U.S. Economy Growth Surges By 3% Amid Consumer Resilience
U.S. economy growth is a significant topic of discussion as recent reports reveal a surprising surge in the second quarter, indicative of renewed momentum. Fueled by strong consumer spending and an improved trade balance, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) expanded by an impressive 3% from April to June, exceeding forecasts. This growth is especially noteworthy following a dip in the first quarter, attributed to tariff uncertainties and a notable drop in imports. As inflation rates stabilize and consumer confidence gradually returns, the resilience of the U.S. economy may signal a recovery path. Analysts emphasize that these trends not only showcase economic strength but also highlight an evolving landscape for the trade balance and domestic consumption in the months ahead.
The latest developments surrounding the expansion of the American economy draws attention to its noteworthy resurgence following a period of uncertainty. As the nation faces shifting dynamics in consumer behavior and international trade relations, the resurgence in gross domestic product (GDP) has become a focal point for economists and policymakers alike. With consumer expenditures experiencing robust increases and evolving trade agreements, such growth indicates a significant turnaround. Additionally, measures of economic stability and inflation levels play crucial roles in shaping expectations and strategies for future growth. Analyzing these factors provides a comprehensive understanding of how the U.S. economy is adapting to the challenges it faces and sets the stage for further opportunities.
U.S. Economy Growth: A Strong Second Quarter
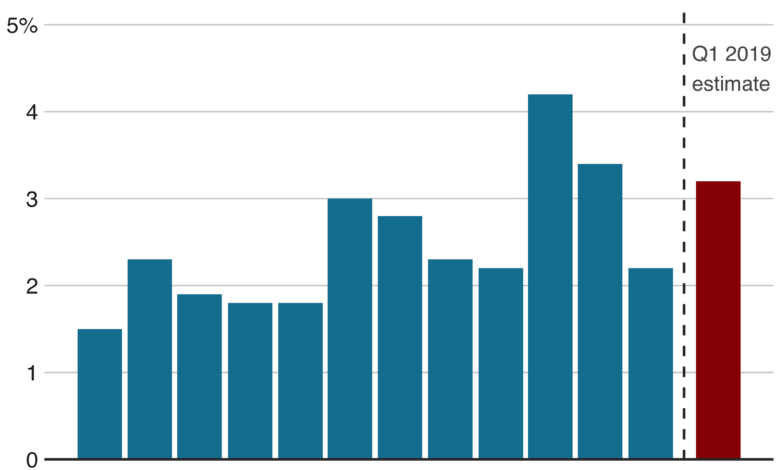
The recent reports detailing the U.S. economy growth for the second quarter have brought optimism among analysts and economists. With a remarkable 3% increase in Gross Domestic Product (GDP), this period showcased significant advancements fueled primarily by a better trade balance and a rebound in consumer spending. Such robust growth not only surpassed the expectations set by analysts but also mitigated the contraction witnessed in the first quarter. This impressive performance reinforces the narrative of economic resilience in challenging times, particularly as consumer confidence appears to be increasing despite ongoing tariff negotiations.
Moreover, the observed growth in GDP reflects a comprehensive improvement across various sectors, pointing towards an economy that’s on its path to recovery. The end of the trade deal uncertainties has led to increases in both domestic and foreign investments, which could further bolster consumer engagement. As the economy navigates through potential risks, the strong second quarter growth indicates that consumers are adapting, managing spending, and responding positively to economic policies that could enhance stability.
The Impact of Consumer Spending on Economic Growth
Consumer spending is a vital component of economic health in the U.S., and the 1.4% increase recorded in the second quarter is a testament to its importance. While the previous quarter saw a sluggish rise in consumer spending, this recent uptick is critical for sustaining the momentum of economic growth. With consumer spending accounting for approximately 70% of GDP, continued enhancement in this area could lead to significant boosts in production and job creation, ultimately contributing to a more favorable economic climate.
However, it is essential to note that while consumer spending is generally a positive indicator, mixed signals from other economic metrics suggest a cautious outlook. The decline in exports coupled with ongoing inflationary pressures may deter consumers from spending more freely. As such, consumer confidence will depend heavily on external factors such as trade policies and the broader global economic landscape, which could either bolster or suppress future consumer spending trends.
Trade Balance and Its Role in Economic Resilience
In the latest report, the improvement of the trade balance has been highlighted as a critical factor contributing to the impressive U.S. economy growth in the second quarter. The significant drop in imports, which plummeted by 30.3%, indicates a strategic shift in consumption patterns amidst ongoing tariff negotiations. This alteration not only reflects domestic consumers adjusting to fiscal policies but also demonstrates a growing domestic production capability that may fulfill demand without relying heavily on imports.
