fed’s monetary policy changes?
During the Jackson Hole Economic Symposium, Jerome Powell announced pivotal changes to the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, indicating a return to traditional inflation targeting. This shift involves abandoning the previous strategy of allowing inflation to average 2%, thereby reinstating a fixed inflation rate target to enhance clarity and guide expectations in a changing economic environment.
What are the implications of the revised inflation rate targets announced by the Federal Reserve?
The revised inflation rate targets emphasize a strict 2% target, moving away from the makeup policy that permitted temporary overshoots. This shift reinforces the Federal Reserve’s commitment to maintaining price stability, which has significant implications for future policy decisions, including interest rate adjustments and economic forecasting.
What is the role of the Jackson Hole Economic Symposium in influencing Fed monetary policy changes?
The Jackson Hole Economic Symposium serves as a critical platform for central bankers, including Jerome Powell, to discuss and announce significant shifts in monetary policy. It provides an opportunity for the Fed to communicate its strategies, such as the recent transition back to traditional inflation targeting, influencing market expectations and investor confidence.
How does the Fed’s traditional inflation targeting framework impact its approach to maximum employment?
The Fed’s traditional inflation targeting framework integrates a balanced approach to maximum employment, now defined as the highest sustainable level while maintaining price stability. This means that the Federal Reserve, under Powell’s guidance, assesses employment goals in conjunction with inflation rate targets, optimizing both economic stability and growth.
What tools does the Federal Reserve utilize under traditional inflation targeting if inflation and employment objectives conflict?
Under traditional inflation targeting, if inflation and employment objectives conflict, the Federal Reserve utilizes tools such as interest rate adjustments, quantitative easing, and enhanced communication strategies. As Jerome Powell noted, a balanced approach will weigh the gap between objectives and the urgency of addressing each scenario.
How frequently will the Federal Reserve review its traditional inflation targeting framework?
The Federal Reserve plans to conduct an annual review of its traditional inflation targeting framework, with a comprehensive public assessment scheduled every five years. This ensures that the Fed remains responsive to changing economic conditions and can adjust its inflation strategy as necessary.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction of Traditional Inflation Targeting | Powell outlines a shift back to a 2% inflation target. |
| Abandoning the Makeup Policy | The Fed will no longer average inflation over time, moving away from policies that allowed for temporary overshooting. |
| Redefinition of Maximum Employment | Maximum employment is now defined as sustainable levels that do not compromise price stability. |
| Communication and Flexibility | The new strategy aims to enhance clarity and adapt to current economic conditions while providing tools for various scenarios. |
| Market Reactions | The announcement generated significant attention on social media platforms. |
| Interest Rate Outlook | Powell hinted at potential interest rate cuts in September 2025 if inflation subsides. |
Summary
Traditional Inflation Targeting is a critical shift in monetary policy, as announced by Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell. The move emphasizes a clear commitment to controlling inflation at 2% and redefines the parameters for maximum employment to ensure price stability. This strategic redirection reflects a response to recent economic shifts, aiming to maintain flexibility and adaptiveness in monetary policy amidst fluctuating inflationary pressures.