UK Borrowing Costs: Analyzing Rachel Reeves’ Spending Plans
UK borrowing costs have become a crucial talking point as the government unveils significant spending plans that could reshape the fiscal landscape. Recently, Finance Minister Rachel Reeves announced an ambitious injection of billions into sectors like defense and infrastructure, igniting concerns among market analysts regarding the potential implications for UK interest rates. With rising UK gilts reminiscent of the country’s heightened public debt levels, experts warn that this escalation in borrowing costs could create a chilling effect on economic growth and stability. As borrowing costs reach alarming heights, the sustainability of government debt becomes a pressing issue, particularly as the UK grapples with the repercussions of this spending spree amidst a contracting economy. It remains to be seen how these developments will impact not only defense spending but also the larger framework of UK government spending as policymakers navigate this financial minefield.
The cost of borrowing in the UK, particularly in light of recent fiscal decisions, is at the forefront of economic discussions. Following the unveiling of extensive financial commitments by the UK government, concerns arise over the viability of such extensive outlays against a backdrop of increasing public debt and fluctuating interest rates. Analysts point to the urgency of balancing government funding with the potential burden of elevated borrowing costs, especially as the country continues to issue UK gilts and navigate the complexities of defense spending. In an environment marked by dampened economic growth, it is essential for policymakers to evaluate their financial strategies carefully, ensuring that government spending does not spiral beyond sustainable limits. As interest rates remain volatile, the interaction between borrowing levels and economic stability is more critical than ever.
Impact of UK Government Spending on Fiscal Stability
The recent announcement by UK Finance Minister Rachel Reeves regarding substantial government spending has raised eyebrows among market analysts and economists. The planned billions into sectors such as defense, healthcare, and infrastructure are seen as necessary investments; however, there are concerns that such expenditures could destabilize fiscal conditions. Increased government spending without a clear plan for financing may push public debt levels higher, leading to a cycle of rising borrowing costs that could weaken the economy further.
Fiscal stability hinges on a balanced approach to government spending and revenue generation. With public debt already amounting to approximately $143 billion annually, any misalignment in budgeting could result in a snowball effect that inflates UK borrowing costs significantly. The government must be cautious in how these investments are financed, as reliance on gilts or other debt instruments carries implications for future interest rates, potentially diminishing investor confidence.
The Correlation Between Interest Rates and UK Gilts
In recent months, the yields on UK gilts—government bonds used to fund public debt—have escalated dramatically, influenced by both domestic fiscal policies and global economic conditions. The current environment has seen yields on long-term gilts climbing above 5%, marking significant volatility that raises concerns among market players. With increased government borrowing anticipated to fund stimulus spending, fears arise that this trend could further exacerbate rising interest rates, ultimately impacting taxpayers.
The relationship between interest rates and gilts is crucial for understanding the financing dynamics of UK government spending. As rates increase, the cost of servicing existing debt surges, creating a tighter fiscal environment for future expenditures. Analysts suggest that if the economic conditions continue on this trajectory, it could lead to an unsustainable debt burden, especially given the current high interest rates that the UK faces. Therefore, careful management of gilt issuance and monitoring of market conditions will be vital in maintaining economic stability.
Rising Borrowing Costs and Public Debt Risks in the UK
The implications of rising borrowing costs are significant for the UK government, especially against the backdrop of increasing public debt. As the finance minister rolls out hefty spending plans, critics warn that unrestrained borrowing could culminate in a dangerous increase in public debt levels. Every pound borrowed at higher interest rates adds to the overall fiscal burden, permanently impacting the UK’s economic landscape.
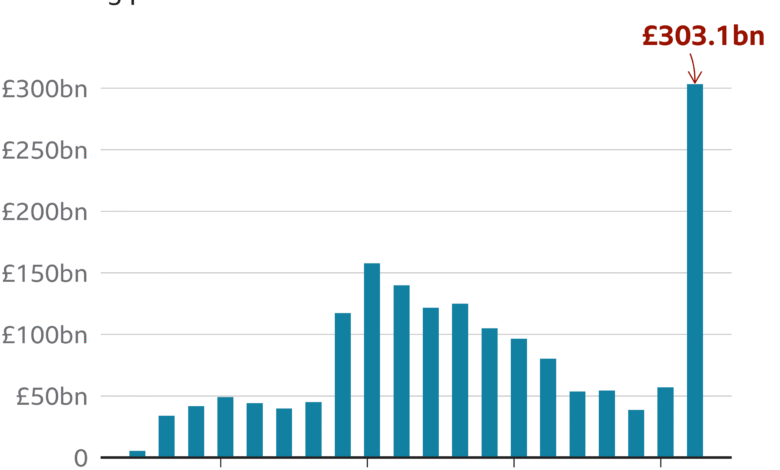
Moreover, with predictions indicating that interest expenditures could reach £105 billion by 2025, the pressure on the Treasury to manage debt effectively intensifies. High borrowing costs reduce the government’s fiscal flexibility, limiting its ability to invest in necessary public services or respond to economic shocks. Policymakers must navigate these challenges delicately, ensuring that financial strategies are in place to counteract this growing fiscal pressure.
Strategic Implications of Increased Defense Spending
Rachel Reeves’ commitment to increasing defense spending comes at a time when geopolitical tensions are escalating, necessitating a robust national defense strategy. However, the strategic implications of this spending raise questions about the sustainability of such fiscal policies. While bolstering defense might provide immediate security assurances, the long-term cost implications could lead to an awkward balance between safety and economic stability.
As more resources are allocated to defense, skeptics like Shadow Chancellor Mel Stride emphasize that without prudent fiscal management, the resulting public debt may surpass appropriate levels. The government faces a critical challenge: matching increased spending needs with anticipated tax revenue and minimizing the risk of elevating interest rates that strain economic growth. A well-formulated strategy is essential to ensure that defense commitments do not adversely affect broader fiscal objectives.
Navigating Economic Contraction and Taxation Pressure
Recent data indicating that the UK economy contracted by 0.3% has raised alarms about the potential for increased taxation. The government may find itself in a precarious position, needing to reconcile the demands for public spending with lower-than-expected revenue. This scenario puts pressure on the Treasury to explore alternative funding solutions, which may lead to further borrowing amidst rising interest rates, creating a vicious cycle.
In addressing these economic contractions, policymakers must consider the long-term impact of increasing taxation on both individuals and businesses. The delicate balance between generating revenue to fund necessary public services and maintaining a conducive environment for growth is critical. Strategic economic policies must be implemented to reduce public debt levels while still accommodating the need for increased government spending.
Market Reactions to Fiscal Policy Announcements
The financial markets have been reacting significantly to the announcements regarding UK government spending strategies. The fluctuation in gilt yields following Rachel Reeves’ spending plans highlights investor sentiment surrounding fiscal health. With concerns around inflation and rising borrowing costs, market analysts closely monitor how government policies may shape future interest rates and overall economic stability.
Moreover, negative market reactions can lead to a higher cost of borrowing for the government, complicating its fiscal maneuvers. If investor confidence diminishes, it puts the UK government at risk of facing a more challenging economic landscape, as persistent high yields make future funding more expensive. Therefore, transparency in fiscal policies and future spending plans is paramount to restoring market trust.
Long-term Economic Perspectives on Borrowing
For the UK government, understanding long-term economic perspectives on borrowing is essential to ensuring fiscal sustainability. While immediate financing may be necessary for public expenditures, policymakers must adopt a holistic view of how increased borrowing may impact future economic growth. This approach includes scrutinizing the balance between necessary investments and the affordability of servicing that debt over time.
Balancing short-term needs with long-term fiscal health will require innovative strategies to manage debt levels effectively. Investors look for a commitment to stable fiscal policies, which can help moderate interest rates and promote economic growth. Without such measures, the UK risks entering a spiral of rising borrowing costs, which could stymie progress and lead to wider economic challenges.
Potential Solutions to Manage Debt Servicing Costs
Addressing the immediate concerns regarding debt servicing costs is crucial to the UK government’s financial future. Experts like April LaRusse advocate for strategic adjustments in the structure of gilt issuance. By effectively managing the maturity profile of government bonds and ensuring an optimal mix of short- and long-term gilts, the government could potentially lower its overall borrowing costs.
However, implementing such solutions requires proactive engagement with market participants and a thorough analysis of prevailing economic conditions. Each adjustment must be weighed concerning its potential impact on interest rates and public debt levels. Finding the right approach to manage debt servicing while accommodating heightened spending needs remains a pivotal focus for policymakers as they navigate this challenging economic landscape.
The Future of UK Public Sector Financing
The trajectory of UK public sector financing is increasingly shaped by both domestic and global economic pressures. With mounting public debt and pressure on government spending, there is no denying the necessity for a comprehensive fiscal strategy. Policymakers must explore innovative financing solutions that not only meet immediate funding needs but also ensure long-term economic stability.
Looking ahead, the UK government must consider how geopolitical factors, market volatility, and public sentiment may influence its financing options. By prioritizing transparency and developing clear frameworks for expenditure and borrowing, the government can work towards restoring confidence among investors while mitigating the risks associated with elevated borrowing costs and public debt.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do UK government spending plans affect borrowing costs?
The UK government spending plans, particularly significant investments in sectors like defense and healthcare, can increase borrowing costs. As the government issues more bonds to finance these expenditures, the rising demand can inflate the yields on UK gilts, leading to higher interest rates and increased borrowing costs for the government.
What role do interest rates play in determining UK borrowing costs?
Interest rates are crucial in determining UK borrowing costs. When the Bank of England raises interest rates to combat inflation, it directly affects the yields on UK gilts. Higher yields mean higher costs for the government to borrow, ultimately increasing public debt servicing expenses, which is projected to exceed £105 billion in the coming fiscal year.
Why are UK gilts considered a barometer for national borrowing costs?
UK gilts are government bonds that serve as a benchmark for national borrowing costs. The yields on these gilts reflect investor sentiment about the government’s creditworthiness and the broader economic conditions. When gilt yields rise due to factors like increased borrowing or market volatility, it signifies higher borrowing costs for the UK government.
What impact does increased defense spending have on UK borrowing costs?
Increased defense spending can elevate UK borrowing costs as it necessitates greater government borrowing, often leading to a rise in gilt issuance. This additional supply can push up yields on UK gilts, resulting in higher interest payments on public debt, thereby straining fiscal resources.
How does public debt affect UK borrowing costs?
Public debt significantly impacts UK borrowing costs. The larger the national debt, the higher the interest rates investors may demand for buying UK gilts. With projected interest expenditures on public debt exceeding £105 billion, concerns over sustainability may lead to higher borrowing costs as market confidence wanes.
What strategies can the UK government employ to manage borrowing costs?
The UK government can manage borrowing costs by optimizing its gilt issuance strategy. Adjusting the structure of bonds issued, considering varying maturities and yields, can help mitigate the impact of high interest rates on future borrowing costs while maintaining essential public spending.
Why might the UK government avoid raising taxes while increasing borrowing?
The UK government may avoid raising taxes despite increasing borrowing to maintain economic growth and public support. This strategy aims to bolster sectors like infrastructure and defense spending without imposing immediate tax burdens, although it may lead to higher long-term borrowing costs associated with increased public debt.
What are the risks of rising UK borrowing costs on the economy?
Rising UK borrowing costs pose several risks to the economy, including increased pressure on government budgets due to higher interest payments. This can divert funds from essential services and be a deterrent to economic growth, potentially triggering a cycle of higher taxation or further borrowing, which could exacerbate inflation.
How does market volatility influence UK borrowing costs?
Market volatility, driven by global economic uncertainties and geopolitical tensions, directly influences UK borrowing costs by affecting investor confidence. When markets are unstable, yields on UK gilts can spike, leading to higher borrowing costs for the government as it struggles to finance public expenditure effectively.
| Key Points |
|---|
| UK Finance Minister Rachel Reeves announced significant spending plans, risking higher UK borrowing costs. |
| Concerns over inflation due to government borrowing leading to instability in bond markets. |
| The UK economy contracted by 0.3% in April, increasing pressure for either higher taxes or more borrowing. |
| Government interest expenditure is forecasted to exceed £105 billion in 2025, with the financing of new spending yet to be explained. |
| Yields on UK gilts have reached multi-decade highs, with long-term borrowing costs remaining volatile and above 5%. |
| Critics warn that ongoing borrowing could drive inflation and lead to higher interest rates, creating an unsustainable debt burden. |
| Potential adjustments to gilt issuance may help manage borrowing costs amid high interest rates. |
Summary
UK borrowing costs are under significant scrutiny as Finance Minister Rachel Reeves’ latest spending plans could lead to an unwanted snowball effect. Analysts are worried that increased government borrowing, coupled with already high yields on gilts, might inflate the national debt further and exert pressure on fiscal stability. With the recent contraction of the UK economy and rising interest expenditure projections, the government’s approach raises concerns about inflation and a potential unsustainable debt burden. As stakeholders assess these developments, the ability to effectively manage UK borrowing costs will be paramount.