Moreover, a robust trade balance forms a crucial part of the overall economic resilience, enabling the U.S. economy to better withstand external shocks. As negotiations with trading partners evolve, the balance between exports and imports will be pivotal in shaping future economic scenarios. A negative trade balance can hinder GDP performance in upcoming quarters if exports continue to dwindle, suggesting that policymakers must focus on stabilizing this aspect to promote sustained economic growth.
Understanding Inflation Rates and Economic Health
Inflation rates have become a focal point in discussions about economic health and its interplay with growth metrics. During the second quarter, the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index reflected a 2.1% rise, indicating that while inflation persists, it has not necessarily inhibited economic advancement. The Federal Reserve’s objectives tend to emphasize keeping inflation within target ranges, with expectations surrounding rates influencing overall economic behavior, including spending and investment.
The nuanced relationship between inflation and economic growth is complex; a moderate inflation rate might indicate a growing economy. However, consumers remain vigilant about price increases, which can impact their spending habits. Tracking core inflation levels, which exclude volatile food and energy prices, offers more clarity on long-term trends relevant to consumer confidence and spending behaviors. As policymakers execute strategies to manage inflation, understanding its broader implications on economic resilience will be critical for maintaining a healthy growth trajectory.
GDP Growth: Analyzing Economic Indicators
The assessment of GDP growth serves as one of the most significant indicators of economic performance, encapsulating the total value of all goods and services produced within the U.S. economy. The recent announcement of a 3% increase in GDP not only provides insights into economic activity but also signals broader implications for employment rates, consumer confidence, and overall economic stability. Additionally, the fact that this growth follows a quarter of contraction can rejuvenate market sentiment and promote increased investments.
In examining GDP growth, it is essential to dissect its components, including consumer spending, government expenditure, and trade balance. Each of these factors contributes uniquely to the aggregate figures, thus guiding policymakers in their responses to economic conditions. Enhanced GDP growth might also prompt discussions about potential interest rate adjustments by the Federal Reserve, which could further influence consumer spending and investment opportunities. Understanding these dynamics will be crucial to navigating future economic decisions.
Shrinking Imports: A Strategic Response to Tariffs
The significant reduction in imports during the second quarter, encountered amidst escalating trade tensions, is a noteworthy aspect. Businesses have adjusted strategies in anticipation of tariffs, opting to scale back on imports while bolstering domestic production. This shift indicates a kind of economic realignment that could have long-term implications for local industries and employment, leading towards a more self-reliant economic framework.
However, this decrease in imports may also signal vulnerabilities, particularly if exports do not recover sufficiently. The balance between imports and exports will remain a critical focus in ongoing economic discourse as the impact of tariffs may ripple through sectors reliant on international supply chains. Monitoring these trends will be essential to understand how the U.S. economy adapts to the evolving landscape of trade and its influence on broader economic dynamics.
Inflation and Interest Rates: A Balancing Act
With inflation rates nearing and occasionally surpassing the target set by the Federal Reserve, discussions surrounding interest rates are becoming increasingly pertinent. The Fed’s goal is to maintain a balanced approach that fosters sustainable growth while keeping inflation in check. As companies adjust their operational strategies in response to rising costs, the impact on consumer spending and overall economic health can be substantial.
President Trump has called for lower interest rates, claiming that reducing borrowing costs would stimulate spending and investment. However, maintaining a delicate balance between encouraging growth and managing inflation is essential for sustainable progress. As the Federal Reserve deliberates its policies, scrutiny on how these decisions will affect consumer behavior and economic activity will provide insights into the market’s future trajectory.
Economic Resilience: The Role of Government Spending
Understanding the connection between economic resilience and government spending is crucial in assessing the broader fiscal landscape. In the recent growth report, a notable decrease in federal expenditures was observed, highlighting that economic expansion can occur independently of government spending. Such a phenomenon raises questions about the effectiveness of fiscal policy in stimulating growth, particularly during periods characterized by uncertainty.
Moreover, an increase in state and local government spending amid declining federal outlays demonstrates a complex interplay that could buffer local economies. By focusing efforts at the local level, targeted investments can drive employment opportunities and bolster economic performance. Future policies may need to consider how best to leverage both federal and local government spending to promote resilience and stable growth across diverse economic segments.
