U.S. Growth Forecast Cut Sharply by OECD Amid Tariff Issues
The U.S. growth forecast has taken a sharp decline, as indicated by the recent report from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The revised projection now stands at a modest **1.6% for 2025** and **1.5% in 2026**, a significant dip from earlier estimates. Contributing to this gloomy outlook are the far-reaching impacts of Trump tariffs, resulting in increased trade policy uncertainty and escalating inflation rates. Analysts highlight that these tariffs dampen not just the U.S. economy but also the global economic outlook, as trade barriers continue to rise. With a generally challenging economic environment, the implications of the OECD’s findings raise concerns for both consumers and businesses alike regarding growth prospects in the coming years.
The United States’ economic forecast has been notably downgraded, reflecting troubling trends in growth and inflation. Recent evaluations by the OECD reveal a startling adjustment in expected economic expansion, now projecting only **1.6% in the current year** and **1.5% for the next**. Factors influencing this revision include the effects of trade restrictions implemented during the Trump administration, which have intensified uncertainty in trade policies. Furthermore, the anticipated inflation rate is now poised to rise significantly, reinforcing apprehensions about the overall economic climate. As the global economic landscape shifts, stakeholders must navigate the complexities wrought by these developments to understand potential outcomes for the U.S. economy.
Implications of the OECD Economic Forecast on U.S. Growth
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has recently revised its U.S. growth forecast downward to 1.6% for the year 2025, representing a significant deviation from earlier projections. This adjustment reflects not only domestic challenges but also a broader global economic environment that is forecasted to be sluggish. The downturn is attributed to several factors, including the impact of Trump tariffs and the rising uncertainty in trade policies which have left businesses wary and reluctant to invest. Such slow growth rates cast a shadow on the vibrancy of the U.S. economy and signal that strategic changes may be necessary to spur recovery.
Moreover, with inflation rates also being adjusted upward, businesses and consumers alike are feeling the pinch of rising costs which adds another layer of complexity to the growth forecast. The OECD’s inflation predictions indicate that the U.S. could see rates nearing 4% by the end of 2025, exacerbated by higher trade tariffs leading to increased costs for imported goods. This scenario signals that to navigate the challenges posed by economic headwinds, a robust and adjusted trade policy geared towards sustaining growth and mitigating inflation will be essential.
The Role of Trump Tariffs in Shaping the Global Economic Landscape
President Trump’s administration has implemented tariffs aimed at protecting domestic industries, yet these measures have inadvertently contributed to a gloomy global economic outlook. The OECD attributes the downward revision of growth forecasts not only to domestic factors but also to the ripple effects felt around the world. The imposition of tariffs has triggered retaliatory measures by trading partners, creating a web of trade distortions that devastate market stability. This ongoing trade policy uncertainty potentially dampens consumer and business confidence, making it increasingly difficult for businesses to strategize effectively in a volatile market landscape.
In essence, the tariffs have had a two-fold effect: while they may benefit certain sectors temporarily, they have also deepened the overall economic malaise, leading to slower growth rates in the U.S. and its trading partners such as Canada and Mexico. As the OECD forecasts a general slowdown in global GDP, with expected growth declining to 2.9%, it highlights that Trump tariffs are one of the primary culprits undermining economic momentum on a broader scale.
Trade Policy Uncertainty and Its Impact on Economic Recovery
Trade policy uncertainty has emerged as a significant barrier to economic recovery in the U.S. According to the OECD’s report, ongoing turbulence in tariff regulations has sown confusion among businesses and investors. Frequent changes in tariffs can derail supply chains and postpone investment decisions, thereby stifling potential growth. The economic forecast indicates that as firms grapple with unpredictable trade environments, they may hold off on hiring and expansion due to the risks of increased costs and market instability. Inaction in this regard could lead to perpetuated cycles of stagnation.
Furthermore, the OECD emphasizes that if current conditions persist, particularly if the Trump tariffs remain enforced amidst ongoing legal challenges, the ramifications for economic growth could be severe. This policy indecision not only hampers immediate growth projections but also sets a troubling precedent for future economic stability, as the ability of businesses to adapt swiftly to changing tariff landscapes is crucial for maintaining a robust economy.
Navigating the Challenges of U.S. Inflation Rates
Amidst the backdrop of revised growth forecasts, the OECD underscored the rising inflation rate in the U.S., expected to climb to 3.2%. This inflationary pressure is largely attributed to the increased costs resulting from trade tariffs, which have profound implications for both consumers and businesses. The higher costs of imports due to tariffs not only lead to a direct increase in consumer prices but also affect businesses’ operational costs, which could further strain profit margins and force companies to make hard choices regarding pricing and employment.
Additionally, the OECD’s inflation outlook indicates a striking contrast between U.S. inflation trends and those of other G20 economies, with the latter expected to see a decrease in inflation rates. As inflation continues to rise, central banks may be compelled to adjust their monetary policies, which could include tightening measures that could further slow economic growth. Therefore, the interplay between tariffs, rising inflation, and sluggish GDP growth underscores the urgent need for coherent trade policies that align with broader economic recovery efforts.
The Global Economic Outlook Amid Rising Trade Barriers
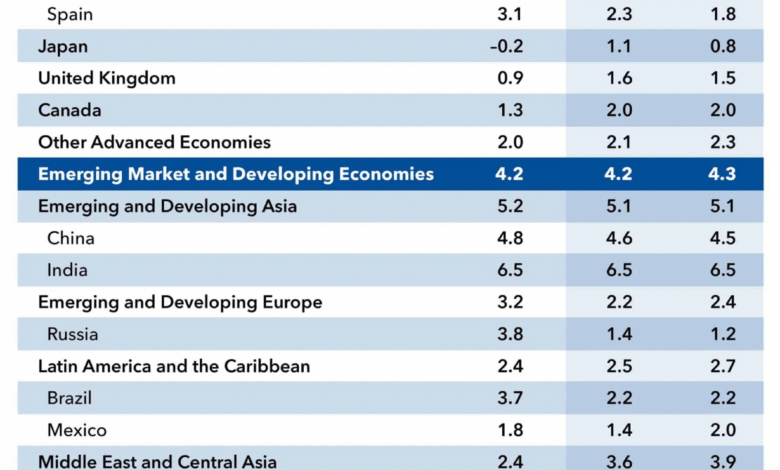
According to the OECD, global GDP growth is projected to slow from 3.3% in 2024 to 2.9% in 2025, reflecting an increasingly challenging economic outlook. The primary drivers of this slowdown include substantial increases in barriers to trade, which disrupt both local and international supply chains. With the U.S. at the epicenter of these tariff escalations, countries that depend on trade with the U.S. are also experiencing adverse economic effects, leading to a synchronized slowdown in North America.
The OECD’s report indicates that the global economy is entering a precarious phase, where trade tensions continue to weigh heavily on economic prospects. As nations grapple with the implications of stringent tariffs and retaliatory measures, the anticipated growth rates reflect a troubling reality for policymakers seeking to foster a revival in global economic activity. Collaborative approaches that promote trade liberalization and rollback of current tariffs could be essential to reversing this downward trajectory.
Forecasting Future Challenges in Global Trade Dynamics
The challenges posed by the recent OECD growth forecasts compel stakeholders to reflect on the dynamics of global trade. With the U.S. growth projections cut sharply, the implications resonate beyond national borders, affecting international partners and global supply chains. The complexities surrounding Trump tariffs and ongoing trade disputes create a precarious environment where businesses are left scrambling to adapt to ever-evolving legislative landscapes. The forecasted slowdown for global GDP growth signals that if the current trend persists, we could witness a prolonged period of economic stagnation.
In light of these challenges, businesses must prioritize adaptability and strategic foresight to navigate the turbulent waters of global trade. Seeking alternatives to traditional trading partnerships and fostering resilience in supply chains will be critical. Moreover, innovative approaches in trade policies will be necessary not only to address the immediate impacts of tariffs but also to set a foundation for sustainable economic growth moving forward.
Evaluating the Short-Term Impact of Increased Trade Costs
As countries impose higher tariffs, the immediate effect translates into increased trade costs that are ultimately passed down to consumers. The OECD has pointed out that although raised tariffs aim to protect domestic industries, they can lead to significant price hikes that diminish purchasing power. Consequently, the projected inflation rates are expected to climb, potentially impacting consumer spending behaviors and overall demand in the economy.
In the short term, businesses may struggle to absorb the cost increases brought on by tariffs, leading to decisions that could involve reducing workforce numbers or minimizing expansion plans. These dynamics highlight the need for policymakers to consider the broader economic implications of tariff policies, as fostering a favorable environment for economic growth demands a careful balance between protectionism and free trade.
The Intersection of Tariffs, Inflation, and Economic Policy
The intersection of tariffs and inflation offers a nuanced view of how economic policies can shape growth trajectories. As the OECD suggests, the dual impact of increased tariffs and the resultant inflation could conjure a challenging environment for monetary authorities aiming to stabilize the economy. The direct correlation between trade barriers and rising inflation complicates the ability to address economic fluctuations without further exacerbating consumer costs.
Effective economic policy will need to respond swiftly to mitigate the adverse impacts of tariffs while seeking to stabilize inflation and sustain growth. Stakeholders across industries must unite to advocate for a recalibration of trade policies that favor more predictable and less costly trade conditions. Creating frameworks that enhance economic resilience will be paramount in confronting the ongoing challenges faced in the evolving economic landscape.
