US Debt Increase: The Impact of One Big Beautiful Bill
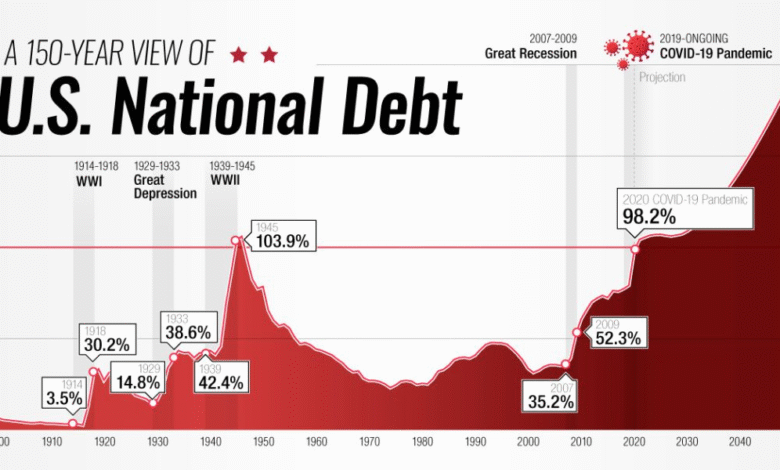
The recent increase in U.S. debt has raised significant concerns among economists and policymakers alike. Projections indicate that the U.S. debt could rise by over $3 trillion, fueled by legislative proposals like the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act,” which prioritizes tax cuts against a backdrop of swelling federal budget deficits. As interest rates climb due to these mounting obligations, the effects on consumer financing may become more pronounced, burdening households with higher borrowing costs. The national debt, already at record levels, threatens economic stability and raises questions about fiscal responsibility. Investors are beginning to express unease, as rising debt levels could disrupt the delicate balance of the financial markets in the coming years.
The escalating financial obligations of the United States, particularly concerning national borrowing, are becoming a focal point of national discourse. Recent legislative actions seem poised to significantly compound this fiscal challenge, risking an increase in the nation’s financial liabilities. Increasingly high interest rates—a reaction to growing federal budget deficits—place additional pressure on consumer financing and economic growth. Noteworthy is the hypothetical scenario where the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act” contributes to an unprecedented surge in debt, potentially eliciting adverse reactions from both investors and the general public. As these developments unfold, understanding the implications of national debt becomes crucial for both consumers and policymakers.
Overview of the U.S. Debt Increase
Recent legislative actions by Republicans in the House, particularly the passage of the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act,” project a staggering increase in U.S. debt, estimated at over $3 trillion. This debt explosion, fueled by substantial tax cuts and shifting fiscal policies, risks heightening the existing national debt which stands on the brink of surpassing $53 trillion. Economists are raising alarms about the long-term sustainability of such a surge in borrowing, pointing to the dire consequences for federal budget deficits that could further strain public finances.
The implications of this increase in debt extend beyond mere numbers on a balance sheet; they resonate throughout the economy. As the U.S. government increases its borrowing to fund various initiatives, investors may begin to shy away from purchasing U.S. Treasury bonds, sensing greater risk. This can lead to rising yields and interest rates — a trend that would significantly impact consumer financing options and everyday financial decisions for millions of Americans, driving costs higher and affecting overall economic health.
Impact on Interest Rates and Household Finances
The substantial increase in U.S. debt also poses serious ramifications for interest rates. Economists like Mark Zandi have pointed out that as the government borrows more, the perceived risk associated with U.S. Treasury securities could lead to higher interest rates across various consumer financing avenues, including mortgages and auto loans. With forecasts suggesting the debt-to-GDP ratio could escalate dramatically, households may find themselves paying significantly more in interest, further straining budgets that are already tight.
For example, a shift in the 10-year Treasury yield due to increased debt burden means that something like a fixed-rate mortgage could see a jump in interest rates, raising monthly payments for homeowners. This deterioration in affordability could particularly disadvantage first-time buyers and lower-income individuals, as they already face difficulty entering the housing market, and now they may have to contend with less favorable lending conditions tied to national fiscal health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How will the proposed U.S. debt increase from the ‘One Big Beautiful Bill Act’ affect the national debt?