Looking Ahead: Predictions for Future Economic Performance
As we reflect on the strong performance of the U.S. economy in the second quarter, questions arise regarding the sustainability of this growth trajectory. Economic indicators such as recent consumer spending trends, fluctuations in trade balances, and ongoing inflation rates will play key roles in predicting how robust the economy will remain. While the past quarter’s results are promising, analysts caution against complacency, as external factors could significantly influence future performance.
Engaging in proactive policy measures will be crucial in navigating any potential headwinds that could arise. Understanding the delicate balance of maintaining consumer confidence, bolstering trade relations, and managing inflation will be fundamental to fostering a resilient economy. As U.S. economic policy unfolds, ongoing assessment and strategic responses will be necessary to ensure that growth remains consistent and sustainable, ultimately benefiting all sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contributed to the recent U.S. economy growth in GDP?
The recent growth in the U.S. economy, specifically the 3% increase in GDP during the second quarter, was primarily driven by improvements in the trade balance and stronger consumer spending. These factors, coupled with a significant drop in imports, reversed previous economic downturns and showcased the economy’s resilience.
How does consumer spending relate to U.S. economy growth?
Consumer spending plays a crucial role in U.S. economy growth, accounting for a substantial portion of GDP. In the second quarter, consumer spending increased by 1.4%, which exceeded the previous quarter’s 0.5% rise, indicating a renewed consumer confidence and drive that positively impacted overall economic growth.
What is the significance of the trade balance in U.S. economy growth?
The trade balance significantly impacts U.S. economy growth as it reflects the difference between exports and imports. In the second quarter, a decrease in imports by 30.3% helped improve the trade balance and contributed positively to the overall GDP growth, highlighting the importance of trade dynamics in economic performance.
What does economic resilience refer to in the context of U.S. economy growth?
Economic resilience refers to the ability of the U.S. economy to withstand shocks and adapt to changes. The recent GDP growth, driven by robust consumer spending and a favorable trade balance, demonstrates this resilience, as the economy continues to perform well amidst uncertainties in trade policies and inflation rates.
How do inflation rates affect U.S. economy growth?
Inflation rates are a critical factor in U.S. economy growth as they influence purchasing power and consumer confidence. Although the personal consumption expenditures price index rose by 2.1%, slightly above the Federal Reserve’s target, the GDP growth did not suffer, indicating a complex relationship between inflation and economic performance.
What role does the Federal Reserve play in U.S. economy growth?
The Federal Reserve plays a vital role in U.S. economy growth by setting monetary policy and adjusting interest rates. The current status of the key overnight borrowing rate within the 4.25%-4.5% range is expected to remain unchanged, influencing borrowing costs and consumer spending, crucial for sustaining economic growth.
Can we expect continued U.S. economy growth based on current indicators?
While the recent U.S. economy growth indicators point to resilience, including strong GDP performance and consumer spending, some signals suggest potential slowdowns, such as reduced final sales to private domestic purchasers. These mixed indicators suggest that vigilance in economic policy is necessary to foster continued growth.
How does the increase in GDP impact the U.S. economy overall?
An increase in GDP is a strong indicator of U.S. economy growth, reflecting heightened economic activity and improved living standards. The recent 3% growth demonstrates healthy economic conditions, likely leading to increased investment and job creation, which are essential for long-term growth.
What are the implications of U.S. economy growth for international trade?
The implications of U.S. economy growth for international trade include increased demand for imports and potential changes in export volumes. As the U.S. economy strengthens, it’s likely to see shifts in trade dynamics, impacting both the trade balance and global economic relationships.
How do recent tariff policies influence U.S. economy growth?
Recent tariff policies have introduced complexities to U.S. economy growth by impacting import levels and consumer prices. Despite fears of negative effects from tariffs, the latest GDP figures show resilience, suggesting that the economy can adapt to these challenges while still achieving growth.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Stronger-than-Expected Growth | The U.S. economy grew by 3% in Q2, surpassing the estimated 2.3%. |
| Consumer Spending | Increased by 1.4% in Q2, up from 0.5% in Q1. |
| Imports and Exports | Imports fell by 30.3%, while exports decreased by 1.8%. |
| Inflation Indicators | Core PCE inflation rose by 2.5%, slightly above the Fed’s target. |
| GDP Components | Strong performance noted across key sectors, no boost from government spending. |
Summary
The U.S. economy growth has shown remarkable resilience and strength in the second quarter, with GDP soaring to 3% amidst improving trade balances and increased consumer spending. Despite challenges, such as tariff-related anxieties and rising mortgage rates, consumers have managed to navigate the economic landscape. The robust growth and favorable consumer trends suggest positive signs for the future; however, attention must be given to ongoing negotiations and potential headwinds that could impact the economy moving forward.