Long-term Considerations in Economic Recovery Strategies
Looking ahead, long-term recovery strategies must take into account the cyclical nature of economic growth influenced by tariff policies. As the OECD forecast indicates, a persistent downturn could have lasting adverse impacts on the potential growth rate of the U.S. economy. To tackle these issues effectively, comprehensive strategies must be instituted that not only address immediate concerns but also lay the groundwork for a more sustainable and robust economic future as the global outlook remains uncertain.
These recovery strategies should focus on enhancing trade relations, fostering innovation across sectors, and minimizing policy uncertainty to build consumer and investor confidence. By prioritizing policies that encourage free trade and leverage international partnerships, the potential for revitalizing economic growth becomes increasingly achievable, enabling nations to better withstand the shocks created by relentless tariff battles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the latest U.S. growth forecast from the OECD indicate for 2025?
The latest U.S. growth forecast from the OECD indicates a downturn, projecting an expansion of only **1.6%** for 2025. This revision marks a significant decrease from the previous forecast of **2.2%**, reflecting the impact of Trump tariffs and overall economic policy uncertainty.
How are Trump tariffs impacting the U.S. growth forecast?
Trump tariffs have contributed to a negative outlook in the U.S. growth forecast by increasing trade barriers and economic policy uncertainty, leading the OECD to lower growth projections to **1.6%** in 2025 and **1.5%** in 2026, down from earlier expectations.
What role does trade policy uncertainty play in the U.S. growth outlook?
Trade policy uncertainty has a significant adverse effect on the U.S. growth forecast, causing fluctuations in business and consumer confidence. This uncertainty is partly due to ongoing changes related to Trump tariffs, which the OECD cites as a key reason for its reduced growth projections.
What is the correlation between U.S. inflation rates and the OECD’s growth forecast?
The OECD’s growth forecast adjusts U.S. inflation rates upward to **3.2%** for 2025, influenced by higher trade costs due to tariffs. This inflation outlook is critical as it reflects how trade policies directly affect economic growth and consumer prices.
How does the OECD’s U.S. growth forecast compare with the global economic outlook?
The OECD’s U.S. growth forecast is considerably lower than the global economic outlook, which projects global GDP growth to slow from **3.3%** in 2024 to **2.9%** in 2025. The slowdown is primarily concentrated in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico, indicating that the U.S. economy is facing particularly severe headwinds.
What long-term effects might Trump tariffs have on the U.S. economy according to the OECD?
According to the OECD, long-term effects of Trump tariffs may include heightened economic policy uncertainty and sustained declines in growth rates, with forecasts suggesting **1.5%** growth in 2026. Continued trade barriers could exacerbate inflation and undermine overall economic confidence.
What factors led to the OECD downgrading the U.S. growth forecast?
The downgrade of the U.S. growth forecast by the OECD is attributed to factors including the adverse effects of Trump tariffs, economic policy uncertainty, a slowdown in net immigration, and a reduction in the federal workforce, all of which collectively hinder economic performance.
How might tariff rates affect the global economic outlook in 2025?
Tariff rates, particularly those set by the U.S. under Trump, are expected to adversely influence the global economic outlook, contributing to slower growth projections. The OECD notes that if high tariffs persist, this could result in a number of negative outcomes for both U.S. and international economies.
What is the OECD’s current inflation rate forecast for the U.S. against other major economies?
The OECD forecasts the U.S. inflation rate to reach **3.2%** in 2025, which is significantly higher than the projected **3.6%** inflation for G20 countries. This disparity illustrates the unique pressures the U.S. faces due to tariffs and trade conditions.
Why is the OECD’s growth forecast critically important for U.S. economic policy?
The OECD’s growth forecast is crucial as it impacts U.S. economic policy decisions by highlighting the potential consequences of tariffs and trade uncertainties, shaping investor confidence, fiscal strategies, and overall economic planning.
| Key Factors | U.S. Growth Forecast 2025 | Global Growth Forecast 2025 | Inflation Forecast 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trump Tariffs | 1.6% | 2.9% | 3.2% |
| Policy Uncertainty | 1.5% (2026) | Projected lower compared to previous forecasts | Projected closer to 4% towards the end of 2025 |
| Decreased Immigration | |||
| Smaller Federal Workforce |
Summary
The U.S. growth forecast has been cut sharply by the OECD, reflecting a troubling economic outlook heavily influenced by Trump tariffs and ongoing policy uncertainties. With growth expectations now at just 1.6% for this year and a slight decline to 1.5% in 2026, the forecast indicates significant challenges ahead for the American economy, particularly amidst rising inflation and barriers to international trade. As the global economy also adjusts to these changes, the outlook for continued economic growth remains precarious.