The ‘One Big Beautiful Bill Act’ is projected to increase the national debt by over $3 trillion, with some estimates reaching as high as $3.8 trillion when accounting for interest and economic impacts. This significant increase may raise concerns regarding the sustainability of the U.S. national debt, which could grow to approximately $53 trillion.
What are the implications of the U.S. debt increase on consumer financing costs?
An increase in U.S. debt levels is likely to result in higher interest rates for consumer financing. As the U.S. Treasury borrows more to fund its operations, yields on Treasury bonds may rise, leading to increased borrowing costs for consumers on loans such as mortgages and auto financing.
In what way does the federal budget deficit relate to the proposed increase in U.S. debt?
The federal budget deficit is closely tied to the proposed increase in U.S. debt, as the new legislation is expected to exacerbate the deficit significantly. With increased spending and tax cuts, the government may borrow more, thus raising the national debt and potentially leading to higher interest payments.
How does the national debt impact interest rates in the U.S.?
The national debt influences interest rates because the cost of borrowing is linked to bond yields. If the U.S. debt continues to grow without a corresponding increase in tax revenue, investors may demand higher yields to compensate for the perceived risk, which in turn raises interest rates for consumers.
What kind of tax implications does the ‘One Big Beautiful Bill Act’ have for U.S. households?
The ‘One Big Beautiful Bill Act’ proposes tax cuts amounting to around $4 trillion, primarily benefiting wealthier households. However, funding these cuts may involve reductions in safety-net programs, which will have broader implications for the federal budget and national debt.
Can increasing U.S. debt affect bond investors, and how?
Yes, increasing U.S. debt can negatively affect bond investors. As the debt rises, investors may view Treasury bonds as riskier, potentially leading to lower demand and higher yields, which would decrease the value of existing bonds held by investors.
What did economists say about the consumer perception of rising national debt?
Economists indicate that while consumers may not perceive rising national debt as critical, it has substantial implications for household finances, including increased borrowing costs and higher interest rates on loans, which can significantly affect their financial situations.
How does the projected U.S. debt increase relate to interest payments and defense spending?
Currently, interest payments on U.S. debt have begun to exceed national defense spending, making them the second-largest expenditure after Social Security. As the debt rises, these payments are expected to escalate, further straining the federal budget.
What reactions have lawmakers had to the increase in national debt proposed in House legislation?
Some lawmakers, including Rep. Thomas Massie and Senator Rand Paul, have expressed serious concerns regarding the proposed legislation’s potential to significantly increase the national debt, labeling it as a ‘debt bomb ticking’ and stating that the mathematics of the bill does not add up.
What is the expected impact of Treasury yields associated with increased national debt?
If the national debt increases, Treasury yields are projected to rise, which could have a cascading effect on mortgage rates and other consumer loans. For instance, a rise in the debt-to-GDP ratio could lead to higher yields for the 10-year Treasury, making borrowing more expensive for consumers.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Projected Increase in Debt | Legislation may increase U.S. debt by over $3 trillion. |
| Effects on Household Finances | Increasing debt could raise borrowing costs and devalue bonds held by investors. |
| Republican Bill Objections | GOP lawmaker described the bill as a ‘debt bomb ticking.’ |
| Interest Payment Exceeding Defense Spending | Interest payments on U.S. debt now exceed national defense spending. |
| Consumer Impact of Rising Debt | Higher national debt could lead to higher interest rates for consumers. |
| Future Projections | Debt-to-GDP ratio could rise to 148% by 2034 under current legislation. |
Summary
The increase in U.S. debt is a pressing concern as recent legislation is projected to elevate it significantly. The proposed tax cuts, described as a potential “debt bomb,” could add trillions, further straining household finances by inflating borrowing costs. As interest payments on debt now outstrip national defense spending, the economic implications of the U.S. debt increase can substantially affect consumers and investors alike. The ripple effects of this rising debt, tied to perceptions of U.S. Treasury bonds, may lead to higher interest rates affecting mortgages and loans, ultimately impacting the economy at